| The CAPABILITY Procedure |
Dictionary of Options
The following entries provide detailed descriptions of the options in the PROC CAPABILITY statement. The notes Traditional Graphics and Line Printer identify options that apply to traditional graphics and line printer plots, respectively.
- ALL
requests all of the tables generated by the FREQ, MODES, NEXTRVAL=5, CIBASIC, CIPCTLDF, and CIPCTLNORMAL options. If a WEIGHT statement is not used, the ALL option also requests the tables generated by the LOCCOUNT, NORMALTEST, ROBUSTSCALE, TRIMMED=.25, and WINSORIZED=.25 options. PROC CAPABILITY uses any values that you specify with the ALPHA=, MUO=, NEXTRVAL=, CIBASIC, CIPCTLDF, CIPCTLNORMAL, TRIMMED=, or WINSORIZED= options in conjunction with the ALL option.
- ALPHA=value
specifies the default confidence level for all confidence limits computed by the CAPABILITY procedure1. The coverage percent for the confidence limits is
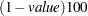 . For example, ALPHA=0.10 results in 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05.
. For example, ALPHA=0.10 results in 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05. Note that specialized ALPHA= options are available for a number of confidence interval options. For example, you can specify CIBASIC( ALPHA=0.10 ) to request a table of Basic Confidence Limits at the 90% level. The default values of these options default to the value of the general ALPHA= option.
- ANNOTATE=SAS-data-set
- ANNO=SAS-data-set
[Traditional Graphics] specifies an input data set containing annotate variables as described in SAS/GRAPH documentation. You can use this data set to add features to traditional graphics. Use this data set only when creating traditional graphics; it is ignored when the LINEPRINTER option is specified and when ODS Graphics is in effect. Features provided in this data set are added to every plot produced in the current run of the procedure.
- CHECKINDICES<(TEST = SW | KS | AD | CVM | NONE> <ALPHA=value>)>
specifies the test of normality used in conjunction with process capability indices that are displayed in the Process Capability Indices table. If the p-value for the test is less than the cutoff probability value specified with the ALPHA= option2, a warning is added to the table, as illustrated in Figure 5.3. See Tests for Normality for details concerning the test.
data Process; input P1-P10; datalines; 72 223 332 138 110 145 23 293 353 458 97 54 61 196 275 171 117 72 81 141 56 170 140 400 371 72 60 20 484 138 124 6 332 493 214 43 125 55 372 30 152 236 222 76 187 126 192 334 109 546 5 260 194 277 176 96 109 184 240 261 161 253 153 300 37 156 282 293 451 299 128 121 254 297 363 132 209 257 429 295 116 152 331 27 442 103 80 393 383 94 43 178 278 159 25 180 253 333 51 225 34 128 182 415 524 112 13 186 145 131 142 236 234 255 211 80 281 135 179 11 108 215 335 66 254 196 190 363 226 379 62 232 219 474 31 139 15 56 429 298 177 218 275 171 457 146 163 18 155 129 0 235 83 239 398 99 226 389 498 18 147 199 324 258 504 2 218 295 422 287 39 161 156 198 214 58 238 19 231 548 120 42 372 420 232 112 157 79 197 166 178 83 238 492 463 68 46 386 45 81 161 267 372 296 501 96 11 288 330 74 14 2 52 81 169 63 194 161 173 54 22 181 92 272 417 94 188 180 367 342 55 248 214 422 133 193 144 318 271 479 56 83 169 30 379 5 296 320 396 597 ; run;
proc capability data=Process; var p2; specs lsl=10 usl=275; run;Figure 5.3 Warning Message Printed with Capability IndicesProcess Capability Indices Index Value 95% Confidence Limits Cp 0.541072 0.388938 0.692946 CPL 0.642426 0.417087 0.862984 CPU 0.439718 0.257339 0.617184 Cpk 0.439718 0.259310 0.620126
Warning: Normality is rejected for alpha = 0.05 using the Shapiro-Wilk test
- ALPHA=value
specifies the cutoff probability for p-values for a test for normality used in conjunction with process capability indices. The value must be between zero and 0.5. The default value is 0.05.
- TEST = SW | KS | AD | CVM | NONE
specifies the test of normality used in conjunction with process capability indices that are displayed in the Process Capability Indices table. The tests available are Shapiro-Wilk (SW), Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS), Anderson-Darling (AD), and Cramér-von Mises (CVM). The default test is the Shapiro-Wilk test if the sample size is less than or equal to 2000 and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test if the sample size is greater than 2000.
- CIBASIC<(<TYPE=keyword> <ALPHA=value>)>
requests confidence limits for the mean, standard deviation, and variance based on the assumption that the data are normally distributed. With large sample sizes, this assumption is not required for confidence limits for the mean.
- ALPHA=value
specifies the confidence level. The coverage percent for the confidence limits is
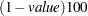 . For example, ALPHA=0.10 requests 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05.
. For example, ALPHA=0.10 requests 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05. - TYPE=keyword
specifies the type of confidence limit, where keyword is LOWER, UPPER, or TWOSIDED. The default value is TWOSIDED.
- CIINDICES<(<TYPE=keyword><ALPHA=value>)>
specifies the type and level of the confidence limits for standard capability indices displayed in the table labeled Process Capability Indices.
- ALPHA=value
specifies the confidence level. The coverage percent for the confidence limits is
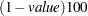 . For example, ALPHA=0.10 requests 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05.
. For example, ALPHA=0.10 requests 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05. - TYPE=keyword
specifies the type of confidence limit, where keyword is LOWER, UPPER, or TWOSIDED. The default value is TWOSIDED.
- CIPCTLDF<(TYPE=keyword><ALPHA=value>)>
- CIQUANTDF<(TYPE=keyword><ALPHA=value>)>
requests confidence limits for quantiles computed using a distribution-free method. In other words, no specific parametric distribution (such as the normal) is assumed for the data. Order statistics are used to compute the confidence limits as described in Section 5.2 of Hahn and Meeker (1991). This option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement.
- ALPHA=value
specifies the confidence level. The coverage percent for the confidence limits is
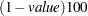 . For example, ALPHA=0.10 requests 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05.
. For example, ALPHA=0.10 requests 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05. - TYPE=keyword
specifies the type of confidence limit, where keyword is LOWER, UPPER, SYMMETRIC, or ASYMMETRIC. The default value is SYMMETRIC.
- CIPCTLNORMAL<(TYPE=keyword><ALPHA=value>)>
- CIQUANTNORMAL<(TYPE=keyword> <ALPHA=value>)
requests confidence limits for quantiles based on the assumption that the data are normally distributed. The computational method is described in Section 4.4.1 of Hahn and Meeker (1991) and uses the noncentral
 distribution as given by Odeh and Owen (1980). This option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement.
distribution as given by Odeh and Owen (1980). This option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement. - ALPHA=value
specifies the confidence level. The coverage percent for the confidence limits is
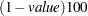 . For example, ALPHA=0.10 requests 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05.
. For example, ALPHA=0.10 requests 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05. - TYPE=keyword
specifies the type of confidence limit, where keyword is LOWER, UPPER, or TWOSIDED. The default value is TWOSIDED.
- CIPROBEX<(TYPE=keyword><ALPHA=value>)>
requests confidence limits for
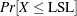 and
and 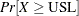 , where
, where 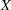 is the analysis variable, LSL is the lower specification limit, and USL is the upper specification limit. The computational method, which assumes that
is the analysis variable, LSL is the lower specification limit, and USL is the upper specification limit. The computational method, which assumes that 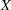 is normally distributed, is described in Section 4.5 of Hahn and Meeker (1991) and uses the noncentral
is normally distributed, is described in Section 4.5 of Hahn and Meeker (1991) and uses the noncentral  distribution as given by Odeh and Owen (1980). This option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement.
distribution as given by Odeh and Owen (1980). This option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement. - ALPHA=value
specifies the confidence level. The coverage percent for the confidence limits is
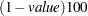 . For example, ALPHA=0.10 requests 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05.
. For example, ALPHA=0.10 requests 90% confidence limits. The default value is 0.05. - TYPE=keyword
specifies the type of confidence limit, where keyword is LOWER, UPPER, or TWOSIDED. The default value is TWOSIDED.
- CPMA=value
specifies the value of the parameter
 for the capability index
for the capability index  . This option has been superseded by the SPECIALINDICES(CPMA=) option.
. This option has been superseded by the SPECIALINDICES(CPMA=) option. - DATA=SAS-data-set
specifies the input data set containing the observations to be analyzed. If the DATA= option is omitted, the procedure uses the most recently created SAS data set.
- DEF=index
is an alias for the PCTLDEF= option. See the entry for the PCTLDEF= option.
- EXCLNPWGT
excludes observations with non-positive weight values (zero or nonnegative) for the analysis. By default, PROC CAPABILITY treats observations with negative weights like those with zero weights and counts them in the total number of observations. This option is applicable only if you specify a WEIGHT statement.
- FORMCHAR(index)='string'
[Line Printer] defines characters used for features on plots, where index is a number ranging from 1 to 11, and string is a character or hexadecimal string. The index identifies which features are controlled with the string characters, as discussed in the table that follows. If you specify the FORMCHAR= option omitting the index, the string controls all 11 features.
By default, the form character list specified with the SAS system option FORMCHAR= is used; otherwise, the default is FORMCHAR=’|—-|+|—’. If you print to a PC screen or your device supports the ASCII symbol set (1 or 2), the following is recommended:
formchar='B3,C4,DA,C2,BF,C3,C5,B4,C0,C1,D9'X
As an example, suppose you want to plot the data values of the empirical cumulative distribution function with asterisks (*). You can change the appropriate character by using the following:
formchar(2)='*'
Note that the FORMCHAR= option in the PROC CAPABILITY statement enables you to temporarily override the values of the SAS system option with the same name. The values of the SAS system option are not altered by using the FORMCHAR= option in PROC CAPABILITY statement.
The features associated with values of index are as follows:
Value of
index
Description of Character
Chart Feature
1
vertical bar
frame, ecdf line, HREF= lines
2
horizontal bar
frame, ecdf line, VREF= lines
3
box character (upper left)
frame, ecdf line, histogram bars
4
box character (upper middle)
histogram bars, tick marks (horizontal axis)
5
box character (upper right)
frame, histogram bars
6
box character (middle left)
histogram bars
7
box character (middle middle)
not used
8
box character (middle right)
histogram bars, tick marks (vertical axis)
9
box character (lower left)
frame
10
box character (lower middle)
histogram bars
11
box character (lower right)
frame, ecdf line
- FREQ
requests a frequency table in the printed output that contains the variable values, frequencies, percentages, and cumulative percentages. See Figure 5.2 for an example.
- GOUT=graphics-catalog
[Traditional Graphics] specifies a graphics catalog in which to save graphics output.
- LINEPRINTER
[Line Printer] requests that line printer plots be produced by the CDFPLOT, HISTOGRAM, PROBPLOT, PPPLOT, and QQPLOT statements. By default, these statements create traditional graphics output. 3 The CLASS and COMPHISTOGRAM statements cannot be used when the LINEPRINTER option is specified.
- LOCCOUNT
requests a table with the number of observations greater than, not equal to, and less than the value of MUO=. PROC CAPABILITY uses these values to construct the sign test and signed rank test. This option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement.
- MODES
- MODE
requests a table of all possible modes. By default, when the data contains multiple modes, PROC CAPABILITY displays the lowest mode in the table of basic statistical measures. When all values are unique, PROC CAPABILITY does not produce a table of modes.
- MUO=value(s)
- LOCATION=value(s)
specifies the value of the mean or location parameter (
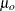 ) in the null hypothesis for the tests summarized in the table labeled Tests for Location: Mu0=value. If you specify a single value, PROC CAPABILITY tests the same null hypothesis for all analysis variables. If you specify multiple values, a VAR statement is required, and PROC CAPABILITY tests a different null hypothesis for each analysis variable by matching the VAR variables with the values in the corresponding order. The default value is 0.
) in the null hypothesis for the tests summarized in the table labeled Tests for Location: Mu0=value. If you specify a single value, PROC CAPABILITY tests the same null hypothesis for all analysis variables. If you specify multiple values, a VAR statement is required, and PROC CAPABILITY tests a different null hypothesis for each analysis variable by matching the VAR variables with the values in the corresponding order. The default value is 0. - NEXTROBS=n
specifies the number of extreme observations in the table labeled Extreme Observations. The table lists the n lowest observations and the n highest observations. The default value is 5. The value of n must be an integer between 0 and half the number of observations. You can specify NEXTROBS=0 to suppress the table.
- NEXTRVAL=n
requests the table labeled Extreme Values and specifies the number of extreme values in the table. The table lists the n lowest unique values and the n highest unique values. The value of n must be an integer between 0 and half the maximum number of observations. By default,
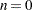 and no table is displayed.
and no table is displayed. - NOBYSPECS
specifies that specification limits in SPEC= data set be applied to all BY groups. If you use a BY statement and specify a SPECS= data set that does not contain the BY variables, you must specify the NOBYSPECS option.
- NOPRINT
suppresses the tables of descriptive statistics and capability indices which are created by the PROC CAPABILITY statement. The NOPRINT option does not suppress the tables created by the INTERVALS or plot statements. You can use the NOPRINT options in these statements to suppress the creation of their tables.
- NORMALTEST
- NORMAL
requests a table of Tests for Normality for each of the analysis variables. The table provides test statistics and p-values for the Shapiro-Wilk test (provided the sample size is less than or equal to 2000), the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, the Anderson-Darling test, and the Cramér-von Mises test. See Tests for Normality for details. If specification limits are provided, the NORMALTEST option is assumed.
- OUTTABLE=SAS-data-set
specifies an output data set that contains univariate statistics and capability indices arranged in tabular form. See OUTTABLE= Data Set for details.
- PCTLDEF=index
- DEF=index
specifies one of five definitions used to calculate percentiles. The value of index can be 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5. See Percentile Computations for details. By default, PCTLDEF=5.
- ROBUSTSCALE
requests a table of robust measures of scale. These measures include the interquartile range, Gini’s mean difference, the median absolute deviation about the median (MAD), and two statistics proposed by Rousseeuw and Croux (1993),
 , and
, and 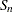 . This option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement.
. This option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement. - ROUND=value-list
specifies units used to round variable values. The ROUND= option reduces the number of unique values for each variable and hence reduces the memory required for temporary storage. Values must be greater than 0 for rounding to occur.
If you use only one value, the procedure uses this unit for all variables. If you use a list of values, you must also use a VAR statement. The procedure then uses the roundoff values for variables in the order given in the VAR statement. For example, the following statements specify a roundoff value of 1 for Yieldstrength and a roundoff value of 0.5 for TENSTREN.
proc capability round=1 0.5; var Yieldstrength tenstren; run;
When a variable value is midway between the two nearest rounded points, the value is rounded to the nearest even multiple of the roundoff value. For example, with a roundoff value of 1, the variable values of
 2.5,
2.5,  2.2, and
2.2, and  1.5 are rounded to
1.5 are rounded to  2; the values of
2; the values of  0.5, 0.2, and 0.5 are rounded to 0; and the values of 0.6, 1.2, and 1.4 are rounded to 1.
0.5, 0.2, and 0.5 are rounded to 0; and the values of 0.6, 1.2, and 1.4 are rounded to 1. - SPECIALINDICES
requests a table of specialized process capability indices. These indices include
 , Boyles’ modified
, Boyles’ modified 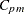 (also denoted as
(also denoted as 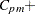 ),
), 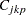 ,
,  ,
, 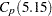 ,
, 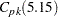 ,
, 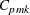 , Wright’s
, Wright’s 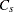 , Boyles’
, Boyles’ 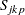 ,
, 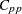 ,
, 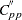 ,
,  ,
, 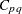 ,
, 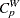 ,
, 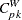 ,
, 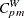 ,
, 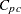 , and Vännmann’s
, and Vännmann’s  and
and  .
. You can provide values for the parameters
 for
for  ,
,  and
and  for
for  and
and  , and for the
, and for the 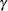 multiplier for
multiplier for 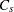 by specifying the following options in parentheses after the SPECIALINDICES option.
by specifying the following options in parentheses after the SPECIALINDICES option. - CPMA=value
specifies the value of the parameter
 for the capability index
for the capability index  described in Section 3.7 of Kotz and Johnson (1993). The value must be positive. The default value is 0.5. The existing CPMA= option in the PROC CAPABILITY statement is considered obsolete but still works.
described in Section 3.7 of Kotz and Johnson (1993). The value must be positive. The default value is 0.5. The existing CPMA= option in the PROC CAPABILITY statement is considered obsolete but still works. - CPU=value
specifies the value of the parameter
 for Vännmann’s capability index
for Vännmann’s capability index  . The value must be greater than or equal to zero. The default value is zero.
. The value must be greater than or equal to zero. The default value is zero. - CPV=value
specifies the value of the parameter
 for Vännmann’s capability indices
for Vännmann’s capability indices  and
and  . The value must be greater than or equal to zero. The default value is 4.
. The value must be greater than or equal to zero. The default value is 4. - CSGAMMA=value
specifies the value of the
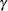 multiplier suggested by Chen and Kotz (1996) for Wright’s capability index
multiplier suggested by Chen and Kotz (1996) for Wright’s capability index 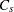 . The value must be greater than zero. The default value is 1.
. The value must be greater than zero. The default value is 1.
- SPECS=SAS-data-set
- SPEC=SAS-data-set
specifies an input data set containing specification limits for each of the variables in the VAR statement. This option is an alternative to the SPEC statement, which also provides specification limits. See SPEC= Data Set for details on SPEC= data sets, and Example 5.1 for an example. If you use both the SPEC= option and a SPEC statement, the SPEC= option is ignored.
- TRIMMED=values(s) <(TYPE=keyword><ALPHA=value>)
requests a table of trimmed means, where each value specifies the number or the proportion of trimmed observations. If the value is the number
 of trimmed observations,
of trimmed observations,  must be between 0 and half the number of nonmissing observations. If the value is a proportion p between 0 and 0.5, the number of observations trimmed is the smallest integer greater than or equal to np, where n is the number of observations. To obtain confidence limits for the mean and the student t-test, you must use the default value of VARDEF= which is DF. The TRIMMED= option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement.
must be between 0 and half the number of nonmissing observations. If the value is a proportion p between 0 and 0.5, the number of observations trimmed is the smallest integer greater than or equal to np, where n is the number of observations. To obtain confidence limits for the mean and the student t-test, you must use the default value of VARDEF= which is DF. The TRIMMED= option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement. - VARDEF=DF | N | WDF | WEIGHT | WGT
specifies the divisor used in calculating variances and standard deviations. The values and associated divisors are shown in the following table. By default, VARDEF=DF.
Value
Divisor
Formula
DF
degrees of freedom

N
number of observations

WEIGHT | WGT
sum of weight

WDF
sum of weights minus one
(
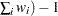
- WINSORIZED=values(s) <(<TYPE=keyword> <ALPHA=value>)>
- WINSOR=values(s) <(<TYPE=keyword> <ALPHA=value>)>
requests a table of winsorized means, where each value specifies the number or the proportion of winsorized observations. If the value is the number
 of winsorized observations,
of winsorized observations,  must be between 0 and half the number of nonmissing observations. If the value is a proportion p between 0 and 0.5, the number of observations winsorized is the smallest integer greater than or equal to np, where n is the number of observations. To obtain confidence limits for the mean and the student t-test, you must use the default value of VARDEF= which is DF. The WINSORIZED= option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement.
must be between 0 and half the number of nonmissing observations. If the value is a proportion p between 0 and 0.5, the number of observations winsorized is the smallest integer greater than or equal to np, where n is the number of observations. To obtain confidence limits for the mean and the student t-test, you must use the default value of VARDEF= which is DF. The WINSORIZED= option is not available if you specify a WEIGHT statement.
Footnotes
- In SAS 6.12 and earlier releases, the level for confidence limits for capability indices was specified with the GAMMA= option in the SPEC statement. This option still works but is considered obsolete.
- In SAS 6.12 and earlier releases, this value was specified with the ALPHA= option in the SPEC statement. This option still works but is considered obsolete.
- In SAS 6.12 and previous releases of SAS/QC software, line printer plots were created by default and the GRAPHICS option was required in the PROC CAPABILITY statement to produce traditional graphics output.
Copyright © SAS Institute, Inc. All Rights Reserved.