| The NETFLOW Procedure |
Handling Excess Supply or Demand
The supdem value of a node can be specified in the following formats:
- in the NODEDATA= data set, using the _supdem_ or _sd_ list variable
- in the ARCDATA= data set, using the _SUPPLY_ and _DEMAND_ list variables
If there is only one supply (demand) node, then use the SOURCE= (SINK=) option to refer to it, and use the SUPPLY= (DEMAND=) option to specify its supdem value.
To ensure feasibility, there are different methods by which flow can be added to or drained from the network. This extra flow can be added to or drained from the network at either the supply or demand nodes. The new EXCESS= option is used to address such instances.
For pure networks there are two valid values that can be specified for the EXCESS= option: EXCESS=ARCS and EXCESS=SLACKS.
EXCESS=ARCS is the default value. An extra node, referred to as _EXCESS_, is added to the network and is connected to the actual network by "excess" arcs.
- If total supply exceeds total demand, then _EXCESS_ is an extra demand node with demand equal to total supply minus total demand.
- If the THRUNET option is specified, the "excess" arcs are directed away from any actual demand node (even nodes with missing D demand) and toward _EXCESS_.
- Or else if there are demand nodes with missing D demands, the "excess" arcs are directed away from these nodes and toward _EXCESS_.
- Or else the "excess" arcs are directed away from the supply nodes and toward _EXCESS_.
- If the total demand exceeds the total supply, then _EXCESS_ is an extra supply node with supply equal to the total demand minus the total supply.
- If the THRUNET option is specified, the "excess" arcs are directed away from _EXCESS_ and toward any actual supply node (even nodes with missing S supply.)
- Or else if there are supply nodes with missing S supplies, the "excess" arcs are directed away from _EXCESS_ and toward these nodes.
- Or else the "excess" arcs are directed away from _EXCESS_ and toward the demand nodes.
The node _EXCESS_ and the associated arcs are created to ensure that the problem presented to the optimizer has a total supply equal to the total demand. They are neither displayed in the optimal solution nor saved in any output SAS data set.
If EXCESS=SLACKS is specified, then slack variables are created for some flow conservation constraints instead of having the node _EXCESS_ and "excess" arcs. The flow conservation constraint (which was an inequality) is now converted to an equality with the addition of the slack variable. Alternatively, you can think of these slacks as arcs with one of their end nodes missing --- they are directed from a node but not toward any other node (or directed toward a node but not from any other node). Figure 5.28 presents a clearer picture of this.
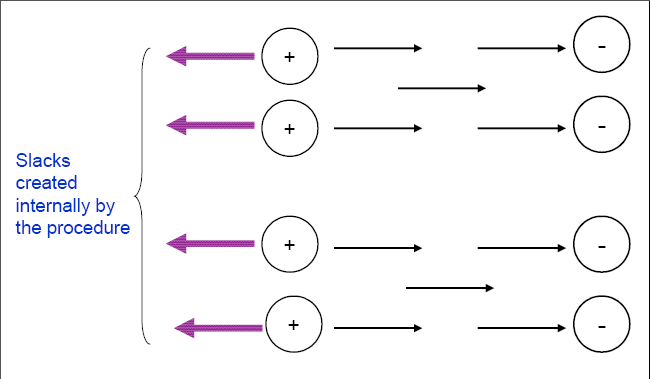
|
Figure 5.28: EXCESS=SLACKS, Total Supply Exceeds Total Demand, THRUNET Not Specified, No Nodes with Missing Demand
Note: When you specify EXCESS=SLACKS, the interior point solver is used. The output SAS data set needs to be specified by the CONOUT= data set, even if side constraints are not present. Also, when you specify the EXCESS=SLACKS option, the size of the model submitted to the optimizer is smaller than with EXCESS=ARCS since it no longer has the _EXCESS_ node and the excess arcs associated with it.
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.