The SHEWHART Procedure
References
-
Al-Salti, M., and Statham, A. (1994). “A Review of the Literature on the Use of SPC in Batch Production.” Quality and Reliability Engineering International 10:49–62.
-
Alt, F. (1985). “Multivariate Quality Control.” In Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences, vol. 6, edited by S. Kotz, N. L. Johnson, and C. B. Read. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Alwan, L. C., and Roberts, H. V. (1988). “Time Series Modeling for Statistical Process Control.” Journal of Business and Economic Statistics 6:87–95.
-
American Society for Testing and Materials (1976). ASTM Manual on Presentation of Data and Control Chart Analysis. Philadelphia: ASTM.
-
ASQC Automotive Division/AIAG (1990). Fundamental Statistical Process Control: Reference Manual. Southfield, MI: Automotive Industry Action Group.
-
Austin, J. A. (1973). “Control Chart Constants for Largest and Smallest in Sampling from a Normal Distribution Using the Generalized Burr Distribution.” Technometrics 15:931–933.
-
Bissell, A. F. (1990). “How Reliable Is Your Capability Index?” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series C 39:331–340.
-
Box, G. E. P., and Kramer, T. (1992). “Statistical Process Monitoring and Feedback Adjustment: A Discussion.” Technometrics 34:251–285. With discussion.
-
Boyles, R. A. (1997). “Estimating Common-Cause Sigma in the Presence of Special Causes.” Journal of Quality Technology 29:381–395.
-
Burr, I. W. (1969). “Control Charts for Measurements with Varying Sample Sizes.” Journal of Quality Technology 1:163–167.
-
Burr, I. W. (1976). Statistical Quality Control Methods. New York: Marcel Dekker.
-
Champ, S. W., and Woodall, W. H. (1987). “Exact Results for Shewhart Control Charts with Supplementary Runs Rules.” Technometrics 29:393–401.
-
Champ, S. W., and Woodall, W. H. (1990). “A Program to Evaluate the Run Length Distribution of a Shewhart Control Chart with Supplementary Run Rules.” Journal of Quality Technology 29:393–399.
-
Deming, W. E. (1982). Out of the Crisis. Cambridge, MA: Center for Advanced Engineering Study, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
-
Doganaksoy, N., Faltin, F. W., and Tucker, W. T. (1991). “Identification of Out-of-Control Quality Characteristics in a Multivariate Manufacturing Environment.” Communications in Statistics—Theory and Methods 20:2775–2790.
-
Draper, N. R., and Smith, H. (1981). Applied Regression Analysis. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Gnanadesikan, R., and Kettenring, J. R. (1972). “Robust Estimates, Residuals, and Outlier Detection with Multiresponse Data.” Biometrics 28:81–124.
-
Grant, E. L., and Leavenworth, R. S. (1988). Statistical Quality Control. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
-
Hawkins, D. M. (1991). “Multivariate Quality Control Based on Regression-Adjusted Variables.” Technometrics 33:61–75.
-
Hawkins, D. M. (1993). “Regression Adjustment for Variables in Multivariate Quality Control.” Journal of Quality Technology 25:170–182.
-
Hillier, F. S. (1969). “
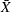 - and R-Chart Control Limits Based on a Small Number of Subgroups.” Journal of Quality Technology 1:17–26.
- and R-Chart Control Limits Based on a Small Number of Subgroups.” Journal of Quality Technology 1:17–26.
-
Hunter, J. S. (1986). “The Exponentially Weighted Moving Average.” Journal of Quality Technology 18:203–210.
-
Hunter, J. S. (1988). “The Digidot Plot.” American Statistician 24:54.
-
Iglewicz, B., and Hoaglin, D. C. (1987). “Use of Boxplots for Process Evaluation.” Journal of Quality Technology 19:180–190.
-
Jackson, J. E. (1980). “Principal Components and Factor Analysis, Part 1: Principal Components.” Journal of Quality Technology 12:201–213.
-
Jackson, J. E. (1991). A User’s Guide to Principal Components. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Johnson, N. L., Kotz, S., and Kemp, A. W. (1992). Univariate Discrete Distributions. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Kendall, M. G. (1955). Rank Correlation Methods. 2nd ed. London: Charles Griffin.
-
Kume, H. (1985). Statistical Methods for Quality Improvement. Tokyo: AOTS Chosakai.
-
MacGregor, J. F. (1987). “Interfaces between Process Control and Online Statistical Process Control.” Computing and Systems Technology Division Communications 10:9–20.
-
MacGregor, J. F. (1990). “A Different View of the Funnel Experiment.” Journal of Quality Technology 22:255–259.
-
MacGregor, J. F., Hunter, J. S., and Harris, T. (1988). “SPC Interfaces.” Short course notes.
-
Mason, R. L., Tracy, N. D., and Young, J. C. (1993). “Use of Hotelling’s
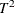 Statistic in Multivariate Control Charts.” Unpublished paper.
Statistic in Multivariate Control Charts.” Unpublished paper.
-
McGill, R., Tukey, J. W., and Larsen, W. A. (1978). “Variations of Box Plots.” American Statistician 32:12–16.
-
Montgomery, D. C. (1996). Introduction to Statistical Quality Control. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Montgomery, D. C., Keats, J. B., Runger, G. C., and Messina, W. S. (1994). “Integrating Statistical Process Control and Engineering Process Control.” Journal of Quality Technology 26:79–87.
-
Montgomery, D. C., and Mastrangelo, C. M. (1991). “Some Statistical Process Control Methods for Autocorrelated Data.” Journal of Quality Technology 23:179–204. With discussion.
-
Nelson, L. S. (1982). “Control Charts for Individual Measurements.” Journal of Quality Technology 14:172–174.
-
Nelson, L. S. (1984). “The Shewhart Control Chart—Tests for Special Causes.” Journal of Quality Technology 15:237–239.
-
Nelson, L. S. (1985). “Interpreting Shewhart
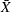 Control Charts.” Journal of Quality Technology 17:114–116.
Control Charts.” Journal of Quality Technology 17:114–116.
-
Nelson, L. S. (1989). “Standardization of Shewhart Control Charts.” Journal of Quality Technology 21:287–289.
-
Nelson, L. S. (1994). “Shewhart Control Charts with Unequal Subgroup Sizes.” Journal of Quality Technology 26:64–67.
-
Quesenberry, C. P. (1991a). “SPC Q Charts for a Binomial Parameter p: Short or Long Runs.” Journal of Quality Technology 23:239–246.
-
Quesenberry, C. P. (1991b). “SPC Q Charts for Start-Up Processes and Short or Long Runs.” Journal of Quality Technology 23:213–224.
-
Quesenberry, C. P. (1993). “The Effect of Sample Size on Estimated Effects.” Journal of Quality Technology 25:237–247.
-
Rocke, D. M. (1989). “Robust Control Charts.” Technometrics 31:173–184.
-
Rodriguez, R. N., and Bynum, R. A. (1992). “Examples of Short Run Process Control Methods with the SHEWHART Procedure in SAS/QC Software.” Unpublished manuscript available from the authors.
-
Ryan, T. P. (1989). Statistical Methods for Quality Improvement. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Schilling, E. G., and Nelson, P. R. (1976). “The Effect of Non-normality on the Control Limits of
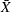 Charts.” Journal of Quality Technology 8:183–187.
Charts.” Journal of Quality Technology 8:183–187.
-
Schneider, H., and Pruett, J. M. (1994). “Control Charting Issues in the Process Industries.” Quality Engineering 6:347–373.
-
Shewhart, W. A. (1931). Economic Control of Quality Manufactured Product. New York: D. Van Nostrand; republished in 1980 by the American Society for Quality Control.
-
Snedecor, G. W., and Cochran, W. G. (1980). Statistical Methods. 7th ed. Ames: Iowa State University Press.
-
Teichroew, D. (1962). “Tables of Expected Values of Order Statistics and Products of Order Statistics for Samples of Size 20 and Less from the Normal Distribution.” In Contributions to Order Statistics, 190–205. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Tracy, N. D., Young, J. C., and Mason, R. L. (1992). “Multivariate Control Charts for Individual Observations.” Journal of Quality Technology 24:88–95.
-
Tukey, J. W. (1977). Exploratory Data Analysis. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
-
Western Electric Company (1956). Statistical Quality Control Handbook. Indianapolis: Western Electric Company.
-
Westgard, J. O. (2002). Basic QC Practices: Training in Statistical Quality Control for Healthcare Laboratories. Madison, WI: Westgard QC.
-
Wetherill, G. B., and Brown, D. B. (1991). Statistical Process Control: Theory and Practice. London: Chapman & Hall.
-
Wheeler, D. J. (1991). “Shewhart’s Chart: Myths, Facts, and Competitors.” Annual Quality Congress Transactions 45:533–538.
-
Wheeler, D. J. (1995). Advanced Topics in Statistical Process Control. Knoxville, TN: SPC Press.
-
Wheeler, D. J., and Chambers, D. S. (1986). Understanding Statistical Process Control. Knoxville, TN: SPC Press.
-
Wilks, S. S. (1962). Mathematical Statistics. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Woodall, W. H. (1993). “Autocorrelated Data and SPC.” ASQC Statistics Division Newsletter 13:18–21.