| Graphics Examples |
Common Arguments
IML graphics commands are available
in the form of call subroutines.
They generally take a set of required arguments
followed by a set of optional arguments.
All graphics primitives take window
and viewport as optional arguments.
Some IML graphics commands, like GPOINT or GPIE, accept
implicit repetition factors in the argument lists.
The GPOINT command places as many markers
as there are well-defined ![]() pairs.
The GPIE command draws as many slices
as there are well-defined pies.
In those cases, some of the attribute matrices can
have more than one element, which are used in order.
If an attribute list is exhausted before the repetition
factor is completed, the last element of the list is
used as the attribute for the remaining primitives.
pairs.
The GPIE command draws as many slices
as there are well-defined pies.
In those cases, some of the attribute matrices can
have more than one element, which are used in order.
If an attribute list is exhausted before the repetition
factor is completed, the last element of the list is
used as the attribute for the remaining primitives.
The arguments to the IML graphics commands are positional. Thus, to skip over an optional argument from the middle of a list, you must specify a comma to hold its place. For example, the following command omits the third argument from the argument list:
call gpoint(x,y, ,"red");
The following list details the arguments commonly used in IML graphics commands:
- color
- is a character matrix or literal that names a
valid color as specified in the GOPTIONS statement.
The default color is the first color specified
in the COLORS= list in the GOPTIONS statement.
If no such list is given, IML uses the
first default color for the graphics device.
Note that color can be specified either as a quoted
literal, such as "RED," a color number, such as 1, or the
name of a matrix containing a reference to a valid color.
A color number
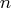 refers to the
refers to the 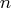 th color in the color list.
th color in the color list.
You can change the default color with the GSET command.
- font
- is a character matrix or quoted literal that specifies a valid font name. The default font is the hardware font, which can be changed by the GSET command unless a viewport is in effect.
- height
- is a numeric matrix or literal that specifies the character height. The unit of height is the gunit of the GOPTIONS statement, when specified; otherwise, the unit is a character cell. The default height is 1 gunit, which you can change by using the GSET command.
- pattern
- is a character matrix or quoted literal that specifies
the pattern to fill the interior of a closed curve.
You specify a pattern by a coded character string as
documented in the V= option in the PATTERN statement
(refer to the chapter on the PATTERN statement
in SAS/GRAPH Software: Reference.
The default pattern set by the IML graphics subsystem is "E," that is, empty. The default pattern can be changed by using the GSET command.
- segment-name
- is a character matrix or quoted literal that specifies
a valid SAS name used to identify a graphics segment.
The segment-name is associated with the
graphics segment opened with a GOPEN command.
If you do not specify segment-name,
IML generates default names.
For example, to create a graphics segment called PLOTA,
use the following statement:
call gopen("plota");Graphics segments are not allowed to have the same name as an existing segment. If you try to create a second segment named PLOTA (that is, when the replace flag is turned off), then the second segment is named PLOTA1. The replace flag is set by the GOPEN command for the segment that is being created. To open a new segment named PLOTA and replace an existing segment with the same name, use the following statement:call gopen("plota",1);If you do not specify a replace argument to the GOPEN command, the default is set by the GSTART command for all subsequent segments that are created. By default, the GSTART command sets the replace flag to 0, so that new segments do not replace like-named segments. - style
- is a numeric matrix or literal that specifies an index corresponding to the line style documented for the SYMBOL statement in the chapter on the SYMBOL statement in SAS/GRAPH Software: Reference. The IML graphics subsystem sets the default line style to be 1, a solid line. The default line style can be changed by using the GSET command.
- symbol
- is a character matrix or quoted literal that specifies either a character string corresponding to a symbol as defined for the V= option of the SYMBOL statement or specifies the corresponding identifying symbol number. STAR is the default symbol used by the IML graphics subsystem.
SAS/IML graphics commands are described in detail in Chapter 20.
Refer also to SAS/GRAPH Software: Reference for additional information.
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.