| ODS Table and Variable Names |
PROC OPTMODEL assigns a name to each table it creates. You can use these names to reference the table when you use the Output Delivery System (ODS) to select tables and create output data sets. The names of tables common to all solvers are listed in Table 4.8. Some solvers can generate additional tables; see the individual solver chapters for more information. For more information about ODS, see SAS Output Delivery System: User’s Guide.
ODS Table Name |
Description |
Statement/Option |
DerivMethods |
List of derivatives used by the solver, including the method of computation |
|
OptStatistics |
Solver-dependent description of the resources required for solution, including function evaluations and solver time |
|
PrintTable |
Specified parameter or variable values |
|
ProblemSummary |
Description of objective, variables, and constraints |
|
SolutionSummary |
Overview of solution, including solver-dependent solution quality values |
|
SolverOptions |
List of solver options and their values |
To guarantee that ODS output data sets contain information from all executed statements, use the PERSIST= option on the ODS OUTPUT statement. For details, see SAS Output Delivery System: User’s Guide.
Table 4.9 lists the variable names of the preceding tables used in the ODS template of the OPTMODEL procedure.
Table Name |
Variables |
DerivMethods |
Label |
OptStatistics |
Label |
PrintTable (matrix form) |
ROW, COL |
PrintTable (table form) |
COL |
ProblemSummary |
Label |
SolutionSummary |
Label |
SolverOptions |
Label |
The PRINT statement produces an ODS table named "PrintTable." The variable names used depend on the display format used. See the section Formatted Output for details about choosing the display format.
For the PRINT statement with table format, the columns that display array indices are named COL –COL
–COL , where
, where  is the number of index elements. Columns that display values from identifier expressions are named based on the expression’s name and suffix. The identifier name becomes the output variable name if no suffix is used. Otherwise the variable name is formed by appending an underscore (_) and the suffix to the identifier name. Columns that display the value of expressions are named COL
is the number of index elements. Columns that display values from identifier expressions are named based on the expression’s name and suffix. The identifier name becomes the output variable name if no suffix is used. Otherwise the variable name is formed by appending an underscore (_) and the suffix to the identifier name. Columns that display the value of expressions are named COL , where
, where  is the column number in the table.
is the column number in the table.
For the PRINT statement with matrix format, the first column has the variable name ROW. The remaining columns are named COL –COL
–COL where
where  is the number of distinct column indices. When an ODS table displays values from identifier expressions, a label is generated based on the expression’s name and suffix, as described for column names in the case of table format.
is the number of distinct column indices. When an ODS table displays values from identifier expressions, a label is generated based on the expression’s name and suffix, as described for column names in the case of table format.
The PRINTLEVEL= option controls the tables produced by the SOLVE statement. When PRINTLEVEL=0, the SOLVE statement produces no ODS tables. When PRINTLEVEL=1, the SOLVE statement produces the "ProblemSummary" and "SolutionSummary" tables. When PRINTLEVEL=2, the SOLVE statement produces the "ProblemSummary," "SolverOptions," "DerivMethods," "SolutionSummary," and "OptStatistics" tables.
The following statements generate several ODS tables and writes each table to a SAS data set:
proc optmodel printlevel=2;
ods output PrintTable=expt ProblemSummary=exps DerivMethods=exdm
SolverOptions=exso SolutionSummary=exss OptStatistics=exos;
var x{1..2} >= 0;
min z = 2*x[1] + 3 * x[2] + x[1]**2 + 10*x[2]**2
+ 2.5*x[1]*x[2] + x[1]**3;
con c1: x[1] - x[2] <= 1;
con c2: x[1] + 2*x[2] >= 100;
solve;
print x;
The data set expt contains the "PrintTable" table and is shown in Figure 4.43. The variable names are COL and x.
and x.
| PrintTable |
| Obs | COL1 | x |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 10.448 |
| 2 | 2 | 44.776 |
The data set exps contains the "ProblemSummary" table and is shown in Figure 4.44. The variable names are Label , cValue1
, cValue1 , and nValue
, and nValue . The rows describe the objective function, variables, and constraints. The rows depend on the form of the problem.
. The rows describe the objective function, variables, and constraints. The rows depend on the form of the problem.
| ProblemSummary |
| Obs | Label1 | cValue1 | nValue1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Objective Sense | Minimization | . |
| 2 | Objective Function | z | . |
| 3 | Objective Type | Nonlinear | . |
| 4 | . | ||
| 5 | Number of Variables | 2 | 2.000000 |
| 6 | Bounded Above | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | Bounded Below | 2 | 2.000000 |
| 8 | Bounded Below and Above | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | Free | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | Fixed | 0 | 0 |
| 11 | . | ||
| 12 | Number of Constraints | 2 | 2.000000 |
| 13 | Linear LE (<=) | 1 | 1.000000 |
| 14 | Linear EQ (=) | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | Linear GE (>=) | 1 | 1.000000 |
| 16 | Linear Range | 0 | 0 |
The data set exso contains the "SolverOptions" table and is shown in Figure 4.45. The variable names are Label , cValue
, cValue , nValue
, nValue , cValue
, cValue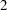 , and nValue
, and nValue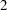 . The rows, which depend on the solver called by PROC OPTMODEL, list the values taken by each of the solver options. The presence of an asterisk (*) next to an option indicates that a value has been specified for that option.
. The rows, which depend on the solver called by PROC OPTMODEL, list the values taken by each of the solver options. The presence of an asterisk (*) next to an option indicates that a value has been specified for that option.
| SolverOptions |
| Obs | Label1 | cValue1 | nValue1 | cValue2 | nValue2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TECH | INTERIORPOINT | . | . | |
| 2 | FEASTOL | 1E-6 | 0.000001000 | . | |
| 3 | HESSTYPE | FULL | . | . | |
| 4 | MAXITER | 5000 | 5000.000000 | . | |
| 5 | MAXTIME | I | I | . | |
| 6 | NOMULTISTART | . | . | ||
| 7 | OBJLIMIT | 1E20 | 1E20 | . | |
| 8 | OPTTOL | 1E-6 | 0.000001000 | . | |
| 9 | PRINTFREQ | 1 | 1.000000 | . | |
| 10 | SOLTYPE | 1 | 1.000000 | . |
The data set exdm contains the "DerivMethods" table, which displays the methods of derivative computation, and is shown in Figure 4.46. The variable names are Label , cValue1
, cValue1 , and nValue
, and nValue . The rows, which depend on the derivatives used by the solver, specify the method used to calculate each derivative.
. The rows, which depend on the derivatives used by the solver, specify the method used to calculate each derivative.
| DerivMethods |
| Obs | Label1 | cValue1 | nValue1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Objective Gradient | Analytic Formulas | . |
| 2 | Objective Hessian | Analytic Formulas | . |
The data set exss contains the "SolutionSummary" table and is shown in Figure 4.47. The variable names are Label , cValue1
, cValue1 , and nValue
, and nValue . The rows give an overview of the solution, including the solver chosen, the objective value, and the solution status. Depending on the values returned by the solver, the "SolutionSummary" table might also include some solution quality values such as optimality error and infeasibility. The values in the "SolutionSummary" table appear in the _OROPTMODEL_ macro variable; each solver chapter has a section that describes the solver’s contribution to this macro variable.
. The rows give an overview of the solution, including the solver chosen, the objective value, and the solution status. Depending on the values returned by the solver, the "SolutionSummary" table might also include some solution quality values such as optimality error and infeasibility. The values in the "SolutionSummary" table appear in the _OROPTMODEL_ macro variable; each solver chapter has a section that describes the solver’s contribution to this macro variable.
| SolutionSummary |
| Obs | Label1 | cValue1 | nValue1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Solver | NLP/INTERIORPOINT | . |
| 2 | Objective Function | z | . |
| 3 | Solution Status | Optimal | . |
| 4 | Objective Value | 22623.347101 | 22623 |
| 5 | Iterations | 5 | 5.000000 |
| 6 | . | ||
| 7 | Optimality Error | 5E-7 | 0.000000500 |
| 8 | Infeasibility | 0 | 0 |
The data set exos contains the "OptStatistics" table, which displays the optimization statistics, and is shown in Figure 4.48. The variable names are Label , cValue1
, cValue1 , and nValue
, and nValue . The rows, which depend on the solver called by PROC OPTMODEL, describe the amount of time and function evaluations used by the solver.
. The rows, which depend on the solver called by PROC OPTMODEL, describe the amount of time and function evaluations used by the solver.
| OptStatistics |
| Obs | Label1 | cValue1 | nValue1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Function Evaluations | 60 | 60.000000 |
| 2 | Gradient Evaluations | 60 | 60.000000 |
| 3 | Hessian Evaluations | 6 | 6.000000 |
| 4 | Problem Generation Time | 0.00 | 0 |
| 5 | Code Generation Time | 0.00 | 0 |
| 6 | Presolver Time | 0.00 | 0 |
| 7 | Solver Time | 0.02 | 0.015000 |