| The OPTMILP Procedure |
Data Input and Output
This subsection describes the PRIMALIN= data set required to warm start PROC OPTMILP, as well as the PRIMALOUT= and DUALOUT= data sets.
Definitions of Variables in the PRIMALIN= Data Set
The PRIMALIN= data set has two required variables defined as follows:- _VAR_
- specifies the variable (column) names of the problem. The values should match the column names in the DATA= data set for the current problem.
- _VALUE_
-
specifies the solution value for each variable in the problem.
Note: If PROC OPTMILP produces a feasible solution, the primal output data set from that run can be used as the PRIMALIN= data set for a subsequent run, provided that the input solution is feasible for the subsequent run.
Definitions of Variables in the PRIMALOUT= Data Set
PROC OPTMILP stores the current best integer feasible solution of the problem in the data set specified by the PRIMALOUT= option. The variables in this data set are defined as follows:- _RHS_ID_
- specifies the identifier of the right-hand side.
- _VAR_
- specifies the variable (column) names.
- _TYPE_
-
specifies the variable type. _TYPE_ can take one of the following values:
- C
- continuous variable
- I
- general integer variable
- B
- binary variable (0 or 1)
- _OBJCOEF_
- specifies the coefficient of the variable in the objective function.
- _LBOUND_
- specifies the lower bound on the variable.
- _UBOUND_
- specifies the upper bound on the variable.
- _VALUE_
- specifies the value of the variable in the current solution.
Definitions of the DUALOUT= Data Set Variables
The DUALOUT= data set contains the constraint activities corresponding to the primal solution in the PRIMALOUT= data set. Information about additional objective rows of the MILP problem is not included. The variables in this data set are defined as follows:- _RHS_ID_
- specifies the identifier of the right-hand side from the input data set.
- _ROW_
- specifies the constraint (row) name.
- _TYPE_
-
specifies the constraint type. _TYPE_ can take one of the following values:
- L
- "less than or equal" constraint
- E
- equality constraint
- G
- "greater than or equal" constraint
- R
- ranged constraint (both "less than or equal" and "greater than or equal")
- _RHS_
- specifies the value of the right-hand side of the constraint. It takes a missing value for a ranged constraint.
- _L_RHS_
- specifies the lower bound of a ranged constraint. It takes a missing value for a non-ranged constraint.
- _U_RHS_
- specifies the upper bound of a ranged constraint. It takes a missing value for a non-ranged constraint.
- _ACTIVITY_
-
specifies the activity of a constraint for a given primal solution. In other words,
the value of _ACTIVITY_ for the
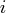 th constraint is equal to
th constraint is equal to
 ,
where
,
where  refers to the
refers to the 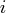 th row of the constraint matrix and
th row of the constraint matrix and  denotes
the vector of the current primal solution.
denotes
the vector of the current primal solution.
Data Magnitude and Variable Bounds
Extremely large numerical values might cause computational difficulties for the OPTMILP procedure, but the occurrence of such difficulties is hard to predict. For this reason, the OPTMILP procedure issues a data error message whenever it detects model data that exceeds a specific threshold number. The value of the threshold number depends on your operating environment and is printed in the log as part of the data error message.The following conditions produce a data error:
- The absolute value of an objective coefficient, constraint coefficient, or range (difference between the upper and lower bounds on a constraint) is greater than the threshold number.
- A variable's lower bound, a
 or
or  constraint's
right-hand side, or a range constraint's lower bound is
greater than the threshold number.
constraint's
right-hand side, or a range constraint's lower bound is
greater than the threshold number.
- A variable's upper bound, a
 or
or  constraint's
right-hand side, or a range constraint's upper bound is
smaller than the negative threshold number.
constraint's
right-hand side, or a range constraint's upper bound is
smaller than the negative threshold number.
If a variable's upper bound is larger than 1E20, then the OPTMILP procedure
treats the bound as ![]() . Similarly, if a variable's lower bound is
smaller than -1E20, then the OPTMILP procedure treats the bound as
. Similarly, if a variable's lower bound is
smaller than -1E20, then the OPTMILP procedure treats the bound as ![]() .
.
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.