| Language Reference |
MVE Call
finds the minimum volume ellipsoid estimator
- CALL MVE( sc, coef, dist, opt,
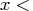 ,
, 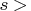 );
);
The MVE call is the robust (resistant) estimation of multivariate location and scatter, defined by minimizing the volume of an ellipsoid containing
The MVE subroutine computes the minimum volume ellipsoid estimator. These robust locations and covariance matrices can be used to detect multivariate outliers and leverage points. For this purpose, the MVE subroutine provides a table of robust distances.
In the following discussion,
- opt
- refers to an options vector with the following components
(missing values are treated as default values):
- opt[1]
- specifies the amount of printed output.
Higher option values request additional
output and include the output of lower values.
- opt[1]=0
- prints no output except error messages.
- opt[1]=1
- prints most of the output.
- opt[1]=2
- additionally prints case numbers of the
observations in the best subset and some
basic history of the optimization process.
- opt[1]=3
- additionally prints how many subsets result in singular linear systems.
The default is opt[1]=0.
- opt[2]
- specifies whether the classical, initial, and
final robust covariance matrices are printed.
The default is opt[2]=0.
Note that the final robust covariance
matrix is always returned in coef.
- opt[3]
- specifies whether the classical, initial, and final
robust correlation matrices are printed or returned:
- opt[3]=0
- does not return or print.
- opt[3]=1
- prints the robust correlation matrix.
- opt[3]=2
- returns the final robust correlation matrix in coef.
- opt[3]=3
- prints and returns the final robust correlation matrix.
- opt[4]
- specifies the quantile
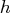 used in the objective function.
The default is opt[5]=
used in the objective function.
The default is opt[5]= ![h = [\frac{n+n+1}2]](images/langref_langrefeq764.gif) .
If the value of
.
If the value of 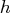 is specified outside the range
is specified outside the range 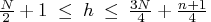 ,
it is reset to the closest boundary of this region.
,
it is reset to the closest boundary of this region.
- opt[5]
- specifies the number
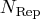 of subset generations.
This option is the same as described
previously for the LMS and LTS subroutines.
Due to computer time restrictions, not all subset combinations
can be inspected for larger values of
of subset generations.
This option is the same as described
previously for the LMS and LTS subroutines.
Due to computer time restrictions, not all subset combinations
can be inspected for larger values of 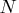 and
and 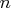 .
If opt[5] is zero or missing, the default
number of subsets is taken from the following table.
.
If opt[5] is zero or missing, the default
number of subsets is taken from the following table.
| n | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 500 | 50 | 22 | 17 | 15 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1414 | 182 | 71 | 43 | 32 | 27 | 24 | 23 | 22 | ||
| 500 | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 2500 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 |
| n | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 22 | 22 | 22 | 23 | 23 | |
| 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 |
- If the number of cases (observations)
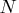 is smaller
than
is smaller
than 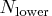 , then all possible subsets are used;
otherwise,
, then all possible subsets are used;
otherwise, 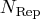 subsets are chosen randomly.
This means that an exhaustive search
is performed for opt[5]=-1.
If
subsets are chosen randomly.
This means that an exhaustive search
is performed for opt[5]=-1.
If 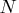 is larger than
is larger than 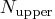 , a note is printed
in the log file indicating how many subsets exist.
, a note is printed
in the log file indicating how many subsets exist.
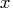
- refers to an
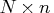 matrix
matrix 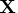 of regressors.
of regressors.
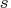
- refers to an
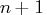 vector containing
vector containing 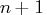 observation
numbers of a subset for which the objective function
should be evaluated, where
observation
numbers of a subset for which the objective function
should be evaluated, where 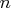 is the number of parameters.
In other words, the MVE algorithm computes the minimum volume of the
ellipsoid containing the observation numbers contained in
is the number of parameters.
In other words, the MVE algorithm computes the minimum volume of the
ellipsoid containing the observation numbers contained in 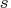 .
.
Missing values are not permitted in
The MVE subroutine returns the following values:
- sc
- is a column vector containing the following scalar information:
- sc[1]
- the quantile
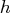 used in the objective function
used in the objective function
- sc[2]
- number of subsets generated
- sc[3]
- number of subsets with singular linear systems
- sc[4]
- number of nonzero weights
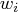
- sc[5]
- lowest value of the objective function
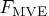 attained (volume of smallest ellipsoid found)
attained (volume of smallest ellipsoid found)
- sc[6]
- Mahalanobis-like distance used in the computation of
the lowest value of the objective function
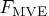
- sc[7]
- the cutoff value used for the outlier decision
- coef
- is a matrix with
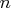 columns containing
the following results in its rows:
columns containing
the following results in its rows:
- coef[1]
- location of ellipsoid center
- coef[2]
- eigenvalues of final robust scatter matrix
- coef[3:2+n]
- the final robust scatter matrix for
opt[2]=1 or opt[2]=3
- coef[2+n+1:2+2n]
- the final robust correlation matrix for
opt[3]=1 or opt[3]=3
- dist
- is a matrix with
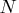 columns containing
the following results in its rows:
columns containing
the following results in its rows:
- dist[1]
- Mahalanobis distances
- dist[2]
- robust distances based on the final estimates
- dist[3]
- weights (=1 for small, =0 for large robust distances)
Example
Consider results for Brownlee's (1965) stackloss data. The three explanatory variables correspond to measurements for a plant oxidizing ammonia to nitric acid on 21 consecutive days:-
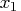 air flow to the plant
air flow to the plant
-
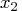 cooling water inlet temperature
cooling water inlet temperature
-
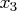 acid concentration
acid concentration
/* X1 X2 X3 Y Stackloss data */
aa = { 1 80 27 89 42,
1 80 27 88 37,
1 75 25 90 37,
1 62 24 87 28,
1 62 22 87 18,
1 62 23 87 18,
1 62 24 93 19,
1 62 24 93 20,
1 58 23 87 15,
1 58 18 80 14,
1 58 18 89 14,
1 58 17 88 13,
1 58 18 82 11,
1 58 19 93 12,
1 50 18 89 8,
1 50 18 86 7,
1 50 19 72 8,
1 50 19 79 8,
1 50 20 80 9,
1 56 20 82 15,
1 70 20 91 15 };
Rousseeuw and Leroy (1987, p. 76) cite a large number of papers where this data set was analyzed and state that most researchers ``concluded that observations 1, 3, 4, and 21 were outliers''; some people also reported observation 2 as an outlier.
By default, subroutine MVE chooses only 2,000 randomly selected subsets in its search. There are in total 5,985 subsets of 4 cases out of 21 cases. Here is the code:
a = aa[,2:4]; optn = j(8,1,.); optn[1]= 2; /* ipri */ optn[2]= 1; /* pcov: print COV */ optn[3]= 1; /* pcor: print CORR */ optn[5]= -1; /* nrep: use all subsets */ CALL MVE(sc,xmve,dist,optn,a);
The first part of the output shows the classical scatter and correlation matrix:
Minimum Volume Ellipsoid (MVE) Estimation
Consider Ellipsoids Containing 12 Cases.
Classical Covariance Matrix
VAR1 VAR2 VAR3
VAR1 84.057142857 22.657142857 24.571428571
VAR2 22.657142857 9.9904761905 6.6214285714
VAR3 24.571428571 6.6214285714 28.714285714
Classical Correlation Matrix
VAR1 VAR2 VAR3
VAR1 1 0.781852333 0.5001428749
VAR2 0.781852333 1 0.3909395378
VAR3 0.5001428749 0.3909395378 1
Classical Mean
VAR1 60.428571429
VAR2 21.095238095
VAR3 86.285714286
There are 5985 subsets of 4 cases out of 21 cases.
All 5985 subsets will be considered.
The second part of the output shows the results of the optimization (complete subset sampling):
Complete Enumeration for MVE
Best
Subset Singular Criterion Percent
1497 22 253.312431 25
2993 46 224.084073 50
4489 77 165.830053 75
5985 156 165.634363 100
Minimum Criterion= 165.63436284
Among 5985 subsets 156 are singular.
Observations of Best Subset
7 10 14 20
Initial MVE Location
Estimates
VAR1 58.5
VAR2 20.25
VAR3 87
Initial MVE Scatter Matrix
VAR1 VAR2 VAR3
VAR1 34.829014749 28.413143611 62.32560534
VAR2 28.413143611 38.036950318 58.659393261
VAR3 62.32560534 58.659393261 267.63348175
The third part of the output shows the optimization results after local improvement:
Final MVE Estimates (Using Local Improvement)
Number of Points with Nonzero Weight=17
Robust MVE Location
Estimates
VAR1 56.705882353
VAR2 20.235294118
VAR3 85.529411765
Robust MVE Scatter Matrix
VAR1 VAR2 VAR3
VAR1 23.470588235 7.5735294118 16.102941176
VAR2 7.5735294118 6.3161764706 5.3676470588
VAR3 16.102941176 5.3676470588 32.389705882
Eigenvalues of Robust
Scatter Matrix
VAR1 46.597431018
VAR2 12.155938483
VAR3 3.423101087
Robust Correlation Matrix
VAR1 VAR2 VAR3
VAR1 1 0.6220269501 0.5840361335
VAR2 0.6220269501 1 0.375278187
VAR3 0.5840361335 0.375278187 1
The final output presents a table containing the classical
Mahalanobis distances, the robust distances, and the weights
identifying the outlying observations (that is leverage points
when explaining ![]() with these three regressor variables):
with these three regressor variables):
Classical Distances and Robust (Rousseeuw) Distances
Unsquared Mahalanobis Distance and
Unsquared Rousseeuw Distance of Each Observation
Mahalanobis Robust
N Distances Distances Weight
1 2.253603 5.528395 0
2 2.324745 5.637357 0
3 1.593712 4.197235 0
4 1.271898 1.588734 1.000000
5 0.303357 1.189335 1.000000
6 0.772895 1.308038 1.000000
7 1.852661 1.715924 1.000000
8 1.852661 1.715924 1.000000
9 1.360622 1.226680 1.000000
10 1.745997 1.936256 1.000000
11 1.465702 1.493509 1.000000
12 1.841504 1.913079 1.000000
13 1.482649 1.659943 1.000000
14 1.778785 1.689210 1.000000
15 1.690241 2.230109 1.000000
16 1.291934 1.767582 1.000000
17 2.700016 2.431021 1.000000
18 1.503155 1.523316 1.000000
19 1.593221 1.710165 1.000000
20 0.807054 0.675124 1.000000
21 2.176761 3.657281 0
Distribution of Robust Distances
MinRes 1st Qu. Median
0.6751244996 1.5084120761 1.7159242054
Mean 3rd Qu. MaxRes
2.2282960174 2.0831826658 5.6373573538
Cutoff Value = 3.0575159206
The cutoff value is the square root of
the 0.975 quantile of the chi square
distribution with 3 degrees of freedom.
There are 4 points with large robust distances receiving
zero weights. These may include boundary cases.
Only points whose robust distances are substantially larger
than the cutoff value should be considered outliers.
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.