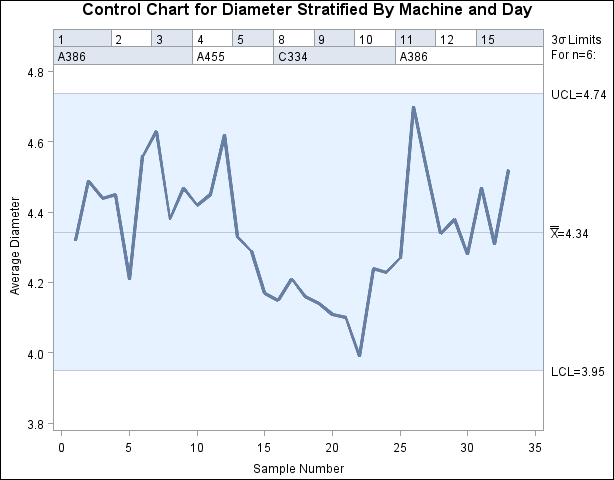
Displaying Stratification in Blocks of Observations
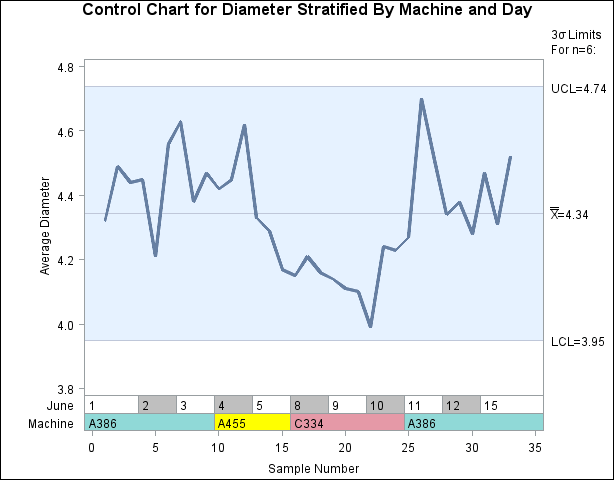
[See SHWBLK in the SAS/QC Sample Library]To display process data stratified into blocks of consecutive observations, specify one or more block-variables in parentheses after the subgroup-variable in the chart statement. The procedure displays a legend identifying blocks of consecutive observations with identical values of the block-variables. The legend displays one track of values for each block-variable. The values are the formatted values of the block-variable. For example, Figure 15.145 displays a legend with a single track for Machine, while Figure 15.146 displays a legend with two tracks corresponding to Machine and Day. You can label the tracks themselves by using the LABEL statement to associate labels with the corresponding block-variables; see Figure 15.147 for an illustration.
By default, the legend is placed above the chart as in Figure 15.145. You can control the position of the legend with the BLOCKPOS= option and the position of the legend labels with the BLOCKLABELPOS= option. See the entries in Dictionary of Options: SHEWHART Procedure as well as the following examples.
The block-variables must be variables in the input data set (a DATA=, HISTORY=, or TABLE= data set). If the input data set is a DATA= data set that contains multiple observations with the same value of the subgroup-variable, the values of a block-variable must be the same for all observations with the same value of the subgroup-variable. In other words, subgroups must be nested within groups determined by block-variables. The following statements create an  chart for the data in Parts stratified by the block-variable Machine. The chart is shown in Figure 15.145.
chart for the data in Parts stratified by the block-variable Machine. The chart is shown in Figure 15.145.
symbol h=3.0 pct;
title 'Control Chart for Diameter Stratified By Machine';
proc shewhart history=Parts;
xchart Diam*Sample (Machine) / stddeviations
nolegend ;
label Sample = 'Sample Number'
DiamX = 'Average Diameter' ;
run;
The unique consecutive values of Machine ('A386', 'A455', 'C334', and 'A386') are displayed in a track above the chart, and they indicate the same relationship between part diameter and machine as the previous example. Note that the track is not labeled (as in Figure 15.147), since no label is associated with Machine. A LABEL statement is used to provide labels for the axes.
Multiple block variables. You can use multiple block-variables to study more than one classification factor with the same chart. The following statements create an 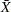 chart for the data in Parts, with Machine and Day as block-variables:
chart for the data in Parts, with Machine and Day as block-variables:
title 'Control Chart for Diameter Stratified By Machine and Day';
proc shewhart history=Parts;
xchart Diam*Sample (Machine Day) / stddeviations
nolegend
blockpos = 2;
label Sample = 'Sample Number'
DiamX = 'Average Diameter' ;
run;
The chart is displayed in Figure 15.146. Specifying BLOCKPOS=2 displays the block-variable legend immediately above the chart, without the gap shown in Figure 15.145. The NOLEGEND option suppresses the sample size legend that appears in the lower left of Figure 15.145.
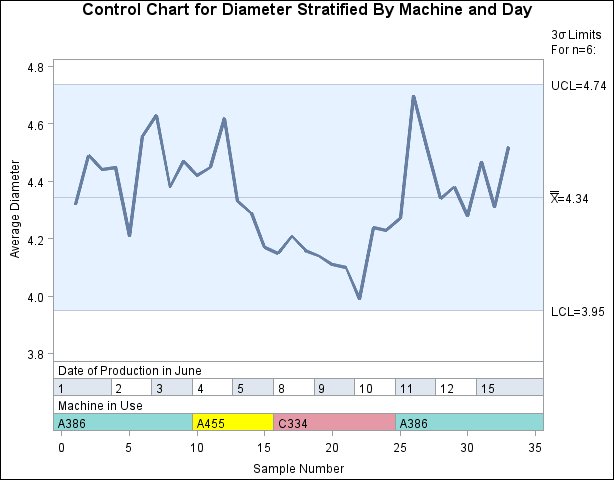
Color fills for legend. You can use the CBLOCKVAR= option to fill the legend track sections with colors corresponding to the values of the block-variables. Provide the colors as values of variables specified with the CBLOCKVAR= option. The procedure matches the color variables with the block-variables in the order specified. Each section is filled with the color for the first observation in the block. For example, the following statements produce an 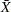 chart using a color variable named CMachine to fill the legend for the block-variable Machine:
chart using a color variable named CMachine to fill the legend for the block-variable Machine:
title 'Control Chart for Diameter Stratified By Machine and Day';
proc shewhart history=Parts2;
xchart Diam*Sample (Machine Day) / stddeviations
nolegend
blockpos = 3
cblockvar = CMachine;
label Sample = 'Sample Number'
DiamX = 'Average Diameter'
Day = 'Date of Production in June'
Machine = 'Machine in Use';
run;
The sections for Machine A386, Machine A455, and Machine C334 are filled with the colors specified as values of CMachine. The legend track for Day is filled with the default alternating colors from the ODS style, because a second color variable was not specified with the CBLOCKVAR= option. Specifying BLOCKPOS=3 positions the legend at the bottom of the chart and facilitates comparison with the subgroup axis. The LABEL statement is used to label the tracks with the labels associated with the block-variables.
The following statements produce an 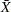 chart in which both legend tracks are filled:
chart in which both legend tracks are filled:
title 'Control Chart for Diameter Stratified By Machine and Day';
proc shewhart history=Parts3;
xchart Diam*Sample (Machine Day) /
stddeviations
nolegend
ltmargin = 5
blockpos = 3
blocklabelpos = left
cblockvar = (CMachine CDay);
label Sample = 'Sample Number'
DiamX = 'Average Diameter'
Day = 'June'
Machine = 'Machine';
run;
The chart is displayed in Figure 15.148. The color values of CMachine are used to fill the track for Machine, and the color values of CDay are used to fill the track for Day. Specifying BLOCKLABELPOS=LEFT displays the block variable labels to the left of the block legend. The LTMARGIN= option provides extra space in the left margin to accommodate the label Machine.