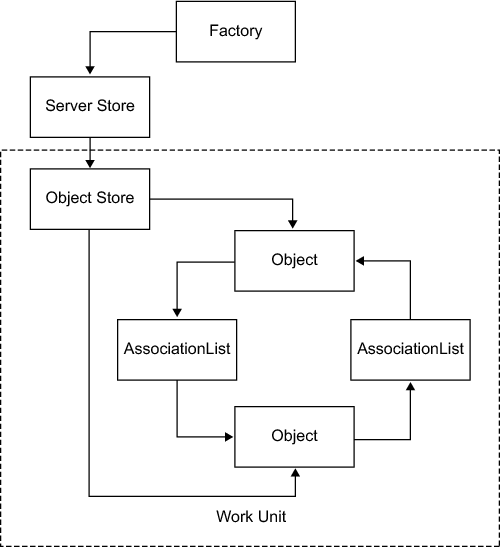
How the SAS Java Metadata Interface Works
The object factory provides
an environment for managing Java objects that represent SAS metadata
object instances.
The object store serves
as a container for Java objects that users create to add or modify
metadata objects in the SAS Metadata Server. The following figure
illustrates the relationship between the objects in an object store.
Using the SAS Java Metadata
Interface, you create a metadata object on the SAS Metadata Server,
or you modify an existing metadata object's attributes, by creating
a Java object representing its SAS metadata type. You then persist
the new or modified Java object to the SAS Metadata Server. A metadata
type refers to one of the metadata types defined in the SAS namespace
of the SAS Metadata Model. Metadata objects live in the SAS Metadata
Server. The Java objects in the object store act as proxies for the
metadata objects in the SAS Metadata Server.
Information about associations
is managed separately from information about attributes. Associations
are managed by creating AssociationList objects. An AssociationList
object stores information about how two metadata objects are related
to each other through an association name. To determine the associations
defined for a specific metadata type, see the “Alphabetical
Listing of SAS Namespace Metadata Types” in the SAS Metadata Model: Reference.
In the figure, Relationship between Objects in an Object Store, the squares named Object represent
metadata objects, and the squares named AssociationList represent
the associations between the metadata objects. Every relationship
in the SAS Metadata Model is a two-way association. That is, there
are two sides to each relationship, and each side has a name. For
example, if the metadata objects in the figure represented a PhysicalTable
and a Column, the PhysicalTable object would have a Columns association
to the Column object. The Column object would have a Table association
to the PhysicalTable object. For more information about associations,
see “Understanding Associations” in SAS
Metadata Model: Reference.
For an overview of the
interfaces used to create the factory, stores, and other objects,
see Interfaces and Classes Summary.
For information about
how to write a SAS Java Metadata Interface client that reads and
writes metadata, see Overview of Creating a SAS Java Metadata Interface Client.