| The CANDISC Procedure |
| PROC CANDISC Statement |
The PROC CANDISC statement invokes the CANDISC procedure. The options listed in Table 27.1 are available in the PROC CANDISC statement.
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
Input Data Set |
|
specifies input SAS data set |
|
Output Data Sets |
|
specifies output data set with canonical scores |
|
specifies output statistics data set |
|
Method Details |
|
specifies the number of canonical variables |
|
specifies a prefix for naming the canonical variables |
|
specifies the singularity criterion |
|
Control Displayed Output |
|
displays all output |
|
displays univariate statistics |
|
displays between correlations |
|
displays between covariances |
|
displays between SSCPs |
|
displays squared Mahalanobis distances |
|
suppresses all displayed output |
|
displays pooled correlations |
|
displays pooled covariances |
|
displays pooled SSCPs |
|
suppresses some displayed output |
|
displays simple descriptive statistics |
|
displays standardized class means |
|
displays total correlations |
|
displays total covariances |
|
displays total SSCPs |
|
displays within correlations |
|
displays within covariances |
|
displays within SSCPs |
|
- ALL
- ANOVA
displays univariate statistics for testing the hypothesis that the class means are equal in the population for each variable.
- BCORR
- BCOV
displays between-class covariances. The between-class covariance matrix equals the between-class SSCP matrix divided by
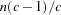 , where
, where  is the number of observations and
is the number of observations and  is the number of classes. The between-class covariances should be interpreted in comparison with the total-sample and within-class covariances, not as formal estimates of population parameters.
is the number of classes. The between-class covariances should be interpreted in comparison with the total-sample and within-class covariances, not as formal estimates of population parameters. - BSSCP
- DATA=SAS-data-set
specifies the data set to be analyzed. The data set can be an ordinary SAS data set or one of several specially structured data sets created by SAS statistical procedures. These specially structured data sets include TYPE=CORR, COV, CSSCP, and SSCP. If you omit the DATA= option, the procedure uses the most recently created SAS data set.
- DISTANCE
- MAHALANOBIS
displays squared Mahalanobis distances between the group means,
 statistics, and the corresponding probabilities of greater squared Mahalanobis distances between the group means.
statistics, and the corresponding probabilities of greater squared Mahalanobis distances between the group means. - NCAN=n
specifies the number of canonical variables to be computed. The value of
 must be less than or equal to the number of variables. If you specify NCAN=0, the procedure displays the canonical correlations, but not the canonical coefficients, structures, or means. A negative value suppresses the canonical analysis entirely. Let
must be less than or equal to the number of variables. If you specify NCAN=0, the procedure displays the canonical correlations, but not the canonical coefficients, structures, or means. A negative value suppresses the canonical analysis entirely. Let  be the number of variables in the VAR statement, and let
be the number of variables in the VAR statement, and let  be the number of classes. If you omit the NCAN= option, only
be the number of classes. If you omit the NCAN= option, only 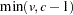 canonical variables are generated; if you also specify an OUT= output data set,
canonical variables are generated; if you also specify an OUT= output data set,  canonical variables are generated, and the last
canonical variables are generated, and the last 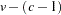 canonical variables have missing values.
canonical variables have missing values. - NOPRINT
suppresses the normal display of results. Note that this option temporarily disables the Output Delivery System (ODS); see Chapter 20, Using the Output Delivery System, for more information.
- OUT=SAS-data-set
creates an output SAS data set containing the original data and the canonical variable scores. To create a permanent SAS data set, specify a two-level name (see SAS Language Reference: Concepts), for more information about permanent SAS data sets).
- OUTSTAT=SAS-data-set
creates a TYPE=CORR output SAS data set that contains various statistics, including class means, standard deviations, correlations, canonical correlations, canonical structures, canonical coefficients, and means of canonical variables for each class. To create a permanent SAS data set, specify a two-level name (see SAS Language Reference: Concepts, for more information about permanent SAS data sets).
- PCORR
displays pooled within-class correlations (partial correlations based on the pooled within-class covariances).
- PCOV
- PREFIX=name
specifies a prefix for naming the canonical variables. By default the names are Can1, Can2, Can3, and so forth. If you specify PREFIX=Abc, the components are named Abc1, Abc2, and so on. The number of characters in the prefix plus the number of digits required to designate the canonical variables should not exceed 32. The prefix is truncated if the combined length exceeds 32.
- PSSCP
- SHORT
suppresses the display of canonical structures, canonical coefficients, and class means on canonical variables; only tables of canonical correlations and multivariate test statistics are displayed.
- SIMPLE
displays simple descriptive statistics for the total sample and within each class.
- SINGULAR=p
specifies the criterion for determining the singularity of the total-sample correlation matrix and the pooled within-class covariance matrix, where
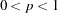 . The default is SINGULAR=1E–8.
. The default is SINGULAR=1E–8. Let
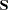 be the total-sample correlation matrix. If the R square for predicting a quantitative variable in the VAR statement from the variables preceding it exceeds
be the total-sample correlation matrix. If the R square for predicting a quantitative variable in the VAR statement from the variables preceding it exceeds 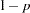 , then
, then 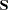 is considered singular. If
is considered singular. If 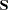 is singular, the probability levels for the multivariate test statistics and canonical correlations are adjusted for the number of variables with R square exceeding
is singular, the probability levels for the multivariate test statistics and canonical correlations are adjusted for the number of variables with R square exceeding 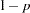 .
. If
 is considered singular and the inverse of
is considered singular and the inverse of  (squared Mahalanobis distances) is required, a quasi inverse is used instead. For details see the section Quasi-inverse in
Chapter 31,
The DISCRIM Procedure.
(squared Mahalanobis distances) is required, a quasi inverse is used instead. For details see the section Quasi-inverse in
Chapter 31,
The DISCRIM Procedure.
- STDMEAN
displays total-sample and pooled within-class standardized class means.
- TCORR
- TCOV
- TSSCP
- WCORR
- WCOV
- WSSCP
displays the within-class corrected SSCP matrix for each class level.
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.