| The UNIVARIATE Procedure |
| CDFPLOT Statement |
- CDFPLOT <variables> < / options> ;
The CDFPLOT statement plots the observed cumulative distribution function (cdf) of a variable, defined as
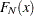 |
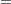 |
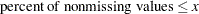 |
|||
 |
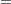 |
 |
where 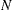 is the number of nonmissing observations. The cdf is an increasing step function that has a vertical jump of
is the number of nonmissing observations. The cdf is an increasing step function that has a vertical jump of 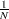 at each value of
at each value of  equal to an observed value. The cdf is also referred to as the empirical cumulative distribution function (ecdf).
equal to an observed value. The cdf is also referred to as the empirical cumulative distribution function (ecdf).
You can use any number of CDFPLOT statements in the UNIVARIATE procedure. The components of the CDFPLOT statement are as follows.
- variables
specify variables for which to create cdf plots. If you specify a VAR statement, the variables must also be listed in the VAR statement. Otherwise, the variables can be any numeric variables in the input data set. If you do not specify a list of variables, then by default the procedure creates a cdf plot for each variable listed in the VAR statement, or for each numeric variable in the DATA= data set if you do not specify a VAR statement.
For example, suppose a data set named Steel contains exactly three numeric variables: Length, Width, and Height. The following statements create a cdf plot for each of the three variables:
proc univariate data=Steel; cdfplot; run;The following statements create a cdf plot for Length and a cdf plot for Width:
proc univariate data=Steel; var Length Width; cdfplot; run;The following statements create a cdf plot for Width:
proc univariate data=Steel; var Length Width; cdfplot Width; run;- options
specify the theoretical distribution for the plot or add features to the plot. If you specify more than one variable, the options apply equally to each variable. Specify all options after the slash (/) in the CDFPLOT statement. You can specify only one option that names a distribution in each CDFPLOT statement, but you can specify any number of other options. The distributions available are the beta, exponential, gamma, lognormal, normal, and three-parameter Weibull. By default, the procedure produces a plot for the normal distribution.
Table 4.2 through Table 4.10 list the CDFPLOT options by function. For complete descriptions, see the sections Dictionary of Options and Dictionary of Common Options. Options can be any of the following:
primary options
secondary options
general options
Distribution Options
Table 4.2 lists primary options for requesting a theoretical distribution.
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
plots two-parameter beta distribution function, parameters |
|
plots one-parameter exponential distribution function, parameter |
|
plots two-parameter gamma distribution function, parameter |
|
plots two-parameter lognormal distribution function, parameter |
|
plots normal distribution function |
|
plots two-parameter Weibull distribution function, parameter |
Table 4.3 through Table 4.9 list secondary options that specify distribution parameters and control the display of a theoretical distribution function. Specify these options in parentheses after the distribution keyword. For example, you can request a normal probability plot with a distribution reference line by specifying the NORMAL option as follows:
proc univariate;
cdfplot / normal(mu=10 sigma=0.5 color=red);
run;
The COLOR= option specifies the color for the curve, and the normal-options MU= and SIGMA= specify the parameters 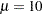 and
and 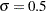 for the distribution function. If you do not specify these parameters, maximum likelihood estimates are computed.
for the distribution function. If you do not specify these parameters, maximum likelihood estimates are computed.
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
specifies color of theoretical distribution function |
|
specifies line type of theoretical distribution function |
|
specifies width of theoretical distribution function |
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
specifies first shape parameter |
|
specifies second shape parameter |
|
specifies scale parameter |
|
specifies lower threshold parameter |
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
specifies scale parameter |
|
specifies threshold parameter |
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
specifies shape parameter |
|
specifies change in successive estimates of |
|
specifies initial value for |
|
specifies maximum number of iterations in the Newton-Raphson approximation of |
|
specifies scale parameter |
|
specifies threshold parameter |
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
specifies shape parameter |
|
specifies threshold parameter |
|
specifies scale parameter |
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
specifies mean |
|
specifies standard deviation |
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
specifies shape parameter |
|
specifies change in successive estimates of |
|
specifies initial value for |
|
specifies maximum number of iterations in the Newton-Raphson approximation of |
|
specifies scale parameter |
|
specifies threshold parameter |
General Options
Table 4.10 summarizes general options for enhancing cdf plots.
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
applies annotation requested in ANNOTATE= data set to key cell only |
|
specifies annotate data set |
|
specifies color for axis |
|
specifies color for frame |
|
specifies color for filling row label frames |
|
specifies color for filling column label frames |
|
specifies color for HREF= lines |
|
specifies table of contents entry for cdf plot grouping |
|
specifies color for proportion of frequency bar |
|
specifies color for text |
|
specifies color for row labels |
|
specifies color for column labels |
|
specifies color for VREF= lines |
|
specifies description for graphics catalog member |
|
specifies text font |
|
specifies AXIS statement for horizontal axis |
|
specifies height of text used outside framed areas |
|
specifies number of horizontal axis minor tick marks |
|
specifies reference lines perpendicular to the horizontal axis |
|
specifies labels for HREF= lines |
|
specifies position for HREF= line labels |
|
specifies software font for text inside framed areas |
|
specifies height of text inside framed areas |
|
specifies distance between tiles in comparative plot |
|
specifies line style for HREF= lines |
|
specifies line style for VREF= lines |
|
specifies name for plot in graphics catalog |
|
specifies number of columns in comparative plot |
|
suppresses plot of empirical (observed) distribution function |
|
suppresses frame around plotting area |
|
suppresses label for horizontal axis |
|
suppresses label for vertical axis |
|
suppresses tick marks and tick mark labels for vertical axis |
|
specifies number of rows in comparative plot |
|
overlays plots for different class levels (ODS Graphics only) |
|
turns and vertically strings out characters in labels for vertical axis |
|
specifies AXIS statement for vertical axis |
|
specifies label for vertical axis |
|
specifies number of vertical axis minor tick marks |
|
specifies reference lines perpendicular to the vertical axis |
|
specifies labels for VREF= lines |
|
specifies position for VREF= line labels |
|
specifies scale for vertical axis |
|
specifies line thickness for axes and frame |
Dictionary of Options
The following entries provide detailed descriptions of the options specific to the CDFPLOT statement. See the section Dictionary of Common Options for detailed descriptions of options common to all plot statements.
- ALPHA=value
specifies the shape parameter
 for distribution functions requested with the BETA and GAMMA options. Enclose the ALPHA= option in parentheses after the BETA or GAMMA keywords. If you do not specify a value for
for distribution functions requested with the BETA and GAMMA options. Enclose the ALPHA= option in parentheses after the BETA or GAMMA keywords. If you do not specify a value for  , the procedure calculates a maximum likelihood estimate. For examples, see the entries for the BETA and GAMMA options.
, the procedure calculates a maximum likelihood estimate. For examples, see the entries for the BETA and GAMMA options. - BETA<(beta-options )>
displays a fitted beta distribution function on the cdf plot. The equation of the fitted cdf is
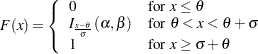
where
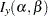 is the incomplete beta function and
is the incomplete beta function and  lower threshold parameter (lower endpoint)
lower threshold parameter (lower endpoint)  scale parameter
scale parameter 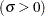
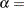 shape parameter
shape parameter 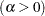
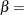 shape parameter
shape parameter 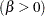
The beta distribution is bounded below by the parameter
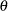 and above by the value
and above by the value 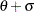 . You can specify
. You can specify 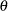 and
and  by using the THETA= and SIGMA= beta-options, as illustrated in the following statements, which fit a beta distribution bounded between 50 and 75. The default values for
by using the THETA= and SIGMA= beta-options, as illustrated in the following statements, which fit a beta distribution bounded between 50 and 75. The default values for 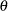 and
and  are 0 and 1, respectively.
are 0 and 1, respectively. proc univariate; cdfplot / beta(theta=50 sigma=25); run;The beta distribution has two shape parameters:
 and
and 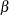 . If these parameters are known, you can specify their values with the ALPHA= and BETA= beta-options. If you do not specify values for
. If these parameters are known, you can specify their values with the ALPHA= and BETA= beta-options. If you do not specify values for  and
and 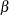 , the procedure calculates maximum likelihood estimates.
, the procedure calculates maximum likelihood estimates. The BETA option can appear only once in a CDFPLOT statement. Table 4.3 and Table 4.4 list options you can specify with the BETA distribution option.
- BETA=value
- B=value
specifies the second shape parameter
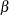 for beta distribution functions requested by the BETA option. Enclose the BETA= option in parentheses after the BETA keyword. If you do not specify a value for
for beta distribution functions requested by the BETA option. Enclose the BETA= option in parentheses after the BETA keyword. If you do not specify a value for 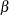 , the procedure calculates a maximum likelihood estimate. For examples, see the preceding entry for the BETA option.
, the procedure calculates a maximum likelihood estimate. For examples, see the preceding entry for the BETA option. - C=value
specifies the shape parameter
 for Weibull distribution functions requested with the WEIBULL option. Enclose the C= option in parentheses after the WEIBULL keyword. If you do not specify a value for
for Weibull distribution functions requested with the WEIBULL option. Enclose the C= option in parentheses after the WEIBULL keyword. If you do not specify a value for  , the procedure calculates a maximum likelihood estimate. You can specify the SHAPE= option as an alias for the C= option.
, the procedure calculates a maximum likelihood estimate. You can specify the SHAPE= option as an alias for the C= option. - EXPONENTIAL<(exponential-options )>
- EXP<(exponential-options )>
displays a fitted exponential distribution function on the cdf plot. The equation of the fitted cdf is

where
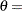 threshold parameter
threshold parameter 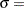 scale parameter
scale parameter 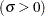
The parameter
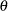 must be less than or equal to the minimum data value. You can specify
must be less than or equal to the minimum data value. You can specify 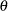 with the THETA= exponential-option. The default value for
with the THETA= exponential-option. The default value for 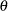 is 0. You can specify
is 0. You can specify  with the SIGMA= exponential-option. By default, a maximum likelihood estimate is computed for
with the SIGMA= exponential-option. By default, a maximum likelihood estimate is computed for  . For example, the following statements fit an exponential distribution with
. For example, the following statements fit an exponential distribution with 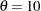 and a maximum likelihood estimate for
and a maximum likelihood estimate for  :
: proc univariate; cdfplot / exponential(theta=10 l=2 color=green); run;The exponential curve is green and has a line type of 2.
The EXPONENTIAL option can appear only once in a CDFPLOT statement. Table 4.3 and Table 4.5 list the options you can specify with the EXPONENTIAL option.
- GAMMA<(gamma-options)>
displays a fitted gamma distribution function on the cdf plot. The equation of the fitted cdf is
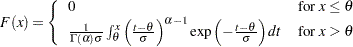
where
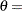 threshold parameter
threshold parameter 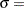 scale parameter
scale parameter 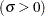
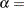 shape parameter
shape parameter 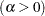
The parameter
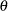 for the gamma distribution must be less than the minimum data value. You can specify
for the gamma distribution must be less than the minimum data value. You can specify 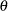 with the THETA= gamma-option. The default value for
with the THETA= gamma-option. The default value for 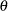 is 0. In addition, the gamma distribution has a shape parameter
is 0. In addition, the gamma distribution has a shape parameter  and a scale parameter
and a scale parameter  . You can specify these parameters with the ALPHA= and SIGMA= gamma-options. By default, maximum likelihood estimates are computed for
. You can specify these parameters with the ALPHA= and SIGMA= gamma-options. By default, maximum likelihood estimates are computed for  and
and  . For example, the following statements fit a gamma distribution function with
. For example, the following statements fit a gamma distribution function with  and maximum likelihood estimates for
and maximum likelihood estimates for  and
and  :
: proc univariate; cdfplot / gamma(theta=4); run;Note that the maximum likelihood estimate of
 is calculated iteratively using the Newton-Raphson approximation. The gamma-options ALPHADELTA=, ALPHAINITIAL=, and MAXITER= control the approximation.
is calculated iteratively using the Newton-Raphson approximation. The gamma-options ALPHADELTA=, ALPHAINITIAL=, and MAXITER= control the approximation. The GAMMA option can appear only once in a CDFPLOT statement. Table 4.3 and Table 4.6 list the options you can specify with the GAMMA option.
- LOGNORMAL<(lognormal-options)>
displays a fitted lognormal distribution function on the cdf plot. The equation of the fitted cdf is
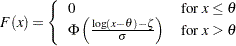
where
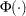 is the standard normal cumulative distribution function and
is the standard normal cumulative distribution function and 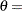 threshold parameter
threshold parameter 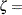 scale parameter
scale parameter 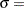 shape parameter
shape parameter 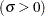
The parameter
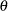 for the lognormal distribution must be less than the minimum data value. You can specify
for the lognormal distribution must be less than the minimum data value. You can specify 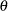 with the THETA= lognormal-option. The default value for
with the THETA= lognormal-option. The default value for 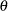 is 0. In addition, the lognormal distribution has a shape parameter
is 0. In addition, the lognormal distribution has a shape parameter  and a scale parameter
and a scale parameter 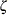 . You can specify these parameters with the SIGMA= and ZETA= lognormal-options. By default, maximum likelihood estimates are computed for
. You can specify these parameters with the SIGMA= and ZETA= lognormal-options. By default, maximum likelihood estimates are computed for  and
and 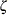 . For example, the following statements fit a lognormal distribution function with
. For example, the following statements fit a lognormal distribution function with 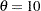 and maximum likelihood estimates for
and maximum likelihood estimates for  and
and 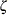 :
: proc univariate; cdfplot / lognormal(theta = 10); run;The LOGNORMAL option can appear only once in a CDFPLOT statement. Table 4.3 and Table 4.7 list options that you can specify with the LOGNORMAL option.
- MU=value
specifies the parameter
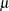 for normal distribution functions requested with the NORMAL option. Enclose the MU= option in parentheses after the NORMAL keyword. The default value is the sample mean.
for normal distribution functions requested with the NORMAL option. Enclose the MU= option in parentheses after the NORMAL keyword. The default value is the sample mean. - NOECDF
suppresses the observed distribution function (the empirical cumulative distribution function) of the variable, which is drawn by default. This option enables you to create theoretical cdf plots without displaying the data distribution. The NOECDF option can be used only with a theoretical distribution (such as the NORMAL option).
- NORMAL<(normal-options)>
displays a fitted normal distribution function on the cdf plot. The equation of the fitted cdf is
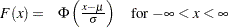
where
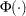 is the standard normal cumulative distribution function and
is the standard normal cumulative distribution function and 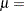 mean
mean 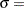 standard deviation
standard deviation 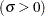
You can specify known values for
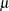 and
and  with the MU= and SIGMA= normal-options, as shown in the following statements:
with the MU= and SIGMA= normal-options, as shown in the following statements: proc univariate; cdfplot / normal(mu=14 sigma=.05); run;By default, the sample mean and sample standard deviation are calculated for
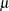 and
and  . The NORMAL option can appear only once in a CDFPLOT statement. Table 4.3 and Table 4.8 list options that you can specify with the NORMAL option.
. The NORMAL option can appear only once in a CDFPLOT statement. Table 4.3 and Table 4.8 list options that you can specify with the NORMAL option. - SIGMA=value | EST
specifies the parameter
 for distribution functions requested by the BETA, EXPONENTIAL, GAMMA, LOGNORMAL, NORMAL, and WEIBULL options. Enclose the SIGMA= option in parentheses after the distribution keyword. The following table summarizes the use of the SIGMA= option:
for distribution functions requested by the BETA, EXPONENTIAL, GAMMA, LOGNORMAL, NORMAL, and WEIBULL options. Enclose the SIGMA= option in parentheses after the distribution keyword. The following table summarizes the use of the SIGMA= option: Distribution Option
SIGMA= Specifies
Default Value
Alias
BETA
scale parameter

1
SCALE=
EXPONENTIAL
scale parameter

maximum likelihood estimate
SCALE=
GAMMA
scale parameter

maximum likelihood estimate
SCALE=
LOGNORMAL
shape parameter

maximum likelihood estimate
SHAPE=
NORMAL
scale parameter

standard deviation
WEIBULL
scale parameter

maximum likelihood estimate
SCALE=
- THETA=value | EST
- THRESHOLD=value | EST
specifies the lower threshold parameter
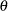 for theoretical cumulative distribution functions requested with the BETA, EXPONENTIAL, GAMMA, LOGNORMAL, and WEIBULL options. Enclose the THETA= option in parentheses after the distribution keyword. The default value is 0.
for theoretical cumulative distribution functions requested with the BETA, EXPONENTIAL, GAMMA, LOGNORMAL, and WEIBULL options. Enclose the THETA= option in parentheses after the distribution keyword. The default value is 0. - VSCALE=PERCENT | PROPORTION
specifies the scale of the vertical axis. The value PERCENT scales the data in units of percent of observations per data unit. The value PROPORTION scales the data in units of proportion of observations per data unit. The default is PERCENT.
- WEIBULL<(Weibull-options)>
displays a fitted Weibull distribution function on the cdf plot. The equation of the fitted cdf is
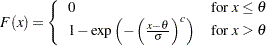
where
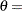 threshold parameter
threshold parameter 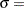 scale parameter
scale parameter 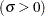
 shape parameter
shape parameter 
The parameter
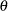 must be less than the minimum data value. You can specify
must be less than the minimum data value. You can specify 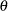 with the THETA= Weibull-option. The default value for
with the THETA= Weibull-option. The default value for 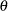 is 0. In addition, the Weibull distribution has a shape parameter
is 0. In addition, the Weibull distribution has a shape parameter  and a scale parameter
and a scale parameter  . You can specify these parameters with the SIGMA= and C= Weibull-options. By default, maximum likelihood estimates are computed for
. You can specify these parameters with the SIGMA= and C= Weibull-options. By default, maximum likelihood estimates are computed for  and
and  . For example, the following statements fit a Weibull distribution function with
. For example, the following statements fit a Weibull distribution function with 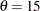 and maximum likelihood estimates for
and maximum likelihood estimates for  and
and  :
: proc univariate; cdfplot / weibull(theta=15); run;Note that the maximum likelihood estimate of
 is calculated iteratively using the Newton-Raphson approximation. The Weibull-options CDELTA=, CINITIAL=, and MAXITER= control the approximation.
is calculated iteratively using the Newton-Raphson approximation. The Weibull-options CDELTA=, CINITIAL=, and MAXITER= control the approximation. The WEIBULL option can appear only once in a CDFPLOT statement. Table 4.3 and Table 4.9 list options that you can specify with the WEIBULL option.
- ZETA=value
specifies a value for the scale parameter
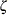 for a lognormal distribution function requested with the LOGNORMAL option. Enclose the ZETA= option in parentheses after the LOGNORMAL keyword. If you do not specify a value for
for a lognormal distribution function requested with the LOGNORMAL option. Enclose the ZETA= option in parentheses after the LOGNORMAL keyword. If you do not specify a value for 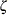 , a maximum likelihood estimate is computed. You can specify the SCALE= option as an alias for the ZETA= option.
, a maximum likelihood estimate is computed. You can specify the SCALE= option as an alias for the ZETA= option.
Copyright © SAS Institute, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
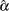 terminates
terminates 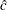 terminates
terminates