The FREQ Procedure
TABLES requests </ options> ;
The TABLES statement requests one-way to n-way frequency and crosstabulation tables and statistics for those tables.
If you omit the TABLES statement, PROC FREQ generates one-way frequency tables for all data set variables that are not listed in the other statements.
The following argument is required in the TABLES statement.
- requests
-
specify the frequency and crosstabulation tables to produce. A request is composed of one variable name or several variable names separated by asterisks. To request a one-way frequency table, use a single variable. To request a two-way crosstabulation table, use an asterisk between two variables. To request a multiway table (an n-way table, where n>2), separate the desired variables with asterisks. The unique values of these variables form the rows, columns, and strata of the table. You can include up to 50 variables in a single multiway table request.
For two-way to multiway tables, the values of the last variable form the crosstabulation table columns, while the values of the next-to-last variable form the rows. Each level (or combination of levels) of the other variables forms one stratum. PROC FREQ produces a separate crosstabulation table for each stratum. For example, a specification of
A*B*C*Din a TABLES statement produces k tables, where k is the number of different combinations of values forAandB. Each table lists the values forCdown the side and the values forDacross the top.You can use multiple TABLES statements in the PROC FREQ step. PROC FREQ builds all the table requests in one pass of the data, so that there is essentially no loss of efficiency. You can also specify any number of table requests in a single TABLES statement. To specify multiple table requests quickly, use a grouping syntax by placing parentheses around several variables and joining other variables or variable combinations. For example, the statements shown in Table 3.8 illustrate grouping syntax.
Table 3.8: Grouping Syntax
TABLES Request
Equivalent to
A*(B C)A*BA*C(
A B)*(C D)A*CB*CA*DB*D(
A B C)*DA*DB*DC*DA– –CABC(
A– –C)*DA*DB*DC*DThe TABLES statement variables are one or more variables from the DATA= input data set. These variables can be either character or numeric, but the procedure treats them as categorical variables. PROC FREQ uses the formatted values of the TABLES variable to determine the categorical variable levels. So if you assign a format to a variable with a FORMAT statement, PROC FREQ formats the values before dividing observations into the levels of a frequency or crosstabulation table. See the FORMAT procedure in the Base SAS Procedures Guide and the FORMAT statement and SAS formats in SAS Formats and Informats: Reference.
If you use PROC FORMAT to create a user-written format that combines missing and nonmissing values into one category, PROC FREQ treats the entire category of formatted values as missing. See the discussion in the section Grouping with Formats for more information.
By default, the frequency or crosstabulation table lists the values of both character and numeric variables in ascending order based on internal (unformatted) variable values. You can change the order of the values in the table by specifying the ORDER= option in the PROC FREQ statement. To list the values in ascending order by formatted value, use ORDER=FORMATTED.
If you request a one-way frequency table for a variable without specifying options, PROC FREQ produces frequencies, cumulative frequencies, percentages of the total frequency, and cumulative percentages for each value of the variable. If you request a two-way or an n-way crosstabulation table without specifying options, PROC FREQ produces crosstabulation tables that include cell frequencies, cell percentages of the total frequency, cell percentages of row frequencies, and cell percentages of column frequencies. The procedure excludes observations with missing values from the table but displays the total frequency of missing observations below each table.
Table 3.9 lists the options available in the TABLES statement. Descriptions of the options follow in alphabetical order.
Table 3.9: TABLES Statement Options
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Control Statistical Analysis |
|
|
Requests tests and measures of classification agreement |
|
|
Requests tests and measures of association produced by the |
|
|
Sets the confidence level for confidence limits |
|
|
Requests binomial proportions, confidence limits, and tests |
|
|
for one-way tables |
|
|
Requests chi-square tests and measures based on chi-square |
|
|
Requests confidence limits for MEASURES statistics |
|
|
Requests all Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel statistics |
|
|
Requests CMH correlation statistic, adjusted odds ratios, |
|
|
and adjusted relative risks |
|
|
Requests CMH correlation and row mean scores (ANOVA) |
|
|
statistics, adjusted odds ratios, and adjusted relative risks |
|
|
Specifies convergence criterion for polychoric correlation |
|
|
Requests Fisher’s exact test for tables larger than |
|
|
Requests Gail-Simon test for qualitative interactions |
|
|
Requests Jonckheere-Terpstra test |
|
|
Specifies maximum number of iterations for polychoric correlation |
|
|
Requests measures of association |
|
|
Treats missing values as nonmissing |
|
|
Requests polychoric correlation |
|
|
Requests odds ratios and relative risks for |
|
|
Requests risks and risk differences for |
|
|
Specifies the type of row and column scores |
|
|
Requests Cochran-Armitage test for trend |
|
|
Control Additional Table Information |
|
|
Displays cell contributions to the Pearson chi-square statistic |
|
|
Displays cumulative column percentages |
|
|
Displays deviations of cell frequencies from expected values |
|
|
Displays expected cell frequencies |
|
|
Displays missing value frequencies |
|
|
Includes all possible combinations of variable levels in the |
|
|
Displays standardized residuals in the CROSSLIST table |
|
|
Displays percentages of total frequency for n-way tables (n>2) |
|
|
Control Displayed Output |
|
|
Specifies the contents label for crosstabulation tables |
|
|
Displays crosstabulation tables in ODS column format |
|
|
Formats the frequencies in crosstabulation tables |
|
|
Displays two-way to n-way tables in list format |
|
|
Specifies maximum number of levels to display in one-way tables |
|
|
Suppresses display of column percentages |
|
|
Suppresses display of cumulative frequencies and percentages |
|
|
Suppresses display of frequencies |
|
|
Suppresses display of percentages |
|
|
Suppresses display of crosstabulation tables but displays statistics |
|
|
Suppresses display of row percentages |
|
|
Suppresses zero frequency levels in the CROSSLIST table, |
|
|
Suppresses log warning message for the chi-square test |
|
|
Displays kappa coefficient weights |
|
|
Displays row and column scores |
|
|
Produce Statistical Graphics |
|
|
Requests plots from ODS Graphics |
|
|
Create an Output Data Set |
|
|
Names an output data set to contain frequency counts |
|
|
Includes cumulative frequencies and percentages in the |
|
|
output data set for one-way tables |
|
|
Includes expected frequencies in the output data set |
|
|
Includes row, column, and two-way table percentages in the |
|
|
output data set |
|
You can specify the following options in a TABLES statement.
- AGREE <(WT=FC)>
-
requests tests and measures of classification agreement for square tables. The AGREE option provides McNemar’s test for
 tables and Bowker’s test of symmetry for square tables with more than two response categories. The AGREE option also produces
the simple kappa coefficient, the weighted kappa coefficient, their asymptotic standard errors, and their confidence limits.
When there are multiple strata, the AGREE option provides overall simple and weighted kappas as well as tests for equal kappas
among strata. When there are multiple strata and two response categories, PROC FREQ computes Cochran’s Q test. See the section Tests and Measures of Agreement for details about these statistics.
tables and Bowker’s test of symmetry for square tables with more than two response categories. The AGREE option also produces
the simple kappa coefficient, the weighted kappa coefficient, their asymptotic standard errors, and their confidence limits.
When there are multiple strata, the AGREE option provides overall simple and weighted kappas as well as tests for equal kappas
among strata. When there are multiple strata and two response categories, PROC FREQ computes Cochran’s Q test. See the section Tests and Measures of Agreement for details about these statistics.
If you specify the WT=FC option in parentheses after the AGREE option, PROC FREQ uses Fleiss-Cohen weights to compute the weighted kappa coefficient. By default, PROC FREQ uses Cicchetti-Allison weights. See the section Weighted Kappa Coefficient for details. You can specify the PRINTKWT option to display the kappa coefficient weights.
AGREE statistics are computed only for square tables, where the number of rows equals the number of columns. If your table is not square due to observations with zero weights, you can specify the ZEROS option in the WEIGHT statement to include these observations. For more details, see the section Tables with Zero Rows and Columns.
You can use the TEST statement to request asymptotic tests for the simple and weighted kappa coefficients. You can request exact p-values for the simple and weighted kappa coefficient tests, as well as for McNemar’s test, by specifying the corresponding options in the EXACT statement. See the section Exact Statistics for more information.
- ALL
-
requests all tests and measures that are produced by the CHISQ, MEASURES, and CMH options. You can control the number of CMH statistics to compute by specifying the CMH1 or CMH2 option.
-
ALPHA=

-
specifies the level of confidence limits. The value of
 must be between 0 and 1, and the default is 0.05. A confidence level of
must be between 0 and 1, and the default is 0.05. A confidence level of  produces
produces 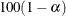 % confidence limits. The default of ALPHA=0.05 produces 95% confidence limits.
% confidence limits. The default of ALPHA=0.05 produces 95% confidence limits.
ALPHA= applies to confidence limits that are requested by TABLES statement options. There is a separate ALPHA= option in the EXACT statement that sets the level of confidence limits for Monte Carlo estimates of exact p-values, which you request by specifying the MC option in the EXACT statement.
- BINOMIAL <(binomial-options)>
-
requests the binomial proportion for one-way tables. When you specify the BINOMIAL option, by default PROC FREQ also provides the asymptotic standard error, asymptotic Wald and exact (Clopper-Pearson) confidence limits, and the asymptotic equality test for the binomial proportion.
You can specify binomial-options in parentheses after the BINOMIAL option. The LEVEL= binomial-option identifies the variable level for which to compute the proportion. If you do not specify LEVEL=, PROC FREQ computes the proportion for the first level that appears in the output. The P= binomial-option specifies the null proportion for the binomial tests. If you do not specify P=, PROC FREQ uses P=0.5 by default.
You can also specify binomial-options to request additional tests and confidence limits for the binomial proportion. The EQUIV, NONINF, and SUP binomial-options request tests of equivalence, noninferiority, and superiority, respectively. The CL= binomial-option requests confidence limits for the binomial proportion. Table 3.10 summarizes the binomial-options.
Available confidence limits for the binomial proportion include Agresti-Coull, exact (Clopper-Pearson), Jeffreys, Wald, and Wilson (score) confidence limits. You can specify more than one type of binomial confidence limits in the same analysis. If you do not specify any confidence limit requests, PROC FREQ computes Wald asymptotic confidence limits and exact (Clopper-Pearson) confidence limits by default. The ALPHA= option determines the confidence level, and the default of ALPHA=0.05 produces 95% confidence limits for the binomial proportion.
As part of the noninferiority, superiority, and equivalence analyses, PROC FREQ provides test-based confidence limits that have a confidence coefficient of
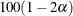 % (Schuirmann, 1999). The ALPHA= option determines the confidence level, and the default of ALPHA=0.05 produces 90% confidence limits. See the sections Noninferiority Test and Equivalence Test for details.
% (Schuirmann, 1999). The ALPHA= option determines the confidence level, and the default of ALPHA=0.05 produces 90% confidence limits. See the sections Noninferiority Test and Equivalence Test for details.
To request exact tests for the binomial proportion, specify the BINOMIAL option in the EXACT statement. PROC FREQ then computes exact p-values for all binomial tests that you request with binomial-options, which can include tests of noninferiority, superiority, and equivalence, in addition to the test of equality.
See the section Binomial Proportion for details.
Table 3.10: BINOMIAL Options
Option
Description
Specifies the variable level
Specifies the null proportion
Requests continuity correction
Request Confidence Limits
Requests Agresti-Coull confidence limits
Requests all confidence limits
Requests Clopper-Pearson confidence limits
Requests Jeffreys confidence limits
Requests Wald confidence limits
Requests Wilson (score) confidence limits
Request Tests
Requests an equivalence test
Requests a noninferiority test
Requests a superiority test
Specifies the test margin
Specifies the test variance
You can specify the following binomial-options in parentheses after the BINOMIAL option:
- CL=type | (types)
-
requests confidence limits for the binomial proportion. You can specify one or more types of confidence limits. When you specify only one type, you can omit the parentheses around the request.
PROC FREQ displays the confidence limits in the “Binomial Confidence Limits” table. The ALPHA= option determines the level of the confidence limits that the CL= binomial-option provides. The default of ALPHA=0.05 produces 95% confidence limits for the binomial proportion. This differs from the test-based confidence limits that are provided with the equivalence, noninferiority, and superiority tests (EQUIV, NONINF, and SUP), which have a confidence coefficient of
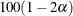 % (Schuirmann, 1999). See the sections Equivalence Test and Noninferiority Test for details.
% (Schuirmann, 1999). See the sections Equivalence Test and Noninferiority Test for details.
You can specify the CL= binomial-option with or without requests for binomial tests. The confidence limits that CL= produces do not depend on the tests that you request and do not use the value of the test margin (which you specify by using the MARGIN= binomial-option).
The following types of binomial confidence limits are available:
- AGRESTICOULL | AC
-
requests Agresti-Coull confidence limits for the binomial proportion. See the section Agresti-Coull Confidence Limits for details.
- ALL
-
requests all available types of confidence limits for the binomial proportion. These include the following: Agresti-Coull, exact (Clopper-Pearson), Jeffreys, Wald, and Wilson (score) confidence limits.
- EXACT | CLOPPERPEARSON
-
requests exact (Clopper-Pearson) confidence limits for the binomial proportion. See the section Exact (Clopper-Pearson) Confidence Limits for details. If you do not request any binomial confidence limits by specifying the CL= binomial-option, PROC FREQ produces Wald and exact (Clopper-Pearson) confidence limits by default. To request exact tests for the binomial proportion, specify the BINOMIAL option in the EXACT statement.
- JEFFREYS | J
-
requests Jeffreys confidence limits for the binomial proportion. See the section Jeffreys Confidence Limits for details.
- WALD < (CORRECT) >
-
requests Wald confidence limits for the binomial proportion. See the section Wald Confidence Limits for details. If you do not request any binomial confidence limits by specifying the CL= binomial-option, PROC FREQ produces Wald and exact (Clopper-Pearson) confidence limits by default.
If you specify CL=WALD(CORRECT), the Wald confidence limits include a continuity correction. If you specify the CORRECT binomial-option, the Wald confidence limits and the Wald tests include continuity corrections.
- WILSON | W | SCORE < (CORRECT) >
-
requests Wilson confidence limits for the binomial proportion. These are also known as score confidence limits. See the section Wilson (Score) Confidence Limits for details.
If you specify CL=WILSON(CORRECT) or the CORRECT binomial-option, the Wilson confidence limits include a continuity correction.
- CORRECT
-
includes a continuity correction in the Wald confidence limits, Wald tests, and Wilson confidence limits.
You can request continuity corrections individually for Wald or Wilson confidence limits by specifying the CL=WALD(CORRECT) or CL=WILSON(CORRECT) binomial-option, respectively.
- EQUIV | EQUIVALENCE
-
requests a test of equivalence for the binomial proportion. See the section Equivalence Test for details. You can specify the equivalence test margins, the null proportion, and the variance type with the MARGIN=, P=, and VAR= binomial-options, respectively. To request an exact equivalence test, specify the BINOMIAL option in the EXACT statement.
- LEVEL=level-number | 'level-value'
-
specifies the variable level for the binomial proportion. By default, PROC FREQ computes the proportion of observations for the first variable level that appears in the output. To request a different level, use LEVEL=level-number or LEVEL='level-value', where level-number is the variable level’s number or order in the output, and level-value is the formatted value of the variable level. The value of level-number must be a positive integer. You must enclose level-value in single quotes.
- MARGIN=value | (lower,upper)
-
specifies the margin for the noninferiority, superiority, and equivalence tests, which you request with the NONINF, SUP, and EQUIV binomial-options, respectively. If you do not specify MARGIN=, PROC FREQ uses a margin of 0.2 by default.
For noninferiority and superiority tests, specify a single value for the MARGIN= option. The MARGIN= value must be a positive number. You can specify value as a number between 0 and 1. Or you can specify value in percentage form as a number between 1 and 100, and PROC FREQ converts that number to a proportion. The procedure treats the value 1 as 1%.
For noninferiority and superiority tests, the test limits must be between 0 and 1. The limits are determined by the null proportion value (which you can specify with the P= binomial-option) and by the margin value. The noninferiority limit equals the null proportion minus the margin. By default, the null proportion equals 0.5 and the margin equals 0.2, which gives a noninferiority limit of 0.3. The superiority limit equals the null proportion plus the margin, which is 0.7 by default.
For an equivalence test, you can specify a single MARGIN= value, or you can specify both lower and upper values. If you specify a single MARGIN= value, it must be a positive number, as described previously. If you specify a single MARGIN= value for an equivalence test, PROC FREQ uses –value as the lower margin and value as the upper margin for the test. If you specify both lower and upper values for an equivalence test, you can specify them in proportion form as numbers between –1 or 1. Or you can specify them in percentage form as numbers between –100 and 100, and PROC FREQ converts the numbers to proportions. The value of lower must be less than the value of upper.
The equivalence limits must be between 0 and 1. The equivalence limits are determined by the null proportion value (which you can specify with the P= binomial-option) and by the margin values. The lower equivalence limit equals the null proportion plus the lower margin. By default, the null proportion equals 0.5 and the lower margin equals –0.2, which gives a lower equivalence limit of 0.3. The upper equivalence limit equals the null proportion plus the upper margin, which is 0.7 by default.
See the sections Noninferiority Test and Equivalence Test for details.
- NONINF | NONINFERIORITY
-
requests a test of noninferiority for the binomial proportion. See the section Noninferiority Test for details. You can specify the noninferiority test margin, the null proportion, and the variance type with the MARGIN=, P=, and VAR= binomial-options, respectively. To request an exact noninferiority test, specify the BINOMIAL option in the EXACT statement.
- P=value
-
specifies the null hypothesis proportion for the binomial tests. If you omit the P= option, PROC FREQ uses 0.5 as the null proportion. The null proportion value must be a positive number. You can specify value as a number between 0 and 1. Or you can specify value in percentage form as a number between 1 and 100, and PROC FREQ converts that number to a proportion. The procedure treats the value 1 as 1%.
- SUP | SUPERIORITY
-
requests a test of superiority for the binomial proportion. See the section Superiority Test for details. You can specify the superiority test margin, the null proportion, and the variance type with the MARGIN=, P=, and VAR= binomial-options, respectively. To request an exact superiority test, specify the BINOMIAL option in the EXACT statement.
- VAR=SAMPLE | NULL
-
specifies the type of variance estimate to use in the Wald tests of noninferiority, superiority, and equivalence. The default is VAR=SAMPLE, which estimates the variance from the sample proportion. VAR=NULL uses a test-based variance that is computed from the null hypothesis proportion (which is specified by the P= binomial-option). See the sections Noninferiority Test and Equivalence Test for details.
- CELLCHI2
-
displays each crosstabulation table cell’s contribution to the total Pearson chi-square statistic. The cell contribution is computed as
![\[ (\emph{frequency} - \emph{expected})^2 ~ / ~ \emph{expected} \]](images/procstat_freq0022.png)
where frequency is the table cell frequency or count and expected is the expected cell frequency, which is computed under the null hypothesis that the row and column variables are independent. See the section Pearson Chi-Square Test for Two-Way Tables for details.
The CELLCHI2 option has no effect for one-way tables or for tables that are displayed with the LIST option.
- CHISQ <(chisq-options)>
-
requests chi-square tests of homogeneity or independence and measures of association that are based on the chi-square statistic. For two-way tables, the chi-square tests include the Pearson chi-square, likelihood ratio chi-square, and Mantel-Haenszel chi-square tests. The chi-square measures include the phi coefficient, contingency coefficient, and Cramér’s V. For
 tables, the CHISQ option also provides Fisher’s exact test and the continuity-adjusted chi-square test. See the section Chi-Square Tests and Statistics for details.
tables, the CHISQ option also provides Fisher’s exact test and the continuity-adjusted chi-square test. See the section Chi-Square Tests and Statistics for details.
For one-way tables, the CHISQ option provides the Pearson chi-square goodness-of-fit test. You can also request the likelihood ratio goodness-of-fit test for one-way tables by specifying the LRCHISQ chisq-option in parentheses after the CHISQ option. By default, the one-way chi-square tests are based on the null hypothesis of equal proportions. Alternatively, you can provide null hypothesis proportions or frequencies by specifying the TESTP= or TESTF= chisq-option, respectively. See the section Chi-Square Test for One-Way Tables for more information.
To request Fisher’s exact test for tables larger than
 , specify the FISHER option in the EXACT statement. Exact p-values are also available for the Pearson, likelihood ratio, and Mantel-Haenszel chi-square tests. See the description of
the EXACT statement for more information.
, specify the FISHER option in the EXACT statement. Exact p-values are also available for the Pearson, likelihood ratio, and Mantel-Haenszel chi-square tests. See the description of
the EXACT statement for more information.
You can specify the following chisq-options in parentheses after the CHISQ option:
- DF=df
-
specifies the degrees of freedom for the chi-square tests. The value of df must not be zero. If the value of df is positive, PROC FREQ uses df as the degrees of freedom for the chi-square tests. If the value of df is negative, PROC FREQ uses df to adjust the default degrees of freedom for the chi-square tests.
By default for one-way tables, the value of df is (n – 1), where n is the number of variable levels in the table. By default for two-way tables, the value of df is (r – 1) (c – 1), where r is the number of rows in the table and c is the number of columns. See the sections Chi-Square Test for One-Way Tables and Chi-Square Tests and Statistics for more information.
If you specify a negative value of df, PROC FREQ adjusts the default degrees of freedom by adding the (negative) value of df to the default value to produce the adjusted degrees of freedom. The adjusted degrees of freedom must be positive.
The DF= chisq-option specifies or adjusts the degrees of freedom for the following chi-square tests: the Pearson and likelihood ratio goodness-of-fit tests for one-way tables; and the Pearson, likelihood ratio, and Mantel-Haenszel chi-square tests for two-way tables.
- LRCHISQ
-
requests the likelihood ratio goodness-of-fit test for one-way tables. See the section Likelihood Ratio Chi-Square Test for One-Way Tables for more information.
By default, this test is based on the null hypothesis of equal proportions. You can provide null hypothesis proportions or frequencies by specifying the TESTP= or TESTF= chisq-option, respectively. You can request an exact likelihood ratio goodness-of-fit test by specifying the LRCHI option in the EXACT statement.
- TESTF=(values) | SAS-data-set
-
specifies null hypothesis frequencies for the one-way chi-square goodness-of-fit tests. See the section Chi-Square Test for One-Way Tables for details. You can list the null frequencies as values in parentheses after TESTF=. Or you can provide the null frequencies in a secondary input data set by specifying TESTF=SAS-data-set. The TESTF=SAS-data-set cannot be the same data set that you specify in the DATA= option. You can specify only one TESTF= or TESTP= data set in a single invocation of the procedure.
If you list the null frequencies as values, you can separate the values with blanks or commas. The values must be positive numbers. The number of values must equal the number of variable levels in the one-way table. The sum of the values must equal the total frequency for the one-way table. Order the values to match the order in which the corresponding variable levels appear in the one-way frequency table.
If you provide the null frequencies in a secondary input data set (TESTF=SAS-data-set), the variable that contains the null frequencies should be named
_TESTF_,TestFrequency, orFrequency. The null frequencies must be positive numbers. The number of frequencies must equal the number of levels in the one-way frequency table, and the sum of the frequencies must equal the total frequency for the one-way table. Order the null frequencies in the data set to match the order in which the corresponding variable levels appear in the one-way frequency table. - TESTP=(values) | SAS-data-set
-
specifies null hypothesis proportions for the one-way chi-square goodness-of-fit tests. See the section Chi-Square Test for One-Way Tables for details. You can list the null proportions as values in parentheses after TESTP=. Or you can provide the null proportions in a secondary input data set by specifying TESTP=SAS-data-set. The TESTP=SAS-data-set cannot be the same data set that you specify in the DATA= option. You can specify only one TESTF= or TESTP= data set in a single invocation of the procedure.
If you list the null proportions as values, you can separate the values with blanks or commas. The values must be positive numbers. The number of values must equal the number of variable levels in the one-way table. Order the values to match the order in which the corresponding variable levels appear in the one-way frequency table. You can specify values in probability form as numbers between 0 and 1, where the proportions sum to 1. Or you can specify values in percentage form as numbers between 0 and 100, where the percentages sum to 100.
If you provide the null proportions in a secondary input data set (TESTP=SAS-data-set), the variable that contains the null proportions should be named
_TESTP_,TestPercent, orPercent. The null proportions must be positive numbers. The number of proportions must equal the number of levels in the one-way frequency table. You can provide the proportions in probability form as numbers between 0 and 1, where the proportions sum to 1. Or you can provide the proportions in percentage form as numbers between 0 and 100, where the percentages sum to 100. Order the null proportions in the data set to match the order in which the corresponding variable levels appear in the one-way frequency table. - WARN=value | (values)
-
controls the warning message for the validity of the asymptotic Pearson chi-square test. By default, PROC FREQ displays a warning message when more than 20% of the table cells have expected frequencies that are less than 5. If you specify the NOPRINT option in the PROC FREQ statement, the procedure displays the warning in the log; otherwise, the procedure displays the warning as a footnote in the chi-square table. You can use the WARN= option to suppress the warning and to include a warning indicator in the output data set.
The WARN= option can take one or more of the following values. If you specify more than one value, enclose the values in parentheses after WARN=. For example,
warn = (output noprint).Value of WARN=
Description
OUTPUT
Adds a warning indicator variable to the output data set
NOLOG
Suppresses the chi-square warning message in the log
NOPRINT
Suppresses the chi-square warning message in the display
NONE
Suppresses the chi-square warning message entirely
If you specify the WARN=OUTPUT option, the ODS output data set
ChiSqcontains a variable namedWarningthat equals 1 for the Pearson chi-square observation when more than 20% of the table cells have expected frequencies that are less than 5 and equals 0 otherwise. If you specify WARN=OUTPUT and also specify the CHISQ option in the OUTPUT statement, the statistics output data set contains a variable namedWARN_PCHIthat indicates the warning.The WARN=NOLOG option has the same effect as the NOWARN option in the TABLES statement.
- CL
-
requests confidence limits for the MEASURES statistics. If you omit the MEASURES option, the CL option invokes MEASURES. You can set the level of the confidence limits by using the ALPHA= option. The default of ALPHA=0.5 produces 95% confidence limits. See the sections Measures of Association and Confidence Limits for more information.
- CMH <(cmh-options)>
-
requests Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel statistics, which test for association between the row and column variables after adjusting for the remaining variables in a multiway table. The Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel statistics include the nonzero correlation statistic, the row mean scores (ANOVA) statistic, and the general association statistic. In addition, for
 tables, the CMH option provides the adjusted Mantel-Haenszel and logit estimates of the odds ratio and relative risks, together
with their confidence limits. For stratified
tables, the CMH option provides the adjusted Mantel-Haenszel and logit estimates of the odds ratio and relative risks, together
with their confidence limits. For stratified  tables, the CMH option provides the Breslow-Day test for homogeneity of odds ratios. (To request Tarone’s adjustment for
the Breslow-Day test, specify the BDT cmh-option.) See the section Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel Statistics for details.
tables, the CMH option provides the Breslow-Day test for homogeneity of odds ratios. (To request Tarone’s adjustment for
the Breslow-Day test, specify the BDT cmh-option.) See the section Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel Statistics for details.
You can use the CMH1 or CMH2 option to control the number of CMH statistics that PROC FREQ computes.
For stratified
 tables, you can request Zelen’s exact test for equal odds ratios by specifying the EQOR option in the EXACT statement. See the section Zelen’s Exact Test for Equal Odds Ratios for details. You can request exact confidence limits for the common odds ratio by specifying the COMOR option in the EXACT
statement. This option also provides a common odds ratio test. See the section Exact Confidence Limits for the Common Odds Ratio for details.
tables, you can request Zelen’s exact test for equal odds ratios by specifying the EQOR option in the EXACT statement. See the section Zelen’s Exact Test for Equal Odds Ratios for details. You can request exact confidence limits for the common odds ratio by specifying the COMOR option in the EXACT
statement. This option also provides a common odds ratio test. See the section Exact Confidence Limits for the Common Odds Ratio for details.
You can specify the following cmh-options in parentheses after the CMH option. These cmh-options, which apply to stratified
 tables, are also available with the CMH1 or CMH2 option.
tables, are also available with the CMH1 or CMH2 option.
- BDT
-
requests Tarone’s adjustment in the Breslow-Day test for homogeneity of odds ratios. See the section Breslow-Day Test for Homogeneity of the Odds Ratios for details.
- GAILSIMON | GS <(COLUMN=1 | 2)>
-
requests the Gail-Simon test for qualitative interaction, which applies to stratified
 tables. See the section Gail-Simon Test for Qualitative Interactions for details.
tables. See the section Gail-Simon Test for Qualitative Interactions for details.
The COLUMN= option specifies the column of the risk differences to use in computing the Gail-Simon test. By default, PROC FREQ uses column 1 risk differences. If you specify COLUMN=2, PROC FREQ uses column 2 risk differences.
The GAILSIMON cmh-option has the same effect as the GAILSIMON option in the TABLES statement.
- MANTELFLEISS | MF
-
requests the Mantel-Fleiss criterion for the Mantel-Haenszel statistic for stratified
 tables. See the section Mantel-Fleiss Criterion for details.
tables. See the section Mantel-Fleiss Criterion for details.
- CMH1 <(cmh-options)>
-
requests the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel correlation statistic. This option does not provide the CMH row mean scores (ANOVA) statistic or the general association statistic, which are provided by the CMH option. For tables larger than
 , the CMH1 option requires less memory than the CMH option, which can require an enormous amount of memory for large tables.
, the CMH1 option requires less memory than the CMH option, which can require an enormous amount of memory for large tables.
For
 tables, the CMH1 option also provides the adjusted Mantel-Haenszel and logit estimates of the odds ratio and relative risks,
together with their confidence limits. For stratified
tables, the CMH1 option also provides the adjusted Mantel-Haenszel and logit estimates of the odds ratio and relative risks,
together with their confidence limits. For stratified  tables, the CMH1 option provides the Breslow-Day test for homogeneity of odds ratios.
tables, the CMH1 option provides the Breslow-Day test for homogeneity of odds ratios.
The cmh-options for CMH1 are the same as the cmh-options that are available with the CMH option. See the description of the CMH option for details.
- CMH2 <(cmh-options)>
-
requests the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel correlation statistic and the row mean scores (ANOVA) statistic. This option does not provide the CMH general association statistic, which is provided by the CMH option. For tables larger than
 , the CMH2 option requires less memory than the CMH option, which can require an enormous amount of memory for large tables.
, the CMH2 option requires less memory than the CMH option, which can require an enormous amount of memory for large tables.
For
 tables, the CMH1 option also provides the adjusted Mantel-Haenszel and logit estimates of the odds ratio and relative risks,
together with their confidence limits. For stratified
tables, the CMH1 option also provides the adjusted Mantel-Haenszel and logit estimates of the odds ratio and relative risks,
together with their confidence limits. For stratified  tables, the CMH1 option provides the Breslow-Day test for homogeneity of odds ratios.
tables, the CMH1 option provides the Breslow-Day test for homogeneity of odds ratios.
The cmh-options for CMH2 are the same as the cmh-options that are available with the CMH option. See the description of the CMH option for details.
- CONTENTS='string'
-
specifies the label to use for crosstabulation tables in the contents file, the Results window, and the trace record. For information about output presentation, see the SAS Output Delivery System: User's Guide.
If you omit the CONTENTS= option, the contents label for crosstabulation tables is “Cross-Tabular Freq Table” by default.
Note that contents labels for all crosstabulation tables that are produced by a single TABLES statement use the same text. To specify different contents labels for different crosstabulation tables, request the tables in separate TABLES statements and use the CONTENTS= option in each TABLES statement.
To remove the crosstabulation table entry from the contents file, you can specify a null label with CONTENTS=''.
The CONTENTS= option affects only contents labels for crosstabulation tables. It does not affect contents labels for other PROC FREQ tables.
To specify the contents label for any PROC FREQ table, you can use PROC TEMPLATE to create a customized table definition. The CONTENTS_LABEL attribute in the DEFINE TABLE statement of PROC TEMPLATE specifies the contents label for the table. See the chapter “The TEMPLATE Procedure” in the SAS Output Delivery System: User's Guide for more information.
- CONVERGE=value
-
specifies the convergence criterion for computing the polychoric correlation, which you request by specifying the PLCORR option. The CONVERGE= value must be a positive number. By default, CONVERGE=0.0001. Iterative computation of the polychoric correlation stops when the convergence measure falls below value or when the number of iterations exceeds the MAXITER= value, whichever happens first. For parameter values that are less than 0.01, the procedure evaluates convergence by using the absolute difference instead of the relative difference. See the section Polychoric Correlation for details.
- CROSSLIST <STDRES>
-
displays crosstabulation tables in ODS column format instead of the default crosstabulation cell format. In the CROSSLIST table display, the rows correspond to the crosstabulation table cells, and the columns correspond to descriptive statistics such as Frequency and Percent. The CROSSLIST table displays the same information as the default crosstabulation table, but it uses an ODS column format instead of the table cell format. See the section Multiway Tables for details about the contents of the CROSSLIST table.
You can control the contents of a CROSSLIST table by specifying the same options available for the default crosstabulation table. These include the NOFREQ, NOPERCENT, NOROW, and NOCOL options. You can request additional information in a CROSSLIST table by specifying the CELLCHI2, DEVIATION, EXPECTED, MISSPRINT, and TOTPCT options. You can also display standardized residuals in a CROSSLIST table by specifying the CROSSLIST(STDRES) option (which is not available for the default crosstabulation table).
The FORMAT= and CUMCOL options have no effect on CROSSLIST tables. You cannot specify both the LIST option and the CROSSLIST option in the same TABLES statement.
For CROSSLIST tables, you can use the NOSPARSE option to suppress display of variable levels that have zero frequencies. By default, PROC FREQ displays all levels of the column variable within each level of the row variable, including any levels that have zero frequencies. By default for multiway tables displayed as CROSSLIST tables, the procedure displays all levels of the row variable for each stratum of the table, including any row levels with zero frequencies in the stratum.
You can specify the following option in parentheses after the CROSSLIST option:
- STDRES
-
displays the standardized residuals of the table cells in the CROSSLIST table. The standardized residual is the ratio of (frequency – expected) to its standard error, where frequency is the table cell frequency and expected is the expected table cell frequency, which is computed under the null hypothesis that the row and column variables are independent. See the section Standardized Residuals for more information.
- CUMCOL
-
displays the cumulative column percentages in the cells of the crosstabulation table. The CUMCOL option does not apply to crosstabulation tables produced with the LIST or CROSSLIST option.
- DEVIATION
-
displays the deviation of the frequency from the expected frequency for each cell of the crosstabulation table. See the section Pearson Chi-Square Test for Two-Way Tables for details. The DEVIATION option does not apply to crosstabulation tables produced with the LIST option.
- EXPECTED
-
displays the expected cell frequencies under the hypothesis of independence (or homogeneity) for crosstabulation tables. See the section Pearson Chi-Square Test for Two-Way Tables for details. The EXPECTED option does not apply to tables produced with the LIST option.
- FISHER | EXACT
-
requests Fisher’s exact test for tables that are larger than
 . (For
. (For  tables, the CHISQ option provides Fisher’s exact test.) This test is also known as the Freeman-Halton test. See the sections
Fisher’s Exact Test and Exact Statistics for more information.
tables, the CHISQ option provides Fisher’s exact test.) This test is also known as the Freeman-Halton test. See the sections
Fisher’s Exact Test and Exact Statistics for more information.
If you omit the CHISQ option in the TABLES statement, the FISHER option invokes CHISQ. You can also request Fisher’s exact test by specifying the FISHER option in the EXACT statement.
Note: PROC FREQ computes exact tests by using fast and efficient algorithms that are superior to direct enumeration. Exact tests are appropriate when a data set is small, sparse, skewed, or heavily tied. For some large problems, computation of exact tests might require a substantial amount of time and memory. Consider using asymptotic tests for such problems. Alternatively, when asymptotic methods might not be sufficient for such large problems, consider using Monte Carlo estimation of exact p-values. You can request Monte Carlo estimation by specifying the MC computation-option in the EXACT statement. See the section Computational Resources for more information.
- FORMAT=format-name
-
specifies a format for the following crosstabulation table cell values: frequency, expected frequency, and deviation. PROC FREQ also uses the specified format to display the row and column total frequencies and the overall total frequency in crosstabulation tables.
You can specify any standard SAS numeric format or a numeric format defined with the FORMAT procedure. The format length must not exceed 24. If you omit the FORMAT= option, by default PROC FREQ uses the BEST6. format to display frequencies less than 1E6, and the BEST7. format otherwise.
The FORMAT= option applies only to crosstabulation tables displayed in the default format. It does not apply to crosstabulation tables produced with the LIST or CROSSLIST option.
To change display formats in any FREQ table, you can use PROC TEMPLATE. See the chapter “The TEMPLATE Procedure” in the SAS Output Delivery System: User's Guide for more information.
- GAILSIMON | GS <(COLUMN=1 | 2)>
-
requests the Gail-Simon test for qualitative interaction, which applies to stratified
 tables. See the section Gail-Simon Test for Qualitative Interactions for details.
tables. See the section Gail-Simon Test for Qualitative Interactions for details.
The COLUMN= option specifies the column of the risk differences to use in computing the Gail-Simon test. By default, PROC FREQ uses column 1 risk differences. If you specify COLUMN=2, PROC FREQ uses column 2 risk differences.
- JT
-
requests the Jonckheere-Terpstra test. See the section Jonckheere-Terpstra Test for details. To request exact p-values for the Jonckheere-Terpstra test, specify the JT option in the EXACT statement. See the section Exact Statistics for more information.
- LIST
-
displays two-way to n-way crosstabulation tables in a list format instead of the default crosstabulation cell format. The LIST option displays the entire multiway table in one table, instead of displaying a separate two-way table for each stratum. See the section Multiway Tables for details.
The LIST option is not available when you also specify statistical options. You must use the standard crosstabulation table display or the CROSSLIST display when you request statistical tests or measures.
- MAXITER=number
-
specifies the maximum number of iterations for computing the polychoric correlation, which you request by specifying the PLCORR option. The value of number must be a positive integer. By default MAXITER=20. Iterative computation of the polychoric correlation stops when the number of iterations exceeds the MAXITER= value or when the convergence measure falls below the CONVERGE= value, whichever happens first. See the section Polychoric Correlation for details.
- MAXLEVELS=n
-
specifies the maximum number of variable levels to display in one-way frequency tables. The value of n must be a positive integer. PROC FREQ displays the first n variable levels, matching the order in which the levels appear in the one-way frequency table. (The ORDER= option controls the order of the variable levels. By default, ORDER=INTERNAL, which orders the variable levels by unformatted value.)
The MAXLEVELS= option also applies to one-way frequency plots, which you can request by specifying the PLOTS=FREQPLOT option when ODS Graphics is enabled.
If you specify the MISSPRINT option to display missing levels in the frequency table, the MAXLEVELS= option displays the first n nonmissing levels.
The MAXLEVELS= option does not apply to the OUT= output data set, which includes all variable levels. The MAXLEVELS= option does not affect the computation of percentages, statistics, or tests for the one-way table; these values are based on the complete table.
- MEASURES
-
requests measures of association. The MEASURES option provides the following statistics and their asymptotic standard errors: gamma, Kendall’s tau-b, Stuart’s tau-c, Somers’
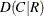 , Somers’
, Somers’ 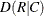 , Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients, lambda (symmetric and asymmetric), and uncertainty coefficients (symmetric
and asymmetric). To request confidence limits for these measures of association, you can specify the CL option.
, Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients, lambda (symmetric and asymmetric), and uncertainty coefficients (symmetric
and asymmetric). To request confidence limits for these measures of association, you can specify the CL option.
For
 tables, the MEASURES option also provides the odds ratio, column 1 relative risk, column 2 relative risk, and the corresponding
confidence limits. Alternatively, you can request the odds ratio and relative risks separately (without the other measures
of association), by specifying the RELRISK option.
tables, the MEASURES option also provides the odds ratio, column 1 relative risk, column 2 relative risk, and the corresponding
confidence limits. Alternatively, you can request the odds ratio and relative risks separately (without the other measures
of association), by specifying the RELRISK option.
See the section Measures of Association for details.
You can use the TEST statement to request asymptotic tests for the following measures of association: gamma, Kendall’s tau-b, Stuart’s tau-c, Somers’
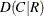 , Somers’
, Somers’ 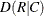 , and Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients. You can use the EXACT statement to request exact confidence limits for the odds ratio, exact unconditional confidence limits for the relative risks,
and exact tests for the following measures of association: Kendall’s tau-b, Stuart’s tau-c, Somers’
, and Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients. You can use the EXACT statement to request exact confidence limits for the odds ratio, exact unconditional confidence limits for the relative risks,
and exact tests for the following measures of association: Kendall’s tau-b, Stuart’s tau-c, Somers’ 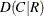 and
and 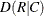 , and Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients. See the descriptions of the TEST and EXACT statements for more information.
, and Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients. See the descriptions of the TEST and EXACT statements for more information.
- MISSING
-
treats missing values as a valid nonmissing level for all TABLES variables. The MISSING option displays the missing levels in frequency and crosstabulation tables and includes them in all calculations of percentages, tests, and measures.
By default, if you do not specify the MISSING or MISSPRINT option, an observation is excluded from a table if it has a missing value for any of the variables in the TABLES request. When PROC FREQ excludes observations with missing values, it displays the total frequency of missing observations below the table. See the section Missing Values for more information.
- MISSPRINT
-
displays missing value frequencies in frequency and crosstabulation tables but does not include the missing value frequencies in any computations of percentages, tests, or measures.
By default, if you do not specify the MISSING or MISSPRINT option, an observation is excluded from a table if it has a missing value for any of the variables in the TABLES request. When PROC FREQ excludes observations with missing values, it displays the total frequency of missing observations below the table. See the section Missing Values for more information.
- NOCOL
-
suppresses the display of column percentages in crosstabulation table cells.
- NOCUM
-
suppresses the display of cumulative frequencies and percentages in one-way frequency tables. The NOCUM option also suppresses the display of cumulative frequencies and percentages in crosstabulation tables in list format, which you request with the LIST option.
- NOFREQ
-
suppresses the display of cell frequencies in crosstabulation tables. The NOFREQ option also suppresses row total frequencies. This option has no effect for one-way tables or for crosstabulation tables in list format, which you request with the LIST option.
- NOPERCENT
-
suppresses the display of overall percentages in crosstabulation tables. These percentages include the cell percentages of the total (two-way) table frequency, as well as the row and column percentages of the total table frequency. To suppress the display of cell percentages of row or column totals, use the NOROW or NOCOL option, respectively.
For one-way frequency tables and crosstabulation tables in list format, the NOPERCENT option suppresses the display of percentages and cumulative percentages.
- NOPRINT
-
suppresses the display of frequency and crosstabulation tables but displays all requested tests and statistics. To suppress the display of all output, including tests and statistics, use the NOPRINT option in the PROC FREQ statement.
- NOROW
-
suppresses the display of row percentages in crosstabulation table cells.
- NOSPARSE
-
suppresses the display of cells with a zero frequency count in LIST output and omits them from the OUT= data set. The NOSPARSE option applies when you specify the ZEROS option in the WEIGHT statement to include observations with zero weights. By default, the ZEROS option invokes the SPARSE option, which displays table cells with a zero frequency count in the LIST output and includes them in the OUT= data set. See the description of the ZEROS option for more information.
The NOSPARSE option also suppresses the display of variable levels with zero frequency in CROSSLIST tables. By default for CROSSLIST tables, PROC FREQ displays all levels of the column variable within each level of the row variable, including any column variable levels with zero frequency for that row. For multiway tables displayed with the CROSSLIST option, the procedure displays all levels of the row variable for each stratum of the table by default, including any row variable levels with zero frequency for the stratum.
- NOWARN
-
suppresses the log warning message for the validity of the asymptotic Pearson chi-square test. By default, PROC FREQ provides a validity warning for the asymptotic Pearson chi-square test when more than 20cells have expected frequencies that are less than 5. This warning message appears in the log if you specify the NOPRINT option in the PROC FREQ statement,
The NOWARN option is equivalent to the CHISQ(WARN=NOLOG) option. You can also use the CHISQ(WARN=) option to suppress the warning message in the display and to request a warning variable in the chi-square ODS output data set or in the OUTPUT data set.
- OUT=SAS-data-set
-
names an output data set that contains frequency or crosstabulation table counts and percentages. If more than one table request appears in the TABLES statement, the contents of the OUT= data set correspond to the last table request in the TABLES statement. The OUT= data set variable
COUNTcontains the frequencies and the variablePERCENTcontains the percentages. See the section Output Data Sets for details. You can specify the following options to include additional information in the OUT= data set: OUTCUM, OUTEXPECT, and OUTPCT. - OUTCUM
-
includes cumulative frequencies and cumulative percentages in the OUT= data set for one-way tables. The variable
CUM_FREQcontains the cumulative frequencies, and the variableCUM_PCTcontains the cumulative percentages. See the section Output Data Sets for details. The OUTCUM option has no effect for two-way or multiway tables. - OUTEXPECT
-
includes expected cell frequencies in the OUT= data set for crosstabulation tables. The variable
EXPECTEDcontains the expected cell frequencies. See the section Output Data Sets for details. The EXPECTED option has no effect for one-way tables. - OUTPCT
-
includes the following additional variables in the OUT= data set for crosstabulation tables:
PCT_COL-
percentage of column frequency
PCT_ROW-
percentage of row frequency
PCT_TABL-
percentage of stratum (two-way table) frequency, for n-way tables where n > 2
See the section Output Data Sets for details. The OUTPCT option has no effect for one-way tables.
- PLCORR
-
requests the polychoric correlation coefficient. For
 tables, this statistic is more commonly known as the tetrachoric correlation coefficient, and it is labeled as such in the
displayed output. See the section Polychoric Correlation for details.
tables, this statistic is more commonly known as the tetrachoric correlation coefficient, and it is labeled as such in the
displayed output. See the section Polychoric Correlation for details.
The PLCORR option provides the polychoric correlation coefficient and its asymptotic standard error. If you also specify the CL option, PROC FREQ provides confidence limits for the polychoric correlation. You can specify the PLCORR option in the TEST statement, to request Wald and likelihood ratio tests for the polychoric correlation. If you omit the MEASURES option, the PLCORR option invokes the MEASURES option.
The CONVERGE= and MAXITER= options control the iterative computation of the polychoric correlation coefficient. The CONVERGE= option specifies the convergence criterion and the MAXITER= option specifies the maximum number of iterations. By default CONVERGE=0.0001 and MAXITER=20. Iterative computation of the polychoric correlation stops when the number of iterations exceeds the MAXITER= value or when the convergence measures falls below the CONVERGE= value, whichever happens first.
-
PLOTS < ( global-plot-options ) > < = plot-request < ( plot-options ) > >
PLOTS < ( global-plot-options ) >
< = ( plot-request < (plot-options) > <…plot-request < (plot-options ) >> )> -
controls the plots that are produced through ODS Graphics. Plot-requests identify the plots, and plot-options control the appearance and content of the plots. You can specify plot-options in parentheses after a plot-request. A global-plot-option applies to all plots for which it is available unless it is altered by a specific plot-option. You can specify global-plot-options in parentheses after the PLOTS option.
When you specify only one plot-request, you can omit the parentheses around the request. For example:
plots=all plots=freqplot plots=(freqplot oddsratioplot) plots(only)=(cumfreqplot deviationplot)
ODS Graphics must be enabled before plots can be requested. For example:
ods graphics on; proc freq; tables treatment*response / chisq plots=freqplot; weight wt; run; ods graphics off;
For more information about enabling and disabling ODS Graphics, see the section “Enabling and Disabling ODS Graphics” in Chapter 21: Statistical Graphics Using ODS in SAS/STAT 12.3 User's Guide.
If ODS Graphics is enabled but you do not specify the PLOTS= option, PROC FREQ produces all plots that are associated with the analyses that you request with the exception of the frequency, cumulative frequency, and mosaic plots. To produce a frequency plot or cumulative frequency plot when ODS Graphics is enabled, you must specify the FREQPLOT or CUMFREQPLOT plot-request, respectively, in the PLOTS= option, or you must specify the PLOTS=ALL option. To produce a mosaic plot when ODS Graphics is enabled, you must specify the MOSAICPLOT plot-request in the PLOTS= option, or you must specify the PLOTS=ALL option.
PROC FREQ produces the remaining plots (listed in Table 3.11) by default when you request the corresponding TABLES statement options. You can suppress default plots and request specific plots by using the PLOTS(ONLY)= option; PLOTS(ONLY)=(plot-requests) produces only the plots that are specified as plot-requests. You can suppress all plots by specifying the PLOTS=NONE option. The PLOTS= option has no effect when you specify the NOPRINT option in the PROC FREQ statement.
Plot Requests
Table 3.11 lists the available plot-requests together with their required TABLES statement options. Descriptions of the plot-requests follow the table in alphabetical order.
Table 3.11: Plot Requests
Plot Request
Description
Required TABLES Statement Option
Agreement plot
AGREE (
 table)
table)
All plots
None
Cumulative frequency plot
One-way table request
Deviation plot
CHISQ (one-way table)
Frequency plot
Any table request
Kappa plot
AGREE (
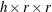 table)
table)
Mosaic plot
Two-way or multiway table request
No plots
None
Odds ratio plot
Relative risk plot
Risk difference plot
RISKDIFF (
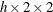 table)
table)
Weighted kappa plot
AGREE (
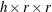 table,
table,  )
)
The following plot-requests are available with the PLOTS= option:
- AGREEPLOT < (plot-options ) >
-
requests an agreement plot (Bangdiwala and Bryan, 1987), An agreement plot displays the strength of agreement in a two-way table, where the row and column variables represent two independent ratings of n subjects. For information about agreement plots, see Bangdiwala (1988); Bangdiwala et al. (2008), and Friendly (2000, Section 3.7.2).
To produce an agreement plot, you must also specify the AGREE option in the TABLES statement. Agreement statistics and plots are available for two-way square tables, where the number of rows equals the number of columns.
Table 3.12 lists the plot-options that are available for agreement plots. See the subsection “Plot Options” for descriptions of the plot-options.
Table 3.12: Plot Options for AGREEPLOT
Plot Option
Description
Values
Legend
YES
 or NO
or NO
Partial agreement
YES
 or NO
or NO
Frequency scale
YES
 or NO
or NO
Statistics
None
 Default
Default
- ALL
-
requests all plots that are associated with the specified analyses. If you specify the PLOTS=ALL option, PROC FREQ produces the frequency, cumulative frequency, and mosaic plots that are associated with the tables that you request. (PROC FREQ does not produce these plots by default when ODS Graphics is enabled.)
- CUMFREQPLOT <(plot-options)>
-
requests a plot of cumulative frequencies. Cumulative frequency plots are available for one-way frequency tables.
To produce a cumulative frequency plot, you must specify the CUMFREQPLOT plot-request in the PLOTS= option, or you must specify the PLOTS=ALL option. PROC FREQ does not produce cumulative frequency plots by default when ODS Graphics is enabled.
Table 3.13 lists the plot-options that are available for cumulative frequency plots. See the subsection “Plot Options” for descriptions of the plot-options.
- DEVIATIONPLOT <(plot-options)>
-
requests a plot of relative deviations from expected frequencies. Deviation plots are available for chi-square analysis of one-way frequency tables. To produce a deviation plot, you must also specify the CHISQ option in the TABLES statement for a one-way frequency table.
Table 3.14 lists the plot-options that are available for deviation plots. See the subsection “Plot Options” for descriptions of the plot-options.
- FREQPLOT <(plot-options)>
-
requests a frequency plot. Frequency plots are available for frequency and crosstabulation tables. For multiway crosstabulation tables, PROC FREQ provides a two-way frequency plot for each stratum (two-way table).
To produce a frequency plot, you must specify the FREQPLOT plot-request in the PLOTS= option, or you must specify the PLOTS=ALL option. PROC FREQ does not produce frequency plots by default when ODS Graphics is enabled.
By default, PROC FREQ displays frequency plots as bar charts. You can specify the TYPE=DOTPLOT plot-option to display frequency plots as dot plots. You can plot percentages instead of frequencies by specifying the SCALE=PERCENT plot-option. There are four frequency plot layouts available, which you can request by specifying the TWOWAY= plot-option. See the subsection “Plot Options” for more information.
By default, the primary grouping of graph cells in a two-way layout is by column variable. Row variable levels are then displayed within column variable levels. You can specify the GROUPBY=ROW plot-option to group first by row variable.
Table 3.15 lists the plot-options that are available for frequency plots. See the subsection “Plot Options” for descriptions of the plot-options.
The following plot-options are available for all frequency plots: ORIENT=, SCALE=, and TYPE=. The following plot-options are available for frequency plots of two-way (and multiway) tables: GROUPBY=, NPANELPOS=, and TWOWAY=. The NPANELPOS= plot-option is not available with the TWOWAY=CLUSTER or TWOWAY=STACKED layout, which is always displayed in a single panel.
Table 3.15: Plot Options for FREQPLOT
Plot Option
Description
Values
Primary group
COLUMN
 or ROW
or ROW
Sections per panel
Number (4
 )
)
Orientation
VERTICAL
 or HORIZONTAL
or HORIZONTAL
Scale
FREQ
 or PERCENT
or PERCENT
Two-way layout
CLUSTER, GROUPHORIZONTAL,
GROUPVERTICAL
 , or STACKED
, or STACKED
Type
BARCHART
 or DOTPLOT
or DOTPLOT
 Default
Default
 For two-way tables
For two-way tables
- KAPPAPLOT <(plot-options)>
-
requests a plot of kappa statistics with confidence limits. Kappa plots are available for multiway square tables and display the kappa statistic (with confidence limits) for each two-way table (stratum). Kappa plots also display the overall kappa statistic unless you specify the COMMON=NO plot-option. To produce a kappa plot, you must specify the AGREE option in the TABLES statement to compute kappa statistics.
Table 3.16 lists the plot-options that are available for kappa plots. See the subsection “Plot Options” for descriptions of the plot-options.
Table 3.16: Plot Options for KAPPAPLOT and WTKAPPAPLOT
Plot Option
Description
Values
Error bar type
SERIF
 , LINE, or BAR
, LINE, or BAR
Overall kappa
YES
 or NO
or NO
Statistics per graphic
Number
Order of two-way levels
ASCENDING or DESCENDING
Range to display
Values or CLIP
Statistics
None
 Default
Default
- MOSAICPLOT <(plot-option)>
-
requests a mosaic plot. Mosaic plots are available for crosstabulation tables. For multiway tables, PROC FREQ provides a mosaic plot for each two-way table (stratum).
To produce a mosaic plot, you must specify the MOSAICPLOT plot-request in the PLOTS= option, or you must specify the PLOTS=ALL option. PROC FREQ does not produce mosaic plots by default when ODS Graphics is enabled.
Mosaic plots display tiles that correspond to the crosstabulation table cells. The areas of the tiles are proportional to the frequencies of the table cells. The column variable is displayed on the X axis, and the tile widths are proportional to the relative frequencies of the column variable levels. The row variable is displayed on the Y axis, and the tile heights are proportional to the relative frequencies of the row levels within column levels. The colors of the tiles correspond to the row variable levels. See Friendly (2000) for more information.
You can specify the following plot-option in parentheses after the MOSAICPLOT plot-request:
- NONE
- ODDSRATIOPLOT <(plot-options)>
-
requests a plot of odds ratios with confidence limits. Odds ratio plots are available for multiway
 tables and display the odds ratio (with confidence limits) for each
tables and display the odds ratio (with confidence limits) for each  table (stratum). To produce an odds ratio plot, you must also specify the MEASURES or RELRISK option in the TABLES statement to compute odds ratios.
table (stratum). To produce an odds ratio plot, you must also specify the MEASURES or RELRISK option in the TABLES statement to compute odds ratios.
If you specify the CMH option in the TABLES statement to compute the common odds ratio for the multiway table, by default the plot displays the common odds ratio. The COMMON=NO plot-option suppresses display of the common odds ratio. If you do not specify the CMH option, the common odds ratio is not available to be displayed in the plot.
By default, odds ratio plots display asymptotic confidence limits. You can specify the CL=EXACT plot-option to display exact confidence limits for the odds ratios. You must also request computation of exact confidence limits by specifying the OR option in the EXACT statement. To display the common odds ratio with exact confidence limits, you must also specify the COMOR option in the EXACT statement.
Table 3.17 lists the plot-options that are available for odds ratio plots. See the subsection “Plot Options” for descriptions of the plot-options.
Table 3.17: Plot Options for ODDSRATIOPLOT, RELRISKPLOT, and RISKDIFFPLOT
Plot Option
Description
Values
Confidence limit type
Type
Error bar type
SERIF
 , LINE, or BAR
, LINE, or BAR
Risk column
1
 or 2
or 2
Axis scale
2, E, or 10
Statistics per graphic
Number (All
 )
)
Order of two-way levels
ASCENDING or DESCENDING
Range to display
Values or CLIP
Statistics
None
 Default
Default
 Available for RELRISKPLOT and RISKDIFFPLOT
Available for RELRISKPLOT and RISKDIFFPLOT
 Available for ODDSRATIOPLOT and RELRISKPLOT
Available for ODDSRATIOPLOT and RELRISKPLOT
- RELRISKPLOT <(plot-options)>
-
requests a plot of relative risks with confidence limits. Relative risk plots are available for multiway
 tables and display the relative risk (with confidence limits) for each
tables and display the relative risk (with confidence limits) for each  table (stratum). To produce a relative risk plot, you must also specify the MEASURES or RELRISK option in the TABLES statement to compute relative risks.
table (stratum). To produce a relative risk plot, you must also specify the MEASURES or RELRISK option in the TABLES statement to compute relative risks.
If you specify the CMH option in the TABLES statement to compute the common relative risk for the multiway table, by default the plot displays the common relative risk. The COMMON=NO plot-option suppresses display of the common relative risk. If you do not specify the CMH option, the common relative risk is not available to be displayed in the plot.
By default, relative risk plots display asymptotic confidence limits. You can specify the CL=EXACT plot-option to display exact confidence limits for the relative risks. You must also request computation of exact confidence limits by specifying the RELRISK option in the EXACT statement. When you specify the CL=EXACT plot-option, the relative risk plot does not display the common relative risk.
Table 3.17 lists the plot-options that are available for relative risk plots. See the subsection “Plot Options” for descriptions of the plot-options.
- RISKDIFFPLOT <(plot-options)>
-
requests a plot of risk (proportion) differences with confidence limits. Risk difference plots are available for multiway
 tables and display the risk difference (with confidence limits) for each
tables and display the risk difference (with confidence limits) for each  table (stratum). To produce a risk difference plot, you must also specify the RISKDIFF option in the TABLES statement to compute risk differences.
table (stratum). To produce a risk difference plot, you must also specify the RISKDIFF option in the TABLES statement to compute risk differences.
By default, risk difference plots display asymptotic Wald confidence limits. You can specify the CL=EXACT plot-option to display exact confidence limits for the risk differences. You must also request computation of exact confidence limits by specifying the RISKDIFF option in the EXACT statement.
In addition to Wald and exact confidence limits, you can display the following confidence limit types in a risk difference plot: Agresti-Caffo, Hauck-Anderson, Miettinen-Nurminen, and Newcombe. See the descriptions of the CL=EXACT plot-option and the RISKDIFF option for more information.
Table 3.17 lists the plot-options that are available for risk difference plots. See the subsection “Plot Options” for descriptions of the plot-options.
- WTKAPPAPLOT <(plot-options)>
-
requests a plot of weighted kappa statistics with confidence limits. Weighted kappa plots are available for multiway square tables and display the weighted kappa statistic (with confidence limits) for each two-way table (stratum). Weighted kappa plots also display the overall weighted kappa statistic unless you specify the COMMON=NO plot-option.
To produce a weighted kappa plot, you must also specify the AGREE option in the TABLES statement to compute weighted kappa statistics. Simple kappa and weighted kappa statistics are equal for
 tables; therefore, PROC FREQ displays weighted kappa statistics and plots only for tables that are larger than
tables; therefore, PROC FREQ displays weighted kappa statistics and plots only for tables that are larger than  .
.
Table 3.16 lists the plot-options that are available for weighted kappa plots. See the subsection “Plot Options” for descriptions of the plot-options.
Global Plot Options
A global-plot-option applies to all plots for which the option is available unless it is altered by an individual plot-option. You can specify global-plot-options in parentheses after the PLOTS option. For example:
plots(order=ascending stats)=(riskdiffplot oddsratioplot) plots(only)=freqplot
The following plot-options are available as global-plot-options: CLDISPLAY=, COLUMN=, COMMON=, EXACT, LOGBASE=, NPANELPOS=, ORDER=, ORIENT=, RANGE=, SCALE=, STATS, and TYPE=. See the subsection “Plot Options” for description of these plot-options.
In addition to these plot-options, you can specify the following global-plot-option in parentheses after the PLOTS option:
You can specify the following plot-options in parentheses after a plot-request:
- CL=type
-
specifies the type of confidence limits to display. The CL= plot-option is available for the following plots: ODDSRATIOPLOT, RELRISKPLOT, and RISKDIFFPLOT.
For odds ratio and relative risk plots, the available confidence limit types are asymptotic and exact, which you can request by specifying CL=ASYMPTOTIC and CL=EXACT, respectively. By default, these plots display asymptotic confidence limits. When you specify CL=EXACT to display exact confidence limits, you must also request computation of exact confidence limits by specifying the corresponding option (OR or RELRISK) in the EXACT statement. See the sections Exact Confidence Limits for the Odds Ratio and Exact Unconditional Confidence Limits for the Relative Risk for more information.
For risk difference plots, the available confidence limit types include the following: CL=AC (Agresti-Caffo), CL=EXACT (exact unconditional), CL=HA (Hauck-Anderson), CL=MN (Miettinen-Nurminen), CL=NEWCOMBE (Newcombe), and CL=WALD (Wald). See the description of the CL= riskdiff-option and see the section Risk Difference Confidence Limits for more information. If you specify CL=EXACT to display exact confidence limits in the plot, you must also request computation of exact confidence limits by specifying the RISKDIFF option in the EXACT statement.
- CLDISPLAY=SERIF | LINE | BAR <width>
-
controls the appearance of the confidence limit error bars. The CLDISPLAY= plot-option is available for the following plots: KAPPAPLOT, ODDSRATIOPLOT, RELRISKPLOT, RISKDIFFPLOT, and WTKAPPAPLOT.
The default value is CLDISPLAY=SERIF, which displays the confidence limits as lines with serifs. CLDISPLAY=LINE displays the confidence limits as plain lines without serifs.
CLDISPLAY=BAR displays the confidence limits as bars. By default, the width of the bars equals the size of the marker for the estimate. You can control the width of the bars and the size of the marker by specifying the value of width as a percentage of the distance between bars,
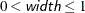 . The bar might disappear when the value of width is very small.
. The bar might disappear when the value of width is very small.
- COLUMN=1 | 2
-
specifies the
 table column to use to compute the risk (proportion). The COLUMN= plot-option is available for the relative risk plot (RELRISKPLOT) and the risk difference plot (RISKDIFFPLOT). If you specify COLUMN=1, the plot displays the column 1 relative risks or the column 1 risk difference. Similarly, if you
specify COLUMN=2, the plot displays the column 2 relative risks or risk difference. The default is COLUMN=1.
table column to use to compute the risk (proportion). The COLUMN= plot-option is available for the relative risk plot (RELRISKPLOT) and the risk difference plot (RISKDIFFPLOT). If you specify COLUMN=1, the plot displays the column 1 relative risks or the column 1 risk difference. Similarly, if you
specify COLUMN=2, the plot displays the column 2 relative risks or risk difference. The default is COLUMN=1.
- COMMON=YES | NO
-
controls the display of the common (overall) statistic in plots that display stratum (two-way table) statistics for a multiway table. The COMMON= plot-option is available for the following plots: KAPPAPLOT, ODDSRATIOPLOT, RELRISKPLOT, and WTKAPPAPLOT.
By default, COMMON=YES and the plots display the common value when it is available. When you specify the AGREE option in the TABLES statement for a multiway table, PROC FREQ computes overall kappa statistics in addition to kappa statistics for each stratum. When you specify the MEASURES or RELRISK option in the TABLES statement, PROC FREQ computes only stratum-level odds ratios and relative risks; to compute common odds ratios and relative risks, you must also specify the CMH option in the TABLES statement.
COMMON=YES is not available for relative risk plots when you specify the CL=EXACT plot-option to display exact confidence limits.
- EXACT
-
requests display of exact confidence limits instead of asymptotic confidence limits. The EXACT plot-option is available for the odds ratio plot (ODDSRATIOPLOT), relative risk plot (RELRISKPLOT), and risk difference plot (RISKDIFFPLOT). The EXACT plot-option is equivalent to the CL=EXACT plot-option.
When you specify the EXACT plot-option, you must also request computation of exact confidence limits by specifying the appropriate statistic-option in the EXACT statement.
- GROUPBY=COLUMN | ROW
-
specifies the primary grouping for two-way frequency plots. The default is GROUPBY=COLUMN, which groups graph cells first by column variable and displays row variable levels within column variable levels. You can specify GROUPBY=ROW to group first by row variable. In two-way and multiway table requests, the column variable is the last variable specified and forms the columns of the crosstabulation table. The row variable is the next-to-last variable specified and forms the rows of the table.
By default for a bar chart that is displayed in the TWOWAY=STACKED layout, bars correspond to the column variable levels, and row levels are displayed (stacked) within each column bar. By default for a bar chart that is displayed in the TWOWAY=CLUSTER layout, bars are first grouped by column variable levels, and row levels are displayed as adjacent bars within each column-level group. You can reverse the default row and column variable grouping by specifying GROUPBY=ROW.
- LOGBASE=2 | E | 10
-
applies to the odds ratio plot (ODDSRATIOPLOT) and the relative risk plot (RELRISKPLOT). LOGBASE= displays the odds ratio or relative risk axis on the log scale that you specify.
- LEGEND=YES | NO
-
applies to the agreement plot (AGREEPLOT). LEGEND=NO suppresses the legend that identifies the areas of exact and partial agreement. The default is LEGEND=YES.
- NOSTAT
-
applies to the deviation plot (DEVIATIONPLOT). NOSTAT suppresses the chi-square p-value that deviation plot displays by default.
- NPANELPOS=n
-
applies to the following plots: FREQPLOT (for two-way and multiway tables), KAPPAPLOT, ODDSRATIOPLOT, RELRISKPLOT, RISKDIFFPLOT, and WTKAPPAPLOT.
For kappa, odds ratio, relative risk, risk difference, and weighted kappa plots, NPANELPOS= divides the plot into multiple panels that display at most
 statistics per panel. If n is positive, the number of statistics per panel is balanced; if n is negative, the number of statistics per panel is not balanced. For example, suppose you want to display 21 odds ratios.
NPANELPOS=20 displays two panels, the first with 11 odds ratios and the second with 10 odds ratios; NPANELPOS=–20 displays
20 odds ratios in the first panel but only one in the second panel. By default, n = 0 and all statistics are displayed in a single panel.
statistics per panel. If n is positive, the number of statistics per panel is balanced; if n is negative, the number of statistics per panel is not balanced. For example, suppose you want to display 21 odds ratios.
NPANELPOS=20 displays two panels, the first with 11 odds ratios and the second with 10 odds ratios; NPANELPOS=–20 displays
20 odds ratios in the first panel but only one in the second panel. By default, n = 0 and all statistics are displayed in a single panel.
For two-way frequency plots, the NPANELPOS= plot-option divides the plot into multiple panels that display at most
 sections per panel. Sections correspond to row or column variable levels, depending on the type of plot and the grouping.
sections per panel. Sections correspond to row or column variable levels, depending on the type of plot and the grouping.
The NPANELPOS= plot-option applies to two-way plots that are displayed in the TWOWAY=GROUPVERTICAL or TWOWAY=GROUPHORIZONTAL layout. The NPANELPOS= plot-option does not apply to the TWOWAY=CLUSTER and TWOWAY=STACKED layouts, which are always displayed in a single panel.
If n is positive, the number of sections per panel is balanced; if n is negative, the number of sections per panel is not balanced. By default for frequency plots, n = 4 and each panel includes at most four sections.
- ORDER=ASCENDING | DESCENDING
-
displays the statistics in sorted order. By default, the statistics are displayed in the order in which the two-way table strata appear in the multiway table display. The ORDER= plot-option applies to the following plots: KAPPAPLOT, ODDSRATIOPLOT, RELRISKPLOT, RISKDIFFPLOT, and WTKAPPAPLOT.
- ORIENT=HORIZONTAL | VERTICAL
-
controls the orientation of the plot. The ORIENT= plot-option applies to the following plots: CUMFREQPLOT, DEVIATIONPLOT, and FREQPLOT.
ORIENT=HORIZONTAL places the variable levels on the Y axis and the frequencies, percentages, or statistic values on the X axis. ORIENT=VERTICAL places the variable levels on the X axis. The default orientation is ORIENT=VERTICAL for bar charts (TYPE=BARCHART) and ORIENT=HORIZONTAL for dot plots (TYPE=DOTPLOT).
- PARTIAL=YES | NO
-
controls the display of partial agreement in the agreement plot (AGREEPLOT). PARTIAL=NO suppresses the display of partial agreement. When you specify PARTIAL=NO, the agreement plot displays only exact agreement. Exact agreement includes the diagonal cells of the square table, where the row and column variable levels are the same. Partial agreement includes the adjacent off-diagonal table cells, where the row and column values are within one level of exact agreement. The default is PARTIAL=YES.
- RANGE=(<min> <,max>) | CLIP
-
specifies the range of values to display. The RANGE= plot-option applies to the following plots: KAPPAPLOT, ODDSRATIOPLOT, RELRISKPLOT, RISKDIFFPLOT, and WTKAPPAPLOT. If you specify RANGE=CLIP, the confidence limits are clipped and the display range is determined by the minimum and maximum values of the statistics. By default, the display range includes all confidence limits.
- SCALE=FREQ | LOG | PERCENT | SQRT
-
specifies the scale of the frequencies to display. The SCALE= plot-option applies to the frequency plot (FREQPLOT) and the cumulative frequency plot (CUMFREQPLOT).
The default is SCALE=FREQ, which displays unscaled frequencies. SCALE=LOG displays log (base 10) frequencies. SCALE=PERCENT displays percentages (relative frequencies). SCALE=SQRT displays square roots of the frequencies, which produces a plot known as a rootogram.
- SHOWSCALE=YES | NO
-
controls the display of the cumulative frequency scale on the right side of the agreement plot (AGREEPLOT). SHOWSCALE=NO suppresses the display of the scale. The default is SHOWSCALE=YES.
- SQUARE
-
requests a square mosaic plot (MOSAICPLOT), where the height of the Y axis equals the width of the X axis. In a square mosaic plot, the scale of the relative frequencies is the same on both axes. By default, the mosaic plot area is rectangular.
- STATS
-
displays statistic values in the plot. For the following plots, the STATS plot-option displays the statistics and their confidence limits on the right side of the plot: KAPPAPLOT, ODDSRATIOPLOT, RELRISKPLOT, RISKDIFFPLOT, and WTKAPPAPLOT.
For the agreement plot (AGREEPLOT), STATS displays the values of the kappa statistic, the weighted kappa statistic, and the
 measure (Bangdiwala and Bryan, 1987).
measure (Bangdiwala and Bryan, 1987).
If you do not request the STATS plot-option, these plots do not display the statistic values.
- TWOWAY=CLUSTER | GROUPHORIZONTAL | GROUPVERTICAL | STACKED
-
specifies the layout for two-way frequency plots.
All TWOWAY= layouts are available for bar charts (TYPE=BARCHART). All TWOWAY= layouts except TWOWAY=CLUSTER are available for dot plots (TYPE=DOTPLOT). The ORIENT= and GROUPBY= plot-options are available for all TWOWAY= layouts.
The default two-way layout is TWOWAY=GROUPVERTICAL, which produces a grouped plot that has a vertical common baseline. By default for bar charts (TYPE=BARCHART, ORIENT=VERTICAL), the X axis displays column variable levels, and the Y axis displays frequencies. The plot includes a vertical (Y-axis) block for each row variable level. The relative positions of the graph cells in this plot layout are the same as the relative positions of the table cells in the crosstabulation table. You can reverse the default row and column grouping by specifying the GROUPBY=ROW plot-option.
The TWOWAY=GROUPHORIZONTAL layout produces a grouped plot that has a horizontal common baseline. By default (GROUPBY=COLUMN), the plot displays a block on the X axis for each column variable level. Within each column-level block, the plot displays row variable levels.
The TWOWAY=STACKED layout produces stacked displays of frequencies. By default (GROUPBY=COLUMN) in a stacked bar chart, the bars correspond to column variable levels, and row levels are stacked within each column level. By default in a stacked dot plot, the dotted lines correspond to column levels, and cell frequencies are plotted as data dots on the corresponding column line. The dot color identifies the row level.
The TWOWAY=CLUSTER layout, which is available only for bar charts, displays groups of adjacent bars. By default, the primary grouping is by column variable level, and row levels are displayed within each column level.
You can reverse the default row and column grouping in any layout by specifying the GROUPBY=ROW plot-option. The default is GROUPBY=COLUMN, which groups first by column variable.
- TYPE=BARCHART | DOTPLOT
-
specifies the plot type for frequency (FREQPLOT), cumulative frequency (CUMFREQPLOT), and deviation plots (DEVIATIONPLOT). TYPE=BARCHART produces a bar chart and TYPE=DOTPLOT produces a dot plot. The default is TYPE=BARCHART.
- PRINTKWT
-
displays the weights that PROC FREQ uses to compute the weighted kappa coefficient. You must also specify the AGREE option to request the weighted kappa coefficient. You can specify (WT=FC) with the AGREE option to request Fleiss-Cohen weights. By default, PROC FREQ uses Cicchetti-Allison weights to compute the weighted kappa coefficient. See the section Weighted Kappa Coefficient for details.
- RELRISK | OR
-
requests relative risk measures and their confidence limits for
 tables. These measures include the odds ratio and the column 1 and 2 relative risks. See the section Odds Ratio and Relative Risks for 2 x 2 Tables for details.
tables. These measures include the odds ratio and the column 1 and 2 relative risks. See the section Odds Ratio and Relative Risks for 2 x 2 Tables for details.
You can also obtain the RELRISK measures by specifying the MEASURES option, which produces other measures of association in addition to the relative risks.
You can request exact confidence limits for the odds ratio by specifying the OR option in the EXACT statement. You can request exact unconditional confidence limits for the relative risks by specifying the RELRISK option in the EXACT statement. See the sections Exact Confidence Limits for the Odds Ratio and Exact Unconditional Confidence Limits for the Relative Risk for more information.
- RISKDIFF <(riskdiff-options)>
-
requests risks (binomial proportions) and risk differences for
 tables. When you specify the RISKDIFF option, PROC FREQ provides the row 1 risk, row 2 risk, total (overall) risk, and risk
difference (row 1 – row 2), together with their asymptotic standard errors and Wald confidence limits. PROC FREQ also provides
exact (Clopper-Pearson) confidence limits for the row 1, row 2, and total risks by default. You can request exact unconditional
confidence limits for the risk difference by specifying the RISKDIFF option in the EXACT statement. See the section Risks and Risk Differences for details. PROC FREQ displays these results in the column 1 and column 2 “Risk Estimates” tables.
tables. When you specify the RISKDIFF option, PROC FREQ provides the row 1 risk, row 2 risk, total (overall) risk, and risk
difference (row 1 – row 2), together with their asymptotic standard errors and Wald confidence limits. PROC FREQ also provides
exact (Clopper-Pearson) confidence limits for the row 1, row 2, and total risks by default. You can request exact unconditional
confidence limits for the risk difference by specifying the RISKDIFF option in the EXACT statement. See the section Risks and Risk Differences for details. PROC FREQ displays these results in the column 1 and column 2 “Risk Estimates” tables.
You can specify riskdiff-options in parentheses after the RISKDIFF option to request tests and additional confidence limits for the risk difference. Table 3.18 summarizes the riskdiff-options.
The EQUIV, NONINF, and SUP riskdiff-options request tests of equivalence, noninferiority, and superiority, respectively, for the risk difference. Available test methods include Farrington-Manning (score), Hauck-Anderson, and Newcombe (hybrid-score), in addition to the Wald test.
As part of the noninferiority, superiority, and equivalence analyses, PROC FREQ provides test-based confidence limits that have a confidence coefficient of
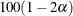 % (Schuirmann, 1999). The ALPHA= option determines the confidence level, and the default of ALPHA=0.05 produces 90% confidence limits. See the sections Noninferiority Tests and Equivalence Tests for details.
% (Schuirmann, 1999). The ALPHA= option determines the confidence level, and the default of ALPHA=0.05 produces 90% confidence limits. See the sections Noninferiority Tests and Equivalence Tests for details.
The CL= riskdiff-option requests confidence limits for the risk difference. Available confidence limit types include Agresti-Caffo, exact unconditional, Hauck-Anderson, Miettinen-Nurminen, Newcombe, and Wald. Continuity-corrected Newcombe and Wald confidence limits are also available. You can request more than one type of confidence limits in the same analysis. PROC FREQ displays the confidence limits in the “Proportion (Risk) Difference Confidence Limits” table.
The ALPHA= option determines the level of the confidence limits that the CL= riskdiff-option provides. The default of ALPHA=0.05 produces 95% confidence limits for the risk difference.
The CL=EXACT riskdiff-option displays exact unconditional confidence limits in the “Proportion (Risk) Difference Confidence Limits” table. When you use CL=EXACT, you must also request computation of the exact confidence limits by specifying the RISKDIFF option in the EXACT statement.
Table 3.18: RISKDIFF (Proportion Difference) Options
Option
Description
Specifies the risk column
Requests continuity correction
Suppresses default risk tables
Request Confidence Limits
Requests Agresti-Caffo confidence limits
Displays exact confidence limits
Requests Hauck-Anderson confidence limits
Requests Miettinen-Nurminen confidence limits
Requests Newcombe confidence limits
Requests Wald confidence limits
Request Tests
Requests an equality test
Requests an equivalence test
Requests a noninferiority test
Requests a superiority test
Specifies the test margin
Specifies the test method
Specifies the test variance
You can specify the following riskdiff-options in parentheses after the RISKDIFF option:
- CL=type | (types)
-
requests confidence limits for the risk difference. You can specify one or more types of confidence limits. When you specify only one type, you can omit the parentheses around the request. PROC FREQ displays the confidence limits in the “Proportion (Risk) Difference Confidence Limits” table.
The ALPHA= option determines the confidence level, and the default of ALPHA=0.05 produces 95% confidence limits for the risk difference. This differs from the test-based confidence limits that are provided with the equivalence, noninferiority, and superiority tests (EQUIV, NONINF, and SUP), which have a confidence coefficient of
 % (Schuirmann, 1999).
% (Schuirmann, 1999).
You can specify CL= with or without requests for risk difference tests. The confidence limits produced by CL= do not depend on the tests that you request and do not use the value of the test margin (which you specify by using MARGIN= riskdiff-option).
You can control the risk column for the confidence limits by specifying the COLUMN= riskdiff-option. If you do not specify COLUMN=, PROC FREQ provides confidence limits for the column 1 risk difference by default.
The following types of confidence limits are available:
- AC | AGRESTICAFFO
-
requests Agresti-Caffo confidence limits for the risk difference. See the subsection “Agresti-Caffo Confidence Limits” in the section Risk Difference Confidence Limits for details.
- EXACT
-
displays exact unconditional confidence limits for the risk difference in the “Proportion (Risk) Difference Confidence Limits” table. You must also request computation of the exact confidence limits by specifying the RISKDIFF option in the EXACT statement.
PROC FREQ computes the confidence limits by inverting two separate one-sided exact tests (tail method), where the tests are based on the unstandardized risk difference by default. If you specify the RISKDIFF(METHOD=SCORE) option in the EXACT statement, the tests are based on the score statistic. See the RISKDIFF option in the EXACT statement and the section Exact Unconditional Confidence Limits for the Risk Difference for more information.
By default, PROC FREQ also displays these exact confidence limits in the “Risk Estimates” table. You can suppress this table by specifying the NORISKS riskdiff-option.
- HA
-
requests Hauck-Anderson confidence limits for the risk difference. See the subsection “Hauck-Anderson Confidence Limits” in the section Risk Difference Confidence Limits for details.
- MN < (CORRECT=NO | MEE) >
-
requests Miettinen-Nurminen confidence limits for the risk difference. See the subsection “Miettinen-Nurminen Confidence Limits” in the section Risk Difference Confidence Limits for details. By default, the Miettinen-Nurminen confidence limits include a bias correction factor (Miettinen and Nurminen, 1985; Newcombe and Nurminen, 2011). If you specify CL=MN(CORRECT=NO), PROC FREQ provides the uncorrected form of the confidence limits (Mee, 1984).
- NEWCOMBE | SCORE | WILSON <(CORRECT)>
-
requests Newcombe hybrid-score confidence limits for the risk difference. If you specify CL=NEWCOMBE(CORRECT) or the CORRECT riskdiff-option, the Newcombe confidence limits include a continuity correction. See the subsection “Newcombe Confidence Limits” in the section Risk Difference Confidence Limits for details.
- WALD < (CORRECT) >
-
requests Wald confidence limits for the risk difference. If you specify CL=WALD(CORRECT) or the CORRECT riskdiff-option, the Wald confidence limits include a continuity correction. See the subsection “Wald Confidence Limits” in the section Risk Difference Confidence Limits for details.
- COLUMN=1 | 2 | BOTH
-
specifies the table column for which to compute the risk difference tests (EQUAL, EQUIV, NONINF, and SUP) and the risk difference confidence limits (which are requested by the CL= riskdiff-option).
If you do not specify COLUMN=, PROC FREQ provides the risk difference tests and confidence limits for column 1 by default. The COLUMN= option has no effect on the “Risk Estimates” table, which is produced for both column 1 and column 2. You can suppress the “Risk Estimates” table by specifying the NORISKS riskdiff-option.
- CORRECT
-
includes a continuity correction in the Wald confidence limits, Wald tests, and Newcombe confidence limits. See the section Risks and Risk Differences for details.
- EQUAL
-
requests a test of the null hypothesis that the risk difference equals zero. PROC FREQ provides an asymptotic Wald test of equality. If you specify the CORRECT riskdiff-option, the Wald test includes a continuity correction. If you specify the VAR=NULL riskdiff-option, the test uses the null (test-based) variance instead of the sample-based variance. See the section Equality Test for details.
- EQUIV | EQUIVALENCE
-
requests a test of equivalence for the risk difference. See the section Equivalence Tests for details. You can specify the equivalence test margins with the MARGIN= riskdiff-option and the test method with the METHOD= riskdiff-option. PROC FREQ uses METHOD=WALD by default.
- MARGIN=value | (lower,upper)
-
specifies the margin for the noninferiority, superiority, and equivalence tests, which you request with the NONINF, SUP, and EQUIV riskdiff-options, respectively. If you do not specify MARGIN=, PROC FREQ uses a margin of 0.2 by default.
For noninferiority and superiority tests, specify a single value for MARGIN=. The MARGIN= value must be a positive number. You can specify value as a number between 0 and 1. Or you can specify value in percentage form as a number between 1 and 100, and PROC FREQ converts that number to a proportion. The procedure treats the value 1 as 1%.
For an equivalence test, you can specify a single MARGIN= value, or you can specify both lower and upper values. If you specify a single MARGIN= value, it must be a positive number, as described previously. If you specify a single MARGIN= value for an equivalence test, PROC FREQ uses –value as the lower margin and value as the upper margin for the test. If you specify both lower and upper values for an equivalence test, you can specify them in proportion form as numbers between –1 or 1. Or you can specify them in percentage form as numbers between –100 and 100, and PROC FREQ converts the numbers to proportions. The value of lower must be less than the value of upper.
- METHOD=method
-
specifies the method for the noninferiority, superiority, and equivalence analyses, which you request with the NONINF, SUP, and EQUIV riskdiff-options, respectively. If you do not specify the METHOD= riskdiff-option, PROC FREQ uses METHOD=WALD by default.
The following methods are available:
- FM
-
requests Farrington-Manning (score) tests and test-based confidence limits for the equivalence, noninferiority, and superiority analyses. See the subsection “Farrington-Manning Test” in the section Noninferiority Tests for details.
- HA
-
requests Hauck-Anderson tests and confidence limits for the equivalence, noninferiority, and superiority analyses. See the subsection “Hauck-Anderson Test” in the section Noninferiority Tests for details.
- NEWCOMBE | SCORE | WILSON
-
requests Newcombe (hybrid-score) confidence limits for the equivalence, noninferiority, and superiority analyses. If you specify the CORRECT riskdiff-option, the Newcombe confidence limits include a continuity correction. See the subsection “Newcombe Noninferiority Analysis” in the section Noninferiority Tests for details.
- WALD
-
requests Wald tests and confidence limits for the equivalence, noninferiority, and superiority analyses. If you specify the CORRECT riskdiff-option, the Wald confidence limits include a continuity correction. If you specify the VAR=NULL riskdiff-option, the tests and confidence limits use the null (test-based) variance instead of the sample-based variance. See the subsection “Wald Test” in the section Noninferiority Tests for details.
- NONINF | NONINFERIORITY
-
requests a test of noninferiority for the risk difference. See the section Noninferiority Tests for details. You can specify the test margin with the MARGIN= riskdiff-option and the test method with the METHOD= riskdiff-option. PROC FREQ uses METHOD=WALD by default.
- NORISKS
-
suppresses display of the “Risk Estimates” tables, which the RISKDIFF option produces by default for column 1 and column 2. The “Risk Estimates” tables contain the risks and risk differences, together with their asymptotic standard errors, Wald confidence limits, and exact confidence limits.
- SUP | SUPERIORITY
-
requests a test of superiority for the binomial proportion. See the section Superiority Test for details. You can specify the test margin with the MARGIN= riskdiff-option and the test method with the METHOD= riskdiff-option. PROC FREQ uses METHOD=WALD by default.
- VAR=SAMPLE | NULL
-
specifies the type of variance estimate to use in the Wald tests of noninferiority, superiority, equivalence, and equality. The default is VAR=SAMPLE, which uses the sample-based variance. VAR=NULL uses a test-based variance that is computed from the null hypothesis risk difference value. See the sections Equality Test and Noninferiority Tests for details.
- SCORES=type
-
specifies the type of row and column scores that PROC FREQ uses to compute the following statistics: Mantel-Haenszel chi-square, Pearson correlation, Cochran-Armitage test for trend, weighted kappa coefficient, and Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel statistics. The value of type can be one of the following:
-
MODRIDIT
-
RANK
-
RIDIT
-
TABLE
See the section Scores for descriptions of these score types.
If you do not specify the SCORES= option, PROC FREQ uses SCORES=TABLE by default. For character variables, the row and column TABLE scores are the row and column numbers. That is, the TABLE score is 1 for row 1, 2 for row 2, and so on. For numeric variables, the row and column TABLE scores equal the variable values. See the section Scores for details. Using MODRIDIT, RANK, or RIDIT scores yields nonparametric analyses.
You can use the SCOROUT option to display the row and column scores.
-
- SCOROUT
-
displays the row and column scores that PROC FREQ uses to compute score-based tests and statistics. You can specify the score type with the SCORES= option. See the section Scores for details.
The scores are computed and displayed only when PROC FREQ computes statistics for two-way tables. You can use ODS to store the scores in an output data set. See the section ODS Table Names for more information.
- SPARSE
-
reports all possible combinations of the variable values for an n-way table when n > 1, even if a combination does not occur in the data. The SPARSE option applies only to crosstabulation tables displayed in LIST format and to the OUT= output data set. If you do not use the LIST or OUT= option, the SPARSE option has no effect.
When you specify the SPARSE and LIST options, PROC FREQ displays all combinations of variable values in the table listing, including those with a frequency count of zero. By default, without the SPARSE option, PROC FREQ does not display zero-frequency levels in LIST output. When you use the SPARSE and OUT= options, PROC FREQ includes empty crosstabulation table cells in the output data set. By default, PROC FREQ does not include zero-frequency table cells in the output data set.
See the section Missing Values for more information.
- TOTPCT
-
displays the percentage of the total multiway table frequency in crosstabulation tables for n-way tables, where n > 2. By default, PROC FREQ displays the percentage of the individual two-way table frequency but does not display the percentage of the total frequency for multiway crosstabulation tables. See the section Multiway Tables for more information.
The percentage of total multiway table frequency is displayed by default when you specify the LIST option. It is also provided by default in the
PERCENTvariable in the OUT= output data set. - TREND
-
requests the Cochran-Armitage test for trend. The table must be
 or
or  to compute the trend test. See the section Cochran-Armitage Test for Trend for details. To request exact p-values for the trend test, specify the TREND option in the EXACT statement. See the section Exact Statistics for more information.
to compute the trend test. See the section Cochran-Armitage Test for Trend for details. To request exact p-values for the trend test, specify the TREND option in the EXACT statement. See the section Exact Statistics for more information.
