| The OPTMILP Procedure |
Macro Variable _OROPTMILP_
The OPTMILP procedure defines a macro variable named _OROPTMILP_. This variable contains a character string that indicates the status of the OPTMILP procedure upon termination. The various terms of the variable are interpreted as follows.
- STATUS
- indicates the solver status at termination. It can take one of the following values:
- OK
- procedure terminated normally
- SYNTAX_ERROR
- incorrect use of syntax
- DATA_ERROR
- inconsistent input data
- OUT_OF_MEMORY
- insufficient memory allocated to the procedure
- IO_ERROR
- problem in reading or writing data
- ERROR
- status that cannot be classified into any of the preceding categories
- SOLUTION_STATUS
- indicates the solution status at termination. It can take one of the following values:
- OPTIMAL
- solution is optimal
- OPTIMAL_AGAP
- optimal solution within absolute gap specified using ABSOBJGAP= option
- OPTIMAL_RGAP
- optimal solution within relative gap specified using RELOBJGAP= option
- OPTIMAL_COND
- solution is optimal, but some infeasibilities (primal, bound, or integer) exceed tolerances due to scaling or choice of small INTTOL= value
- TARGET
- solution not worse than target specified using TARGET= option
- INFEASIBLE
- problem is infeasible
- UNBOUNDED
- problem is unbounded
- INFEASIBLE_OR_UNBOUNDED
- problem is infeasible or unbounded
- SOLUTION_LIM
- solver reached maximum number of solutions specified using option MAXSOLS=
- NODE_LIM_SOL
- solver reached maximum number of nodes specified using MAXNODES= option and found a solution
- NODE_LIM_NOSOL
- solver reached maximum number of nodes specified using MAXNODES= option and did not find a solution
- TIME_LIM_SOL
- solver reached the execution time limit specified using MAXTIME= option and found a solution
- TIME_LIM_NOSOL
- solver reached the execution time limit specified using MAXTIME= option and did not find a solution
- ABORT_SOL
- solver was stopped by user but still found a solution
- ABORT_NOSOL
- solver was stopped by user and did not find a solution
- OUTMEM_SOL
- solver ran out of memory but still found a solution
- OUTMEM_NOSOL
- solver ran out of memory and either did not find a solution or failed to output solution due to insufficient memory
- FAIL_SOL
- solver stopped due to errors but still found a solution
- FAIL_NOSOL
- solver stopped due to errors and did not find a solution
- OBJECTIVE
- indicates the objective value obtained by the solver at termination.
- RELATIVE_GAP
- specifies the relative gap between the best integer objective (BestInteger) and the
objective of the best remaining node (BestBound) upon termination of the MILP solver. The relative gap is equal to
- ABSOLUTE_GAP
- specifies the absolute gap between the best integer objective (BestInteger) and the
objective of the best remaining node (BestBound) upon termination of the MILP solver. The absolute gap is equal to
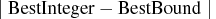 .
. - PRIMAL_INFEASIBILITY
- indicates the maximum (absolute) violation of the primal constraints by the solution.
- BOUND_INFEASIBILITY
- indicates the maximum (absolute) violation by the solution of the lower and/or upper bounds.
- INTEGER_INFEASIBILITY
- indicates the maximum (absolute) violation of the integrality of integer variables returned by the MILP solver.
- BEST_BOUND
- specifies the best LP objective value of all unprocessed nodes on the branch-and-bound tree at the end of execution. A missing value indicates that the OPTMILP procedure has processed either all or none of the nodes on the branch-and-bound tree.
- NODES
- specifies the number of nodes enumerated by the MILP solver by using the branch-and-bound algorithm.
- ITERATIONS
- indicates the number of simplex iterations taken to solve the problem.
- PRESOLVE_TIME
- indicates the time (in seconds) used in preprocessing.
- SOLUTION_TIME
- indicates the time (in seconds) taken to solve the problem.
Note: The time reported in PRESOLVE_TIME and SOLUTION_TIME is either CPU time (default) or real time. The type is determined by the TIMETYPE= option.
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.