The SHEWHART Procedure
The Index 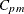
The process capability index 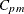 is computed as
is computed as
![\[ C_{pm} = \frac{\min (T-LSL,USL-T)}{3\sqrt {\hat{\sigma }^{2} +(\overline{\overline{X}}-T)^{2}}} \]](images/qcug_shewhart0286.png)
where T is the target value specified with the TARGET= option.
When a single specification limit (SL) and target are specified, 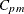 is computed as
is computed as
![\[ C_{pm} = \frac{|T - SL|}{3\sqrt {\hat{\sigma }^{2} +(\overline{\overline{X}}-T)^{2}}} \]](images/qcug_shewhart0287.png)
You can also use the CAPABILITY procedure to compute a variety of capability indices. The SHEWHART procedure and the CAPABILITY
procedure use the same formulas to calculate the indices, but they use different estimates for the process standard deviation
 .
.
-
The SHEWHART procedure calculates
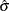 from subgroup estimates of
from subgroup estimates of  . For details, see the previous section, "Methods for Estimating the Standard Deviation."
. For details, see the previous section, "Methods for Estimating the Standard Deviation."
-
The CAPABILITY procedure calculates
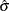 as the sample standard deviation of the entire sample. For details, see the section Standard Deviation.
as the sample standard deviation of the entire sample. For details, see the section Standard Deviation.
Regardless of which method you use, you should verify that the process is in statistical control before interpreting the indices, and you should verify that the data are normally distributed. The CAPABILITY procedure provides a variety of statistical and graphical tests for checking normality.
Some references use different notation and names for capability indices. For example, the manual ASQC Automotive Division/AIAG (1990) uses the term "process capability indices" for the indices listed in this section, and it uses the term "process performance indices" for the indices computed by the CAPABILITY procedure.