Basic Usage
Overview
ODS is used
by all SAS software. However, you can explicitly use ODS with the
following:
Base SAS Reporting Procedures
The Base
SAS reporting procedures, PROC PRINT, PROC REPORT, and PROC TABULATE,
enable you to quickly analyze your data and organize it into easy-to-read
tables. You can use ODS options with the reporting procedures to give
your report another dimension of expression and usability. For example,
you can use the STYLE option with a PROC PRINT, PROC REPORT, or PROC
TABULATE statement to change the appearance of your report. The following
program uses the ODS STYLE option to create the colors in the output
below:
Title "Height and Weight by Gender and Age"; proc report nowd data=sashelp.class style(header)=[background=white]; col age (('gender' sex),(weight height)); define age / style(header)=[background=lightgreen]; define sex / across style(header)=[background=yellow] ' '; define weight / style(header)=[background=orange]; define height / style(header)=[background=tan]; run;
PROC REPORT Output with Styles Applied
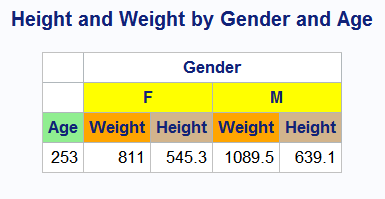
For complete documentation
on the styles and style attributes that you can use with PROC PRINT,
PROC TABULATE, and PROC REPORT, see Base SAS Procedures Guide.
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
Cascading style sheets
(CSS) is a style sheet language that you can use with ODS to control
the look and formatting of ODS output. A cascading style sheet is
an external file that contains label-value pairs that describe the
visual aspects of output, such as fonts, colors, borders, and so on.
You can then apply the CSS to your ODS output. The CSS language that
you can use with ODS is based on the standard CSS syntax found on
the Internet at http://www.w3.org/Style/CSS/. However, with ODS, you can apply
CSS to many different types of output, such as PDF, RTF, and EXCEL.
Using CSS and ODS is an advanced technique. For more information
about advanced ODS techniques, see Next Steps: A Quick Look at Advanced Features . For complete documentation about
using CSS with ODS, see the chapter about CSS in the SAS Output Delivery System: Advanced Topics.
The DOCUMENT Procedure
The combination of the ODS DOCUMENT
statement and the DOCUMENT procedure enables you to store a report’s
individual components, and then modify and replay the report. The
ODS DOCUMENT statement stores the actual ODS objects that are created
when you run a report. You can then use PROC DOCUMENT to rearrange,
duplicate, or remove output from the results of a procedure or a data
query without invoking the procedures from the original report. You
can also use PROC DOCUMENT to do the following:
-
transform a report without rerunning an analysis or repeating a data query
-
modify the structure of output
-
display output to any ODS output format without executing the original procedure or DATA step
-
navigate the current directory and list entries
-
open and list ODS documents
-
manage output
-
store the ODS output objects in raw formNote: The output is kept in the original internal representation as a data component plus a table template.
The DOCUMENT
destination has a graphical user interface (GUI), called the Documents window,
for performing tasks. However, you can perform the same tasks with
batch statement syntax using the DOCUMENT procedure.
For complete documentation about the DOCUMENT procedure,
see The DOCUMENT Procedure in SAS Output Delivery System: Procedures Guide.
ODS Global Statements
Overview
ODS global
statements provide greater flexibility to generate, customize, and
reproduce SAS procedure and DATA step output. You can use ODS global
statements to control different features of ODS. ODS statements can
be used anywhere in your SAS program. Some ODS statements remain in
effect until you explicitly change them. Other ODS statements are
automatically cleared. ODS global statements are organized into two
types, output control statements and ODS destination (report) statements. For complete documentation
on ODS global statements, see Dictionary of ODS Language Statements in SAS Output Delivery System: User’s Guide..
Output Control Statements
Output
Control Statements are statements that provide descriptive information
about the specified output objects, and they indicate whether the
style template or table template is provided by SAS. The ODS EXCLUDE,
ODS SELECT, and ODS TRACE statements are examples of output control
statements. Output control statements can do the following:
-
select specific output objects for specific destinations
-
exclude specific output objects from specific destinations
-
specify the location where you want to search for or store style templates or table templates
-
verify whether you are using a style template or a table template that is provided by SAS
-
provide descriptive information about each specified output object, such as its name, label, template, path, and label path
ODS Destination (Report) Statements
ODS destination (report)
statements are statements that enable you to create output that is
formatted for third-party software, such as HTML, RTF, and PDF. Or,
they enable you to create output that is specific to SAS, such as
an ODS document, LISTING output, or a SAS data set. You can use ODS
destination statements to generate and modify reports in formats such
as HTML, XML, PDF, PostScript, RTF, and Excel. The form for an ODS
destination statement is the ODS statement block, which consists of
ODS statements that open and close one or more ODS destinations sandwiched
around your program. Your results are sent to one or more output destinations.
You can use one or more
ODS destination statements, one or more PROC or DATA steps, and an
ODS CLOSE statement to form an ODS statement block. An ODS block has
the following form:
ODS output-destination
1 <options(s)>;
...
ODS output-destination
(n) <options(s)>
<your
SAS program>
ODS destination
close statement 1;
...
ODS destination
close statement (n)
In the ODS block, output-destination is
the name of a valid ODS destination and option(s) are
options that are valid for that destination. Your SAS program is inserted
between the beginning ODS destination statement and the ODS CLOSE
statement.
In the following example,
the output from PROC PRINT and PROC CONTENTS is sent to the PDF and
RTF destinations. The STYLE= option specifies what table template
to apply to the output. By default, the PDF opens in Adobe Acrobat
and the RTF opens in Microsoft Word.
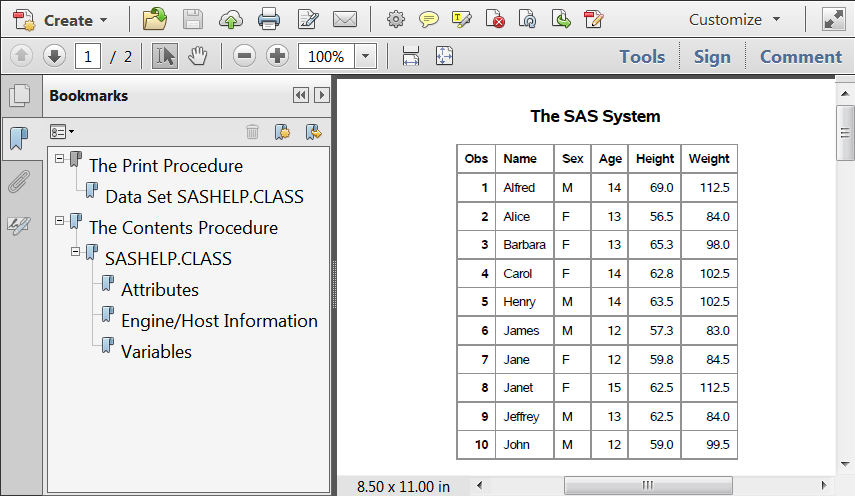
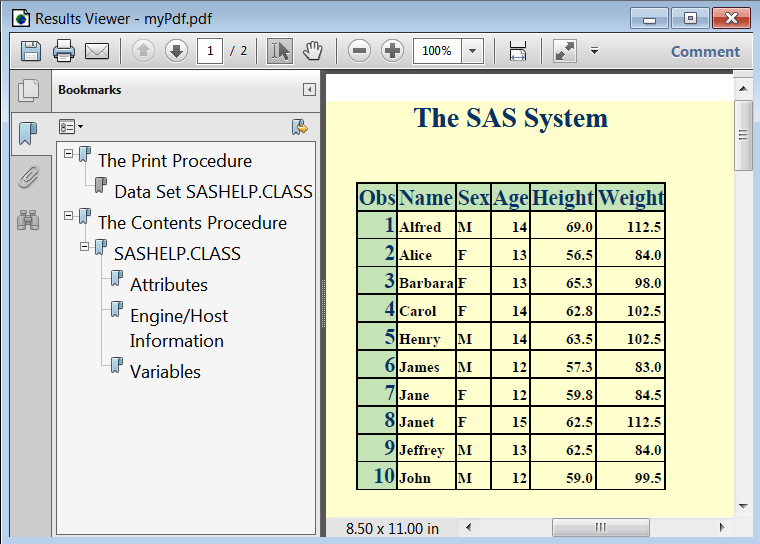
options obs=10 nodate; ods pdf file="myPdf.pdf" style=Banker; ods rtf file="myRTF.rtf" style=BarrettsBlue text="RTF Output"; proc print data=sashelp.class; run; proc contents data=sashelp.class; run; ods pdf close; ods rtf close;
Default PDF Output
PDF Output with Banker Style Applied
Default RTF Output
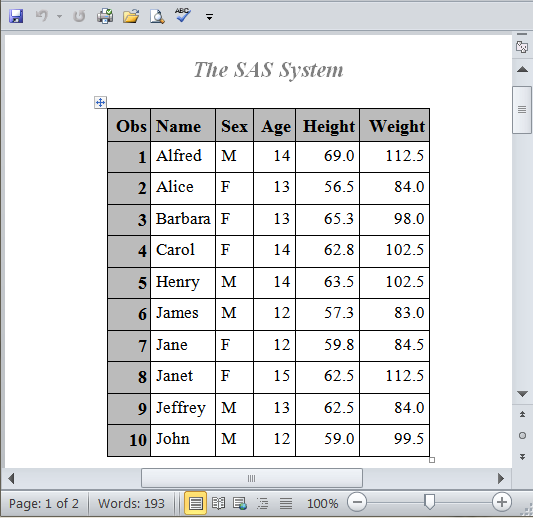
RTF Output with BarrettsBlue Style Applied
ODS destinations are organized into two
categories.
SAS Formatted Destinations
These destinations
produce output that is controlled and interpreted by SAS, such as
a SAS data set, LISTING output, or an ODS document.
Destinations Formatted For a Third Party
These destinations
produce output that is formatted for third-party applications such
as e-book readers, PowerPoint, and Microsoft Word. These statements
enable you to apply styles or markup languages. You can print to physical
printers using page description languages. For example, you can produce
output in PostScript, HTML, XML, or in a markup language that you
created.
The following table
lists the ODS destination categories, the destinations that each category
includes, and the formatted output that results from each destination.
|
Category
|
Destinations
|
Results
|
|---|---|---|
|
Formatted by SAS
|
DOCUMENT
|
ODS document
|
|
LISTING
|
SAS LISTING output
|
|
|
OUTPUT
|
SAS data set
|
|
|
Formatted by a Third
Party
|
EPUB
|
Output formatted for
e-book readers
|
|
EPUB3
|
Output formatted for
e-book readers
|
|
|
HTML
|
HTML file for online
viewing
|
|
|
MARKUP
|
Markup language tagsets
|
|
|
POWERPOINT
|
PowerPoint slides
|
|
|
PRINTER
|
Printable output in
one of three different formats: PCL, PDF, or PS (PostScript)
|
|
|
RTF
|
Output written in Rich
Text Format for use with Microsoft Word 2000
|
As destinations are
added to ODS, they will automatically become available to the DATA
step and all procedures that support ODS.
The Report Writing Interface
The ODS Report Writing
Interface (RWI) enables you to create highly customized reports from
within the DATA step. Because it is fully integrated with ODS, the
RWI enables you to combine the powerful programming features from
the DATA step with ODS features. This combination gives you flexibility
and control over every piece of output in your report. Using the RWI
is an advanced technique. For more information about advanced ODS techniques, see Next Steps: A Quick Look at Advanced Features . For complete documentation
about the RWI, see Introduction to the Report Writing Interface in SAS Output Delivery System: Advanced Topics.
ODS LAYOUT Statements
ODS LAYOUT statements
enable you to create custom reports that easily mix SAS graphics,
images, text, and tables, and then arrange them on a page where you
like.
Using the ODS LAYOUT statements is an advanced technique. For more information
about advanced ODS techniques, see Next Steps: A Quick Look at Advanced Features . For complete documentation
about ODS LAYOUT statements, see Arranging Output with ODS LAYOUT in SAS Output Delivery System: User’s Guide.
-
The ODS LAYOUT GRIDDED statement enables you to format in a gridded layout. The ODS LAYOUT GRIDDED statement follows the traditional ODS statement usage in which you wrap (sandwich) your procedure code with a definitive starting and ending location. ODS layout is designed to allow nested layouts (containers) to provide endless customization.
-
The ODS LAYOUT ABSOLUTE statement enables you to specify the exact location on the page to place a layout and region container. Each container needs to be explicitly placed to ensure that there is no unintended overlap. The ODS LAYOUT ABSOLUTE statement follows the traditional ODS statement usage in which you wrap (sandwich) your procedure code with a definitive starting and ending location. ODS layout is designed to allow nested layouts (containers) to provide endless customization.
ODSLIST Procedure
The ODSLIST procedure
is used to create bulleted list templates. With PROC ODSLIST, you
can do the following:
With PROC ODSLIST, you can use the DATA= option to
bind your data to the template without using a DATA step. PROC ODSLIST
can be used with any output destination. However, PROC ODSLIST is
essential for creating content for the ODS destination for PowerPoint
and e-books. Using the ODSLIST procedure is an advanced technique. For more information
about advanced ODS techniques, see Next Steps: A Quick Look at Advanced Features . For complete documentation
about the ODSLIST procedure, see The ODSLIST Procedure in SAS Output Delivery System: Procedures Guide.
-
create text templates for lists that can be customized and nested an infinite number of times
-
use style attributes and formats to customize your content
-
use WHERE expressions to specify list item content
ODSTABLE Procedure
By default, ODS output
is formatted based on the various definitions or templates that the
procedure or DATA step specify. However, you can create your own new
tabular output templates using the ODSTABLE procedure. ODS uses these
templates to produce customized tabular output. With the ODSTABLE
procedure, you can create table templates and bind them with the input
data set in one statement. You can name your templates and store them
in a template store. Using the ODSTABLE procedure is an advanced technique. For more information
about advanced ODS techniques, see Next Steps: A Quick Look at Advanced Features . For complete documentation
about the ODSTABLE procedure, see The ODSTABLE Procedure in SAS Output Delivery System: Procedures Guide.
ODSTEXT Procedure
The ODSTEXT procedure
is used to create text block templates. These text block templates
create lists and paragraphs for your output. You can use style attributes
and formats to customize your content and WHERE expressions to select
your content. With PROC ODSTEXT, you can use the DATA= option to bind
your data to the template without using a DATA step. PROC ODSTEXT
can be used with any output destination. However, PROC ODSTEXT is
essential for creating content for the ODS destination for PowerPoint
and e-books. Using the ODSTEXT procedure is an advanced technique. For more information
about advanced ODS techniques, see Next Steps: A Quick Look at Advanced Features . For complete documentation
about the ODSTEXT procedure, see The ODSTEXT Procedure in SAS Output Delivery System: Procedures Guide.
TEMPLATE Procedure
All SAS
procedures produce output objects that ODS delivers to various ODS
destinations based on the default specifications for the procedure
or based on your own specifications. Output objects are commonly displayed
as tables, data sets, or graphs. Each output object has an associated
template that is provided by SAS that defines its presentation format.
You can use the TEMPLATE procedure to view or alter a template or
to create a new template by changing the headers, formats, column
order, and so on.
The TEMPLATE procedure
enables you to create or modify a template that you can apply to your
output. You can also use the TEMPLATE procedure to navigate and manage
the templates stored in template stores. ODS then uses these templates
to produce formatted output. Using the TEMPLATE procedure is an advanced
technique. For
more information about advanced ODS techniques, see Next Steps: A Quick Look at Advanced Features .
For complete documentation
on the TEMPLATE procedure, see the TEMPLATE procedure in SAS Output Delivery System: Procedures Guide.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All Rights Reserved.