| Language Reference |
INSERT Function
inserts one matrix inside another
- INSERT(
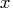 ,
, 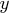 , row<, column>)
, row<, column>)
The inputs to the INSERT function are as follows:
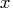
- is the target matrix.
It can be either numeric or character.
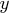
- is the matrix to be inserted into the target.
It can be either numeric or character,
depending on the type of the target matrix.
- row
- is the row where the insertion is to be made.
- column
- is the column where the insertion is to be made.
For example, consider the following statements:
a={1 2, 3 4};
b={5 6, 7 8};
c=insert(a, b, 2, 0);
d=insert(a, b, 0, 3);
These statements produce the following result:
C 4 rows 2 cols (numeric)
1 2
5 6
7 8
3 4
D 2 rows 4 cols (numeric)
1 2 5 6
3 4 7 8
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.