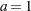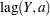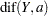| Variable Transformations |
Lag Transformations
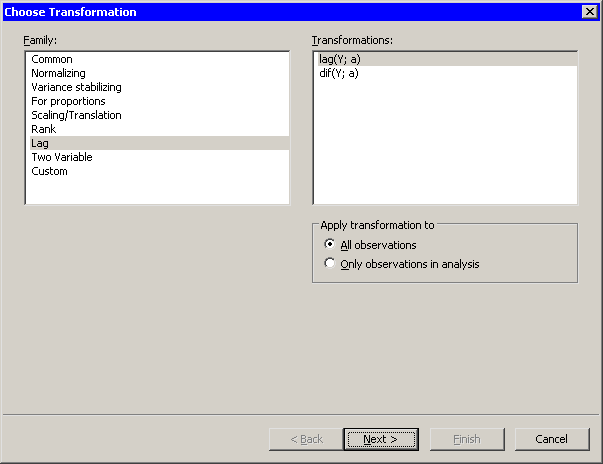
Figure 32.18 shows the transformations that are available when you select Lag from the Family list. These transformations are used to compute lagged transformations of a variable’s value. Equations for these transformations are given in Table 32.7.
Default |
Name of |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Transformation |
Parameter |
New Variable |
Equation |
lag(Y; a) |
|
Lag_Y |
|
dif(Y; a) |
|
Dif_Y |
|
The lag(Y; a) transformation creates a new variable whose 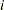 th value is equal to
th value is equal to 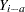 for
for 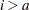 . For
. For 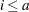 , the new variable contains missing values. For further details, see the documentation for the LAG function in the SAS Language Reference: Dictionary.
, the new variable contains missing values. For further details, see the documentation for the LAG function in the SAS Language Reference: Dictionary.
The dif(Y; a) transformation creates a new variable whose 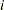 th value is equal to
th value is equal to 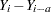 for
for 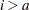 . For
. For 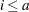 , the new variable contains missing values. If either
, the new variable contains missing values. If either 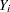 or
or 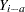 is missing, then so is their difference. For further details, see the documentation for the DIF function in the SAS Language Reference: Dictionary.
is missing, then so is their difference. For further details, see the documentation for the DIF function in the SAS Language Reference: Dictionary.
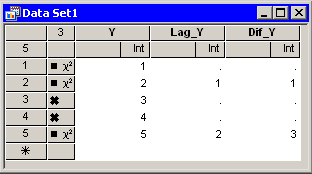
If some observations are excluded from analyses and you select Only observations in analysis, then the lag transformations use only the observations that are included in analyses. Figure 32.19 presents an example of how these transformations behave when some observations are excluded. In the data table, Y has values 1–5, but observations 3 and 4 are excluded from analyses.
The Lag_Y variable is the result of the lag(Y; 1) transformation. The third and fourth values are missing because these observations are excluded from analyses. The fifth value of Lag_Y is 2, the previous value of Y that is included in analyses.
The Dif_Y variable is the result of the dif(Y; 1) transformation. The values are the difference between the first and second columns.
Copyright © SAS Institute, Inc. All Rights Reserved.