| Model Fitting: Generalized Linear Models |
| Output Variables Tab |
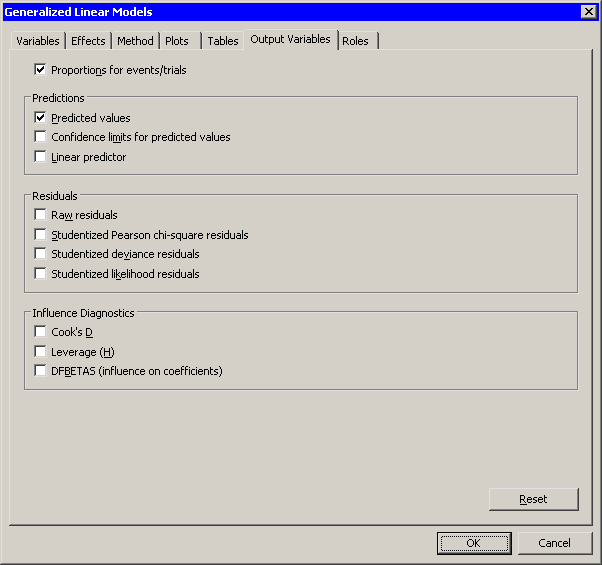
You can use the Output Variables tab to add analysis variables to the data table. (See Figure 24.24.) If you request a plot that uses one of the output variables, then that variable is automatically created even if you did not explicitly select the variable on the Output Variables tab.
For a multinomial response, residuals and influence diagnostics are not available.
The following list describes each output variable and indicates how the output variable is named. 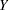 represents the name of the response variable. If you use events/trials syntax, then
represents the name of the response variable. If you use events/trials syntax, then 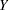 represents the name of the events variable.
represents the name of the events variable.
- Proportions for events/trials
adds a variable named Proportion_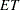 , where
, where 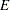 is the name of the events variable and
is the name of the events variable and 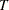 is the name of the trials variable. The value of the variable is the ratio
is the name of the trials variable. The value of the variable is the ratio 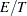 . This variable is added only when you use events/trials syntax.
. This variable is added only when you use events/trials syntax. - Predicted values
adds predicted values. The variable is named GenP_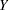 .
. - Confidence limits for predicted values
adds 95% confidence limits for the predicted values. The variables are named GenLclm_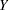 and GenUclm_
and GenUclm_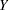 .
. - Linear predictor
adds the linear predictor values. The variable is named GenXBeta_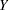 .
. - Raw residuals
adds residuals, which are calculated as observed values minus predicted values. The variable is named GenR_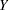 .
. - Pearson chi-square residuals
adds the Pearson chi-square residuals. The variable is named GenChiSqR_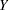 .
. - Deviance residuals
adds the deviance residuals. The variable is named GenDevR_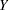 .
. - Likelihood residuals
adds the likelihood residuals. The variable is named GenLikR_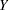 .
. - Cook’s D
adds Cook’s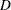 influence statistic. The variable is named GenCooksD_
influence statistic. The variable is named GenCooksD_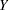 .
. - Leverage (H)
adds the leverage statistic. The variable is named GenH_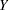 .
. - DFBETAS (influence on coefficients)
adds variables, where
variables, where  is the number of parameters in the model. A classification variable with
is the number of parameters in the model. A classification variable with 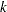 levels counts as
levels counts as 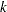 parameters. The variables are scaled measures of the change in each parameter estimate and are calculated by deleting the
parameters. The variables are scaled measures of the change in each parameter estimate and are calculated by deleting the 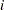 th observation. Large values of DFBETAS indicate observations that are influential in estimating a given parameter. Belsley, Kuh, and Welsch (1980) recommend
th observation. Large values of DFBETAS indicate observations that are influential in estimating a given parameter. Belsley, Kuh, and Welsch (1980) recommend 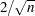 as a size-adjusted cutoff. The variables are named DFBeta
as a size-adjusted cutoff. The variables are named DFBeta , for
, for 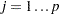 .
.
Copyright © SAS Institute, Inc. All Rights Reserved.