| Division Operator: / |
- matrix1 / matrix2 ;
- matrix / scalar ;
- matrix / vector ;
The division operator (/) divides each element of matrix1 by the corresponding element of matrix2, producing a matrix of quotients.
You can also use the division operator to conveniently divide all elements of a matrix, each column of a matrix, or each row of a matrix.
When you use the matrix / scalar form, each element of the matrix is divided by the scalar value.
-
When you use the matrix / vector form, each row or column of the
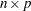 matrix is divided by a corresponding element of the vector.
matrix is divided by a corresponding element of the vector. If you divide by an
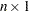 column vector, each row of the matrix is divided by the corresponding row of the vector.
column vector, each row of the matrix is divided by the corresponding row of the vector. If you divide by a
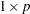 row vector, each column of the matrix is divided by the corresponding column of the vector.
row vector, each column of the matrix is divided by the corresponding column of the vector.
When an element of a matrix contains a missing value, the corresponding element of the quotient is also a missing value.
If a divisor is zero, the operation displays a warning and assigns a missing value for the corresponding element in the result.
The following statements compute the matrices c and d, shown in Figure 23.9:
a = {1 2,
3 4};
b = {5 6,
7 8};
c = a/b;
d = a/4;
print c, d;
| c | |
|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.3333333 |
| 0.4285714 | 0.5 |
| d | |
|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.5 |
| 0.75 | 1 |