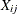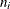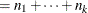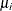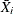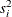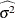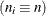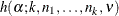BOXCHART Statement: ANOM Procedure
Constructing ANOM Boxcharts
The following notation is used in this section:
|
|
jth response in the ith group |
|
k |
Number of groups |
|
|
Sample size of ith group |
|
N |
Total sample size |
|
|
Expected value of a response in the ith group |
|
|
Standard deviation of response |
|
|
Average response in ith group |
|
|
Weighted average of k group means |
|
|
Sample variance of the responses in the ith group |
|
|
Mean square error (MSE) |
|
|
Degrees of freedom associated with the mean square error |
|
|
Significance level |
|
|
Critical value for analysis of means when the sample sizes |
|
|
Critical value for analysis of means when the sample sizes |
Elements of Box-and-Whisker Plots
A box-and-whisker plot is displayed for the measurements in each group on the ANOM boxchart. Figure 4.9 illustrates the elements of each plot.
Figure 4.9: Box-and-Whisker Plot
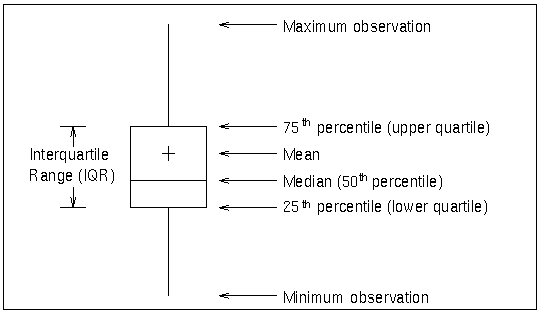
The skeletal style of the box-and-whisker plot shown in Figure 4.9 is the default. You can specify alternative styles with the BOXSTYLE= option; see the entry for the BOXSTYLE= option in Dictionary of Options: SHEWHART Procedure.
Central Line
By default, the central line on an ANOM chart for means represents the weighted average of the group means, which is computed as
![\[ \overline{\overline{X}} = \frac{n_{1}\bar{X_{1}} + \cdots + n_{k}\bar{X_{k}}}{n_{1} + \cdots + n_{k}} \]](images/qcug_anom0020.png)
You can specify a value for 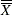 with the MEAN= option in the BOXCHART statement or with the variable
with the MEAN= option in the BOXCHART statement or with the variable _MEAN_ in a LIMITS= data set.
Decision Limits
In the analysis of means for continuous data, it is assumed that the responses in the ith group are at least approximately normally distributed with a constant variance:
![\[ X_{ij} \sim N( \mu _{i}, \sigma ^2 ), \; \; \; \; \; j = 1, \ldots , n_ i \]](images/qcug_anom0021.png)
When the group sizes are constant (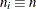 ), then
), then 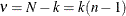 and the decision limits are computed as follows:
and the decision limits are computed as follows:
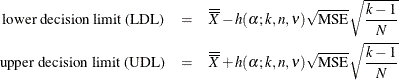
Here the mean square error (MSE) is computed as follows:
![\[ \mbox{MSE} = \widehat{\sigma ^2} = \frac{1}{k} \sum _{j=1}^{k} s_{j}^2 \]](images/qcug_anom0025.png)
For details concerning the function 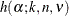 , see Nelson (1981, 1982a, 1993).
, see Nelson (1981, 1982a, 1993).
When the group sizes 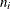 are not constant (the unbalanced case),
are not constant (the unbalanced case), 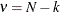 and the decision limits for the ith group are computed as follows:
and the decision limits for the ith group are computed as follows:
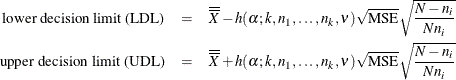
Here the mean square error (MSE) is computed as follows:
![\[ \mbox{MSE} = \widehat{\sigma ^2} = \frac{(n_{1} - 1)s_1^{2} + \cdots + (n_{k} - 1)s_{k}^{2}}{n_{1} + \cdots + n_{k} - k} \]](images/qcug_anom0028.png)
This requires that  be positive. A chart is not produced if
be positive. A chart is not produced if  but MSE is equal to zero (unless you specify the ZEROSTD option). For details concerning the function
but MSE is equal to zero (unless you specify the ZEROSTD option). For details concerning the function  , see Fritzsch and Hsu (1997), Nelson (1982b, 1991), and Soong and Hsu (1997).
, see Fritzsch and Hsu (1997), Nelson (1982b, 1991), and Soong and Hsu (1997).
You can specify parameters for the limits as follows:
-
Specify
 with the ALPHA= option or with the variable
with the ALPHA= option or with the variable _ALPHA_in a LIMITS= data set. By default, = 0.05.
= 0.05.
-
Specify a constant nominal sample size
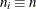 for the decision limits in the balanced case with the LIMITN= option or with the variable
for the decision limits in the balanced case with the LIMITN= option or with the variable _LIMITN_in a LIMITS= data set. By default, n is the observed sample size in the balanced case. -
Specify k with the LIMITK= option or with the variable
_LIMITK_in a LIMITS= data set. By default, k is the number of groups. -
Specify
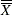 with the MEAN= option or with the variable
with the MEAN= option or with the variable _MEAN_in a LIMITS= data set. By default,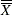 is the weighted average of the responses.
is the weighted average of the responses.
-
Specify
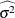 with the MSE= option or with the variable
with the MSE= option or with the variable _MSE_in a LIMITS= data set. By default,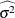 is computed as indicated above.
is computed as indicated above.
-
Specify
 with the DFE= option or with the variable
with the DFE= option or with the variable _DFE_in a LIMITS= data set. By default, is determined as indicated above.
is determined as indicated above.