Copying Metadata-Bound Tables to a Traditional Library
The examples in this topic use the copy action. The
same results occur if tables are moved, except that the original physical
tables are deleted.
Using SAS
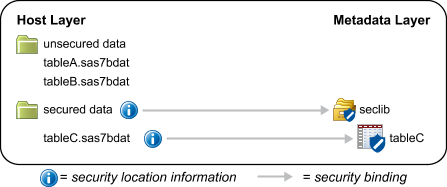
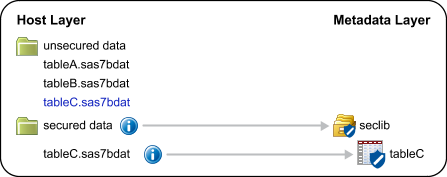
If you use SAS to add a metadata-bound table to a traditional physical library, the added table is not secured. It takes on the
unsecured nature of its new parent library. For this reason, SAS requires that you
have adequate metadata-layer permissions to the original table in order to copy (or
move) it. See Permissions for Metadata-Bound Data.
The following example depicts the impact of using the COPY procedure to copy a physical table (tableC) into the unsecured data folder.
Using Host Commands
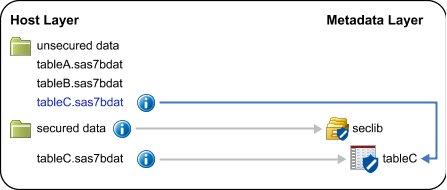
If you use a host command to add a metadata-bound table to a traditional physical
library, the added table is secured. It is bound to the
same metadata object that the original table is bound to. With a host command, SAS isn’t involved, so
metadata-layer permissions can’t be checked. Thus, the original security information
and binding is preserved.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.