IMSTAT Procedure
- Syntax
 Procedure SyntaxPROC IMSTAT StatementBALANCE StatementCOLUMNINFO StatementCOMPUTE StatementDELETEROWS StatementDISTRIBUTIONINFO StatementDROPTABLE StatementFETCH StatementFREE StatementIMPORTCUBE StatementLIFETIME StatementNUMROWS StatementPARTITION StatementPARTITIONINFO StatementPROMOTE StatementPURGETEMPTABLES StatementREPLAY StatementSAVE StatementSCHEMA StatementSCORE StatementSERVERINFO StatementSERVERPARM StatementSERVERTERM StatementSERVERWAIT StatementSET StatementSTORE StatementTABLE StatementTABLEINFO StatementUPDATE StatementQUIT Statement
Procedure SyntaxPROC IMSTAT StatementBALANCE StatementCOLUMNINFO StatementCOMPUTE StatementDELETEROWS StatementDISTRIBUTIONINFO StatementDROPTABLE StatementFETCH StatementFREE StatementIMPORTCUBE StatementLIFETIME StatementNUMROWS StatementPARTITION StatementPARTITIONINFO StatementPROMOTE StatementPURGETEMPTABLES StatementREPLAY StatementSAVE StatementSCHEMA StatementSCORE StatementSERVERINFO StatementSERVERPARM StatementSERVERTERM StatementSERVERWAIT StatementSET StatementSTORE StatementTABLE StatementTABLEINFO StatementUPDATE StatementQUIT Statement - Overview
- Concepts
- Examples

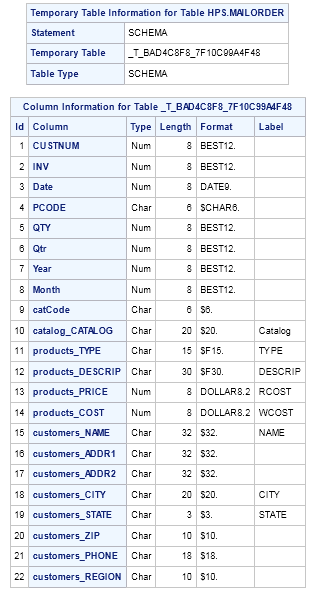
Example 5: Creating a Star Schema
Program Description
-
Once the WHERE clause is specified, it applies to the statements that follow it. It also crosses RUN boundaries.
-
The SAVE statement is subject to the WHERE clause. As a result, the records from the Prdsale table that meet the WHERE clause are saved to /dept/sales/y1994q1.sashdat. The FULLPATH option is used to specify the table name instead of using the name of the active table. This is particularly useful when saving temporary tables.
-
The DELETEROWS statement is also subject to the WHERE clause. The records that were just saved to HDFS are now deleted and purged from memory. (The DELETEROWS statement without the PURGE option would mark the records for deletion and exclude them from being used in calculations, but it does not free the memory resources.)
-
The WHERE clause is cleared and the SUMMARY statement that follows is performed against all the remaining records in the Prdsale table.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.