MACHART Statement: MACONTROL Procedure
Dictionary of Special Options
The notes Traditional Graphics and Line Printer identify options that apply only to traditional graphics and line printer charts, respectively.
- ALPHA=value
-
requests probability limits. If you specify ALPHA=
 , the control limits are computed so that the probability is
, the control limits are computed so that the probability is  that a single moving average exceeds its control limits. The value of
that a single moving average exceeds its control limits. The value of  can range between 0 and 1. This assumes that the process is in statistical control and that the data follow a normal distribution.
For the equations used to compute probability limits, see Control Limits.
can range between 0 and 1. This assumes that the process is in statistical control and that the data follow a normal distribution.
For the equations used to compute probability limits, see Control Limits.
Note the following:
-
As an alternative to specifying ALPHA=
 , you can read
, you can read  from the variable
from the variable _ALPHA_in a LIMITS= data set by specifying the READALPHA option. -
As an alternative to specifying ALPHA=
 (or reading
(or reading _ALPHA_from a LIMITS= data set), you can request “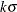 control limits” by specifying SIGMAS=k (or reading
control limits” by specifying SIGMAS=k (or reading _SIGMAS_from a LIMITS= data set).
If you specify neither the ALPHA= option nor the SIGMAS= option, the procedure computes
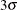 control limits by default.
control limits by default.
-
- ASYMPTOTIC
-
requests constant upper and lower control limits for all subgroups having the following values:
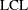
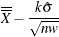
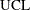
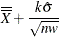
Here w is the span of the moving average, and n is the nominal sample size associated with the control limits. Substitute
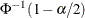 for k if you specify probability limits with the ALPHA= option. When you do not specify the ASYMPTOTIC option, the control limits
are computed using the exact formulas in Table 9.9. Use the ASYMPTOTIC option only if all the subgroup sample sizes are the same or if you specify LIMITN=n.
for k if you specify probability limits with the ALPHA= option. When you do not specify the ASYMPTOTIC option, the control limits
are computed using the exact formulas in Table 9.9. Use the ASYMPTOTIC option only if all the subgroup sample sizes are the same or if you specify LIMITN=n.
- CMEANSYMBOL=color
-
Traditional Graphicsspecifies the color for the symbol requested with the MEANSYMBOL= option.
-
LIMITN=n
LIMITN=VARYING -
specifies either a fixed or varying nominal sample size for the control limits.
If you specify LIMITN=n, moving averages are calculated and displayed only for those subgroups with a sample size equal to n, unless you also specify the ALLN option, which causes all the moving averages to be calculated and displayed. By default (or if you specify LIMITN=VARYING), moving averages are calculated and displayed for all subgroups, regardless of sample size.
- MEANCHAR='character'
-
Line Printerspecifies a character used to plot the subgroup mean for each subgroup. By default, subgroup means are not plotted.
- MEANSYMBOL=keyword
-
Traditional Graphicsspecifies a symbol used to plot the subgroup mean for each subgroup. By default, subgroup means are not plotted.
- MU0=value
-
specifies a known (standard) value
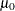 for the process mean
for the process mean 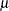 . By default,
. By default, 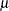 is estimated from the data.
is estimated from the data.
Note: As an alternative to specifying MU0=
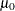 , you can read a predetermined value for
, you can read a predetermined value for 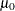 from the variable
from the variable _MEAN_in a LIMITS= data set.See Example 9.6.
- NOREADLIMITS
-
specifies that control limit parameters for each process listed in the MACHART statement are not to be read from the LIMITS= data set specified in the PROC MACONTROL statement. The NOREADLIMITS option is available only in SAS 6.10 and later releases.
The following example illustrates the NOREADLIMITS option:
proc macontrol data=Pistons limits=Diamlim; machart Diameter*Hour; machart Diameter*Hour / noreadlimits span=3; run;
The first MACHART statement reads the control limits from the first observation in the data set
Diamlimfor which the variable_VAR_is equal to 'Diameter' and the variable_SUBGRP_is equal to 'Hour'. The second MACHART statement computes estimates of the process mean and standard deviation for the control limits from the measurements in the data setPistons. Note that the second MACHART statement is equivalent to the following statements, which would be more commonly used:proc macontrol data=Pistons; machart Diameter*Hour / span=3; run;
For more information about reading control limit parameters from a LIMITS= data set, see the READLIMITS option later in this list.
- READALPHA
-
specifies that the variable
_ALPHA_, rather than the variable_SIGMAS_, is to be read from a LIMITS= data set when both variables are available in the data set. Thus the limits displayed are probability limits. If you do not specify the READALPHA option, then_SIGMAS_is read by default. - READINDEX=’value’
-
reads control limit parameters from a LIMITS= data set (specified in the PROC MACONTROL statement) for each process listed in the MACHART statement. The control limit parameters for a particular process are read from the first observation in the LIMITS= data set for which
-
the value of
_VAR_matches process -
the value of
_SUBGRP_matches the subgroup-variable -
the value of
_INDEX_matches value
The value can be up to 48 characters and must be enclosed in quotes.
-
- READLIMITS
-
specifies that control limit parameters are to be read from a LIMITS= data set specified in the PROC MACONTROL statement. The parameters for a particular process are read from the first observation in the LIMITS= data set for which
-
the value of
_VAR_matches process -
the value of
_SUBGRP_matches the subgroup variable
The use of the READLIMITS option depends on which release of SAS/QC software you are using.
-
In SAS 6.10 and later releases, the READLIMITS option is not necessary. To read control limits parameters as described previously, you simply specify a LIMITS= data set. However, even though the READLIMITS option is redundant, it continues to function as in earlier releases.
-
In SAS 6.09 and earlier releases, you must specify the READLIMITS option to read control limits parameters as described previously. If you specify a LIMITS= data set without specifying the READLIMITS option (or the READINDEX= option), the control limits are computed from the data and the span of the moving averages is specified with the SPAN= option.
-
- SIGMA0=value
-
specifies a known (standard) value
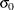 for the process standard deviation
for the process standard deviation  . The value must be positive. By default, the MACONTROL procedure estimates
. The value must be positive. By default, the MACONTROL procedure estimates  from the data using the formulas given in Methods for Estimating the Standard Deviation.
from the data using the formulas given in Methods for Estimating the Standard Deviation.
Note: As an alternative to specifying SIGMA0=
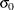 , you can read a predetermined value for
, you can read a predetermined value for 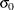 from the variable
from the variable _STDDEV_in a LIMITS= data set. - SIGMAS=value
-
specifies the width of the control limits in terms of the multiple k of the standard error of the plotted moving averages on the chart. The value of k must be positive. By default, k = 3 and the control limits are
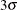 limits.
limits.
- SPAN=value
-
specifies the number of terms used to calculate the moving average (value is an integer greater than 1). The SPAN= option is required unless you read control limit parameters from a LIMITS= data set or a TABLE= data set. See Plotted Points and Choosing the Span of the Moving Average for details.
