| The NETFLOW Procedure |
Example 5.10: Maximum Flow Problem
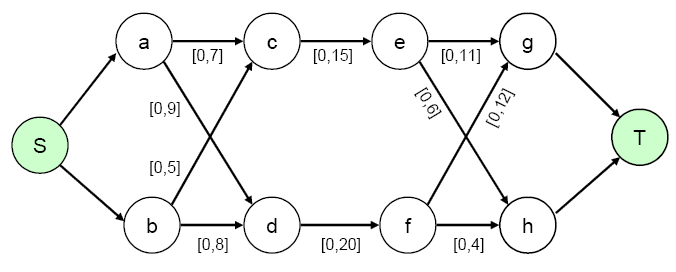
Consider the maximum flow problem depicted in Figure 5.45. The maximum flow between nodes S and T is to be determined. The minimum arc flow and arc capacities are specified as lower and upper bounds in square brackets, respectively.
|
Figure 5.45: Maximum Flow Problem Example
You can solve the problem using either EXCESS=ARCS or EXCESS=SLACKS. Consider using the EXCESS=ARCS option first. You can use the following SAS code to create the input data set:
data arcs;
input _from_ $ _to_ $ _cost_ _capac_;
datalines;
S a . .
S b . .
a c 1 7
b c 2 9
a d 3 5
b d 4 8
c e 5 15
d f 6 20
e g 7 11
f g 8 6
e h 9 12
f h 10 4
g T . .
h T . .
;
You can use the following call to PROC NETFLOW to solve the problem:
title1 'The NETFLOW Procedure';
proc netflow
intpoint
maxflow
excess = arcs
arcdata = arcs
source = S sink = T
conout = gout3;
run;
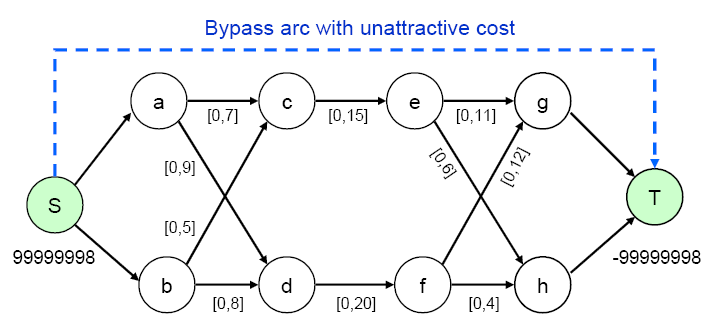
With the EXCESS=ARCS option specified, the problem gets transformed internally to the one depicted in Figure 5.46. Note that there is an additional arc from the source node to the sink node.
|
Figure 5.46: Maximum Flow Problem, EXCESS=ARCS Option Specified
The output SAS data set is displayed in Output 5.10.1.
Output 5.10.1: Maximum Flow Problem,EXCESS=ARCS Option SpecifiedYou can solve the same maximum flow problem, but this time with EXCESS=SLACKS specified. The SAS code is as follows:
title1 'The NETFLOW Procedure';
proc netflow
intpoint
excess = slacks
arcdata = arcs
source = S sink = T
maxflow
conout = gout3b;
run;
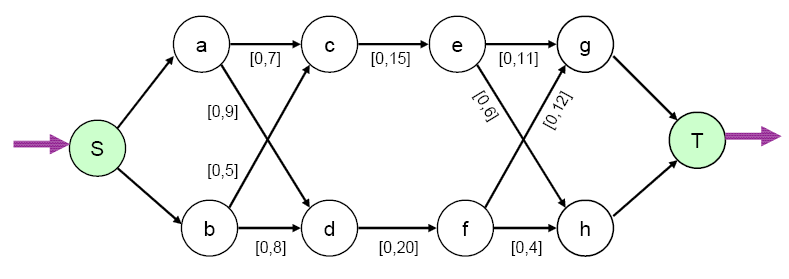
With the EXCESS=SLACKS option specified, the problem gets transformed internally to the one depicted in Figure 5.47. Note that the source node and sink node each have a single-ended "excess" arc attached to them.
|
Figure 5.47: Maximum Flow Problem, EXCESS=SLACKS Option Specified
The solution, as displayed in Output 5.10.2, is the same as before. Note that the _SUPPLY_ value of the source node Y has changed from 99999998 to missing S, and the _DEMAND_ value of the sink node Z has changed from -99999998 to missing D.
Output 5.10.2: Maximal Flow Problem,EXCESS=SLACKS Option Specified
|
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.