Working with the Variable Read Write Node
Overview of the Variable Read Write Node
You can add a Variable
Read Write node to a Flow tab in an orchestration
job to set the value of a job level variable and to retrieve the value.
The node's type is JOBVARIABLE. This node is typically used in a nested
job to publish variables coming from inside of the nested job out
to the outputs of the nested job. It can also be user to read variables
coming into the nested job and make them available. Similar functions
can be performed with the Expression node.
Using the Variable Read Write Node
You can add a Variable
Read Write node to a Flow tab
in an orchestration job to update variables and pass values between
nested jobs. For example, you can create an orchestration job that
consists of an inner job nested within an outer job. Then, you can
use a Variable Read Write node to publish
the variable from the inner job to the outer job.
You can create job
variables and set the description, external use of input or output,
and the default value for each variable. The inner job variables
are shown in the following display:
Inner Job Variables
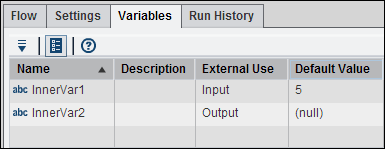
Note that the input
variable InnerVar1 has a default
value of 5. The output variable InnerVar2 has
a null default value.
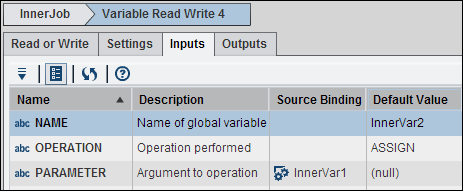
Use the Read
or Write tab in the Variable Read Write node
to select the Write to a job variable (InnerVar2)
and the Operation( Assign), as shown in the
following display:
Read or Write Tab Settings
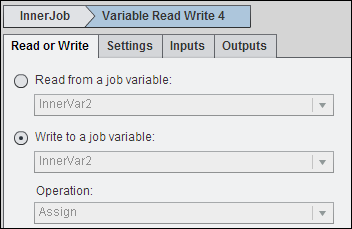
Select Parameter and
bind it to InnerVar1. Because Parameter is the argument to the operation
on Inner Var2, this step binds InnerVar1 to InnerVar2.
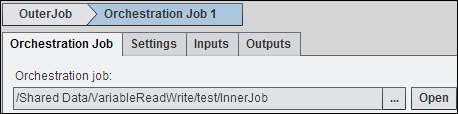
This tab contains a
reference to the inner job in the Orchestration job field.
This reference embeds the inner job into the outer job. For information
about Orchestration Job nodes, see Working with the Orchestration Job Node.
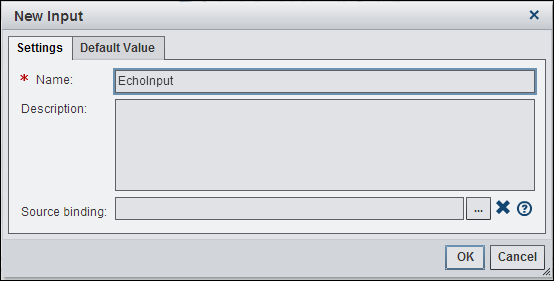
You need to create an
input in the Echo node to capture the output
from the inner job. To do this, open the Inputs tab
in properties for the Echo node and click New
Input.
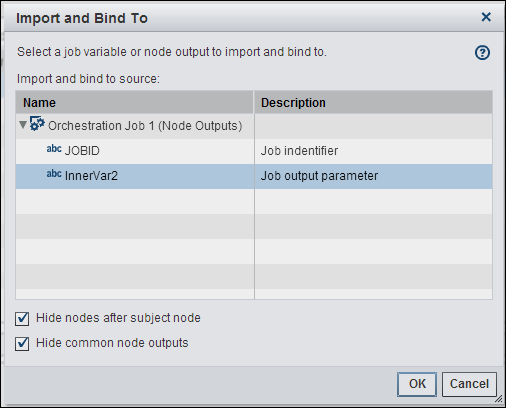
Next, you need to import
and bind the job output parameter from the inner job to the outer
job. Click OK to close the New
Input window and save the echo input. Then, click Import
and Save from the Echo node
properties toolbar. Note that the Variable Read Write node
in the inner job published the variable InnerVar2 as output from the
inner job. Therefore, InnerVar2 can be accessed from any node connected
to the Orchestration Job node that references
the inner job.
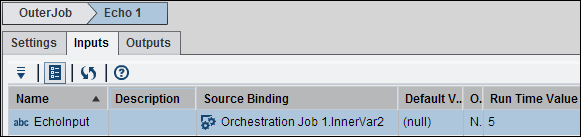
Note that the EchoInput
input is bound to InnerVar2, which is the Orchestration
Job node output from the inner job. If the value of InnerVar2
changes, the value of EchoInput also changes. You can verify the output
from the inner job was passed to the input of the Echo node
in the outer job after you run the outer job. Select the Run
History tab of the outer job after the job is submitted.
Then, double click on the entry for the run. Finally, drill into the
Echo node and select the Inputs tab.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.