Overview
This appendix explains
how an RFC destination is used to get data either directly or indirectly.
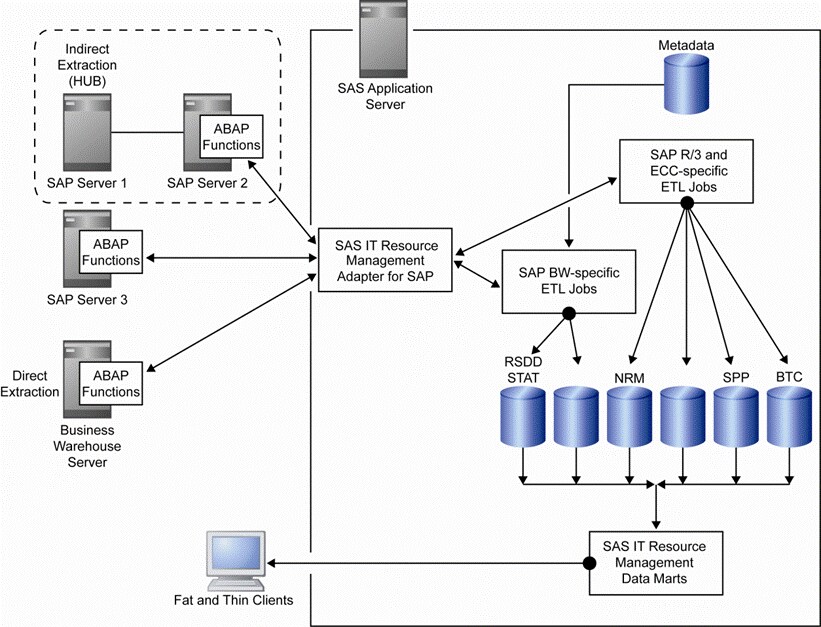
The following figure (also in Chapter 1) shows how data from SAP servers
2 and 3 is extracted directly into SAS.
Note: A hub can retrieve data from
other SAP servers only if they are of the same SAP threaded kernel
release.
Note: If there are no restrictions
on installing ABAP functions on each machine, then you should use
direct access.
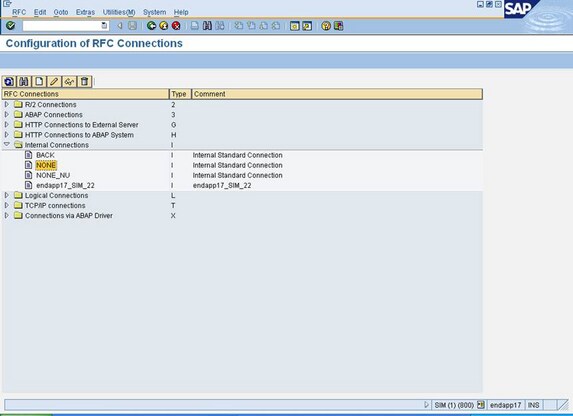
The following example
shows an SAP ECC 6.0 (release 6.10) being used as an adapter gateway
server. The RFC destination for this adapter gateway server is the
predefined NONE internal connection.
Type
SM59 on
the command line to display the RFC destination. The Display and maintain
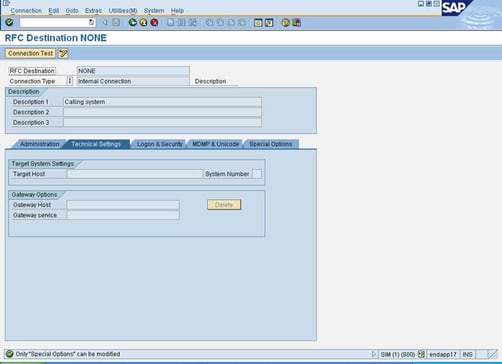
RFC destinations window appears. To display the internal connection
properties for NONE, double-click NONE.