Starting SAS
Use SAS Interactively or in Batch Mode
When running SAS under Windows, you
can start an interactive session to submit programs and view the resulting
output, or you can execute batch SAS jobs, and view the output later.
By default, invoking SAS begins an interactive SAS session. If you have a SAS program
that you want to submit as a batch job, specify the SYSIN system option with the name of the SAS program file when you invoke SAS.
When you start SAS in
an interactive session for the first time, you are asked if you want
to learn some basic tasks by taking the Getting Started Tutorial.
To start the tutorial, click Start Tutorial.
If you do not want to be prompted to take the tutorial, select Do
not show this dialog box again. You can start the tutorial
at any time by selecting Help Getting Started with SAS Software.
Getting Started with SAS Software.
Starting from the Start Menu
To start SAS from the Windows Start Menu:
-
Click Start.
-
Select Programs.
-
Select SAS.
-
Select SAS 9.4 (Language) .
Starting from Custom Shortcuts or Program Items
During installation, the Setup program
automatically creates a program item in the Start menu
that you can use to start SAS. However, you can create multiple SAS
items within a folder to represent several differently configured
SAS sessions. Also, if you want SAS to start every time you start
Windows, you can place a program item or shortcut in the Start up
folder. For information about creating shortcuts, see your Windows
documentation.
After you have created a shortcut
to SAS, you can append system options to the SAS command. To append
system options:
-
Open the SAS Properties window and click the Shortcut tab.
-
In the Target field, append the system options to the SAS command. Remember that double quotation marks are required around pathnames. The following example uses double quotation marks,
"c:\program files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\sas.exe" -config "c:\mydir\sasv9.cfg"
Note: If a system option’s value has a space in it, you must enclose the value in quotation marks on the command line or in a config. file. The following example shows the correct syntax:-bottommargin '2 in';
Starting from the Run Dialog Box or a Command Prompt
Specifying the SAS Configuration File
If
you start SAS by using a command line (either from the Run dialog
box or the Command window), you might want to specify the SAS configuration file location through the CONFIG system option. Even if you use the default configuration
file SASV9.CFG, specify the file to ensure
that SAS uses the configuration file that you want. For more information about how
SAS searches for the configuration file, see How SAS Finds and Processes Configuration Files .
When the WORK and SASUSER system options are set, the Work and Sasuser
data libraries reside in the specified paths regardless of the path
from which you invoke SAS. For more information about the Sasuser
data library, see Profile Catalog .
For more information about the Work data library, see Work Data Library .
Using the Run Dialog Box
To start an interactive session by using the Run dialog
box
-
Select Start
 Run
Run -
In the Open field, enter the path and the exact name of the program file, including the extension and options.
-
Click OK.
For example, if SAS
is installed in the default folder
c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4,
you enter “c:\program files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\sas.exe”,
and the options that you want to specify.
Note: For Windows, you must specify
a fully qualified path to sas.exe in the Start Menu Search entry
field.
Using the SAS Command from the Command Prompt
You can start either an interactive SAS session or a batch SAS job by entering
the
SAS command at the command prompt. For example, the following command starts an interactive session, specifies the
page size and line size, and indicates the location of the SAS configuration file:
"c:\program files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\sas.exe" -ls 80 -ps 60 -config "c:\program files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\sasv9.cfg"
This command starts
a batch SAS job in a similar manner:
"c:\program files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\sas.exe" -sysin c:\mysas\programs\prog1.sas -config "c:\program files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\sasv9.cfg"
Note: These examples are displayed
on multiple lines because of space limitations. When you enter a command
from the command prompt, the command must be on one line.
Starting from a SAS File
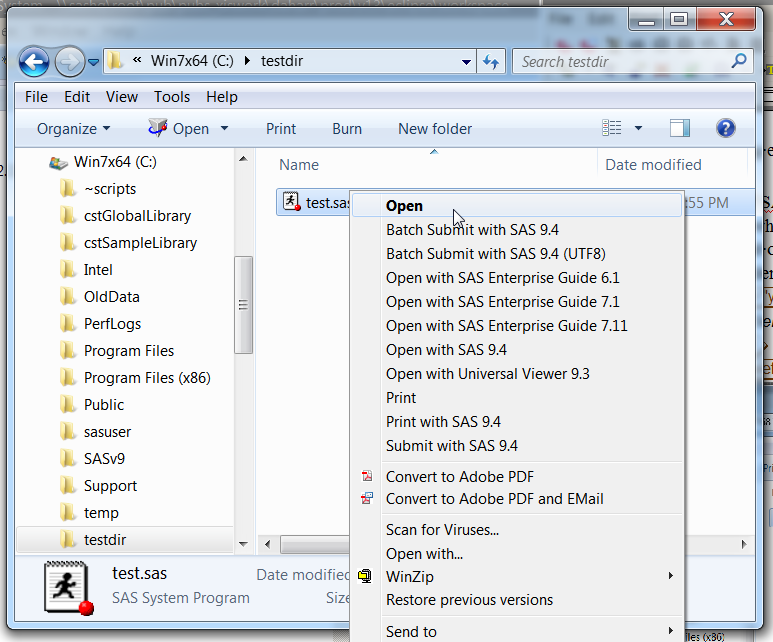
There are two ways to start SAS from a SAS program file
in Windows Explorer.
-
Double-click on a SAS program file
-
Right-click on a SAS program file and select the appropriate action.
Running SAS in Batch Mode
Overview of Running SAS in Batch Mode
You can run SAS jobs in batch mode in the Windows operating environment. Place your SAS statements in a file and submit
them for execution along with the control statements and system commands that are
required at your site.
Submitting a Batch SAS Job
Note: The maximum line length is
32767 bytes.
You can submit a batch
SAS job by using the following methods:
-
Specify the SYSIN system option in the SAS command (issued from the command prompt or in the Run dialog box) and specify the SAS program to submit. Here is an example:
”c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe” -sysin c:\SASPrograms\prog1.sas -config ”c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\sasv9.cfg”. -
Right-click to select a file that has either a .sas, .ss2, .ss7, or .sas7bpgm file extension. From the pop-up menu, select Batch Submit with SAS 9.4.
-
Select and drag your SAS program file icon (for the file that contains the SAS code) in Windows Explorer, and drop the file onto the SAS.EXE file icon or shortcut.Note: If you want to establish a permanent libref, specify the STARTLIB system option when you begin the batch job.Note: The -NOSTATUSWIN option enables you to run SAS in batch mode so that no windows are displayed. You can add options such as -NOTERMINAL, -NOSPLASH, -NOSTATUSWIN, and -NOICON to prevent the windows from being displayed.
The Status Window
When you use batch mode, SAS displays a status window for the SAS job that you submit.
This window tells
you the name of the SAS job that is running and where your log and procedure output
files are written. This window remains available until the SAS job is complete.
If you do not want to see the status window while your batch SAS job is running,
invoke SAS with the ICON system option; the status window becomes an icon when your
job is running. You can also minimize
the status window by clicking the Icon button when the window
appears. The icon shows the busy cursor (usually an hourglass) while
the SAS job is running. The icon disappears when the job is complete.
Canceling a Batch Job
You can cancel a batch job by using the keyboard or
the mouse:
-
press CTRL+BREAK.
-
click Cancel in the status window.
Running Windowing Procedures in a Batch Job
You can run windowing procedures in a batch job along
with SAS/GRAPH,
SAS/INSIGHT, and SAS/ACCESS software. When SAS reaches a point in your program
where interaction is required, the main SAS window appears.
The following examples
show how to execute SAS batch jobs under Windows 7.
Example 1: Creating a Batch File in Notepad or Another Text Editor
This example uses a
BAT file. A BAT file is executed by the operating system.
-
Create a file in Notepad or a similar text editor.
-
Enter a command similar to the following:
"C:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe"-SYSIN c:\job1.bat -NOSPLASH -ICON -PRINT c:\job1.lst –LOG c:\job1.log.Entering a Command in a BAT File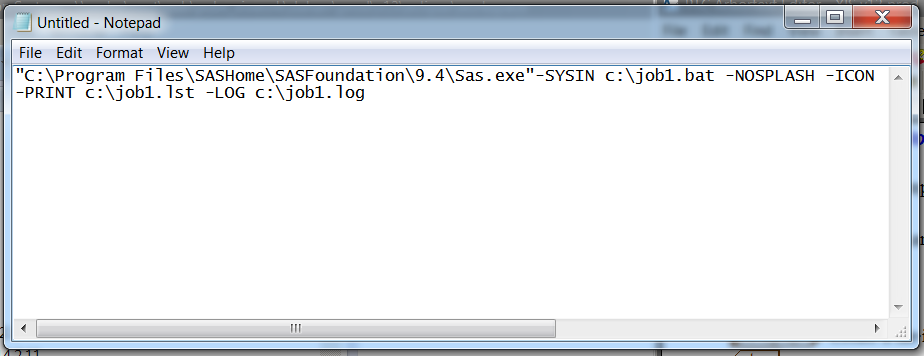
-
Select File
 Save As.
Saving a Batch File
Save As.
Saving a Batch File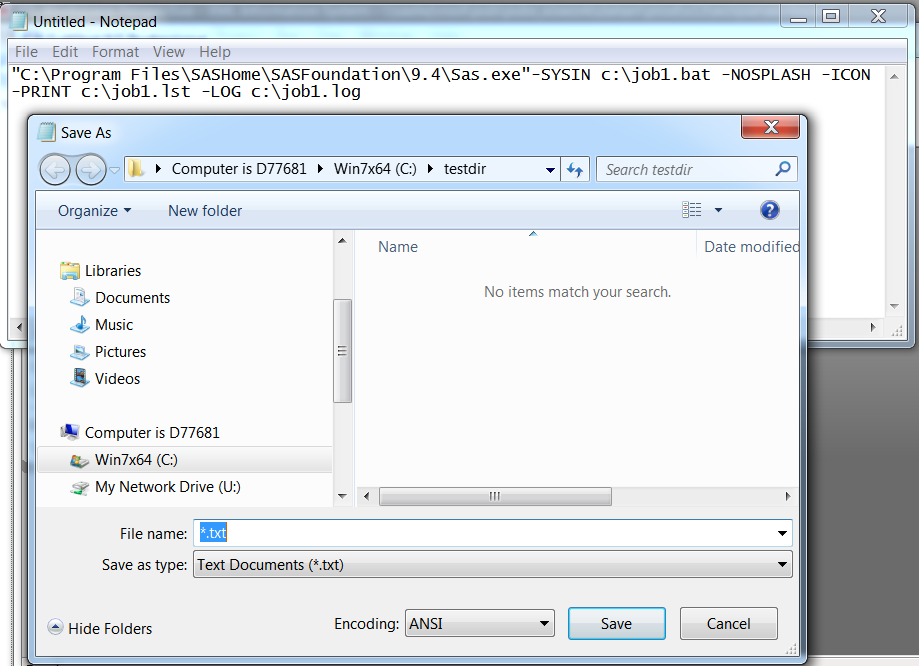
-
The default file extension is .txt. You must change the extension to .bat in order for other programs to access the file.Changing the File Extension to .bat
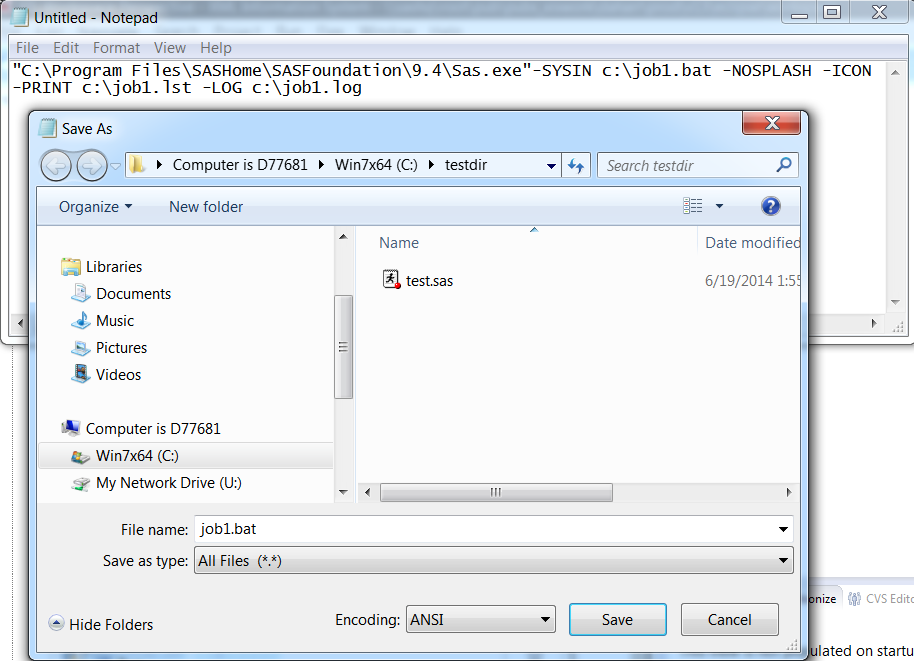
-
To execute the BAT file, select Start
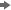 Run or double-click the BAT file.
The resulting LOG file and the LST files reside in the same folder where the BAT file resides. To change the destination of the LOG and LST files, use the -LOG and -PRINT options.Use the -PRINT option to change the destination folder for the output of the program. Use the -LOG option to change the destination folder for the log of the program. Here is an example:
Run or double-click the BAT file.
The resulting LOG file and the LST files reside in the same folder where the BAT file resides. To change the destination of the LOG and LST files, use the -LOG and -PRINT options.Use the -PRINT option to change the destination folder for the output of the program. Use the -LOG option to change the destination folder for the log of the program. Here is an example:"C:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe"-SYSIN c:\job1.bat -NOSPLASH -ICON -PRINT c:\job1.lst –LOG c:\job1.logNote: When you run a BAT program, a DOS window appears and remains available until the job is finished.Submitting a BAT Program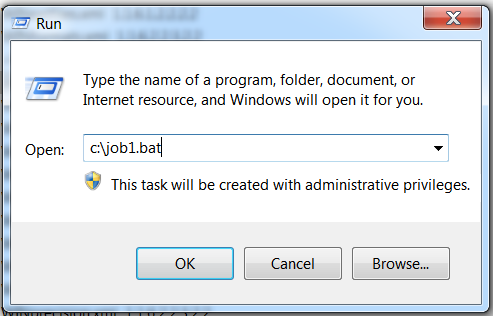
Example 2: Submitting Batch Files from Explorer
-
Open Explorer.
-
Right-click the program.
-
Select Batch Submit with SAS 9.4.Note: By default, the LOG and LST files are located in the same folder as the program.
Selecting the Batch Submit Option
The LOG file is the
log for the program.
The LST file is the
output file for the program. This file is created only if there is
output for the program.
Note: SAS must be properly installed
before you can use batch processing. For information about SAS installation,
see the chapter about SAS Deployment Manager tasks in SAS Deployment Wizard and SAS Deployment Manager 9.4: User’s
Guide.
You can also run SAS
files in batch when you double-click the files within Explorer. The
default action for SAS files must be set to
Batch Submit.
To change the default
action for SAS files:
-
Open Explorer.
-
Select a SAS file.
-
Right-click Open With and select Default program.
-
Select SAS System for Windows.
-
Double-click a SAS file to run the SAS program in batch mode. The LOG and LST files are created in the same folder as the SAS file.
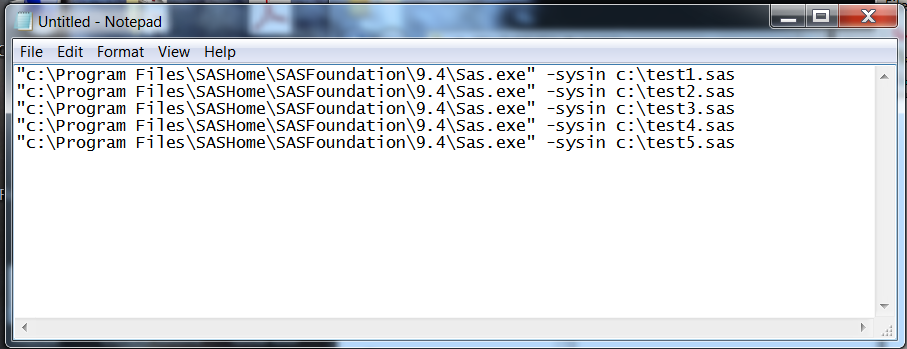
Example 3: Running Multiple Programs within the Batch File
The following example
runs five programs consecutively:
"c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test1.sas "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test2.sas "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test3.sas "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test4.sas "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test5.sas
Example 4: Using the SAS Executable Command with the -SYSIN Option
-
Select Start
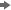 Run.
Run.
-
Enter a command similar to the following:
”c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe” -sysin “c:\test.sas” -LOG “c:\your_log_for_testsas.log” -NOSPLASH -NOLOGO -ICON. Specify the location of the program. This example runs the TEST.SAS program that is located in the root of the C drive. Use the –NOSPLASH option to eliminate the splash screen. Add the –ICON option to minimize the DOS window when the program is started. The resulting LOG and LST files reside in the SAS root directory.The –SYSIN option specifies the SAS program file that runs in batch. The path must be a valid Windows path.Note: Use the –LOG option with the –SYSIN option when scheduling a BAT file to prevent the scheduler from writing the LOG file to an unexpected location.Using the –LOG and –SYSIN Options
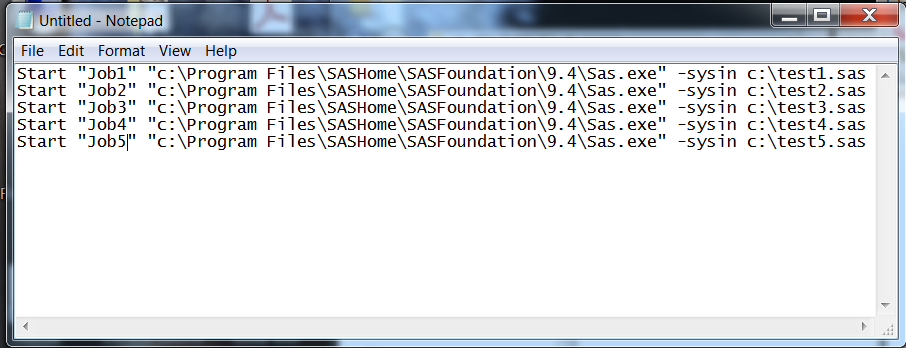
Example 5: Using the START Command to Run Concurrent Batch Jobs
The START command requires
a title. The title must be in double quotation marks.
This example uses Job# as the title.
Enter commands similar
to the following:
Start "Job1" "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test1.sas Start "Job2" "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test2.sas Start "Job3" "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test3.sas Start "Job4" "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test4.sas Start "Job5" "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test5.sas
Running Concurrent Batch Jobs Using the START Command
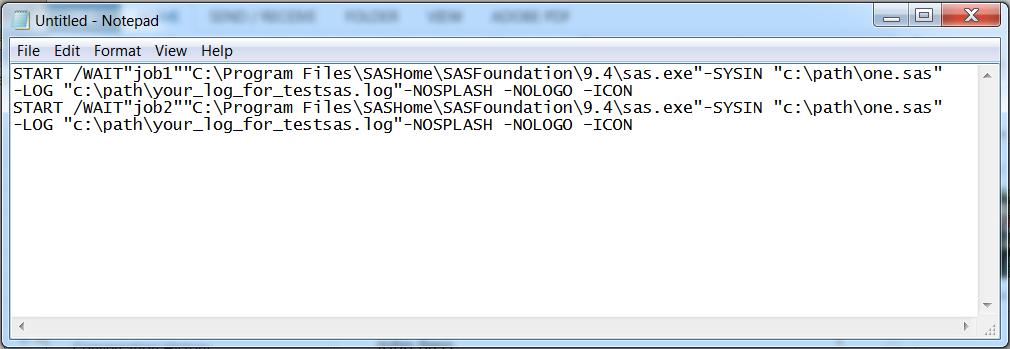
Example 6: Running Jobs Consecutively Using the START and WAIT Commands
When you use the START
and WAIT commands together, the order is as follows: the first job
runs. After the first job is complete, the second job runs. In this
example, Job1 runs first, and then Job2 runs after Job1 is complete.
Using the START and WAIT Commands
Example 7: Creating a Batch File That Runs Programs Consecutively
The log (LOG) and output (LST) files are located in the directory where the BAT
file is located unless you use the –PRINT and –LOG options on the command
line.
Enter the following
commands in the BAT file:
"c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test1.sas "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test2.sas "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test3.sas "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test4.sas "c:\Program Files\SASHome\SASFoundation\9.4\Sas.exe" —sysin c:\test5.sas
Running Concurrent Batch Jobs
Example 8: Using the Task Scheduler to Run SAS Jobs
When jobs are scheduled,
the programs can be executed without operator assistance. The Schedule
Tasks program is located in the Administrative
Tools section in the Control Panel under
Windows.
In this example, job1.bat
is the file that you schedule with Task Scheduler.
-
Click the Schedule Tasks icon to start the Task Scheduler Wizard.Batch Processing with the Task Scheduler
-
Select Create Basic Task or Create Task.
-
Enter the name of the task in the Name field. You can enter a description of the task in the Description field. Select Next.Creating a Basic Task for Batch Processing
-
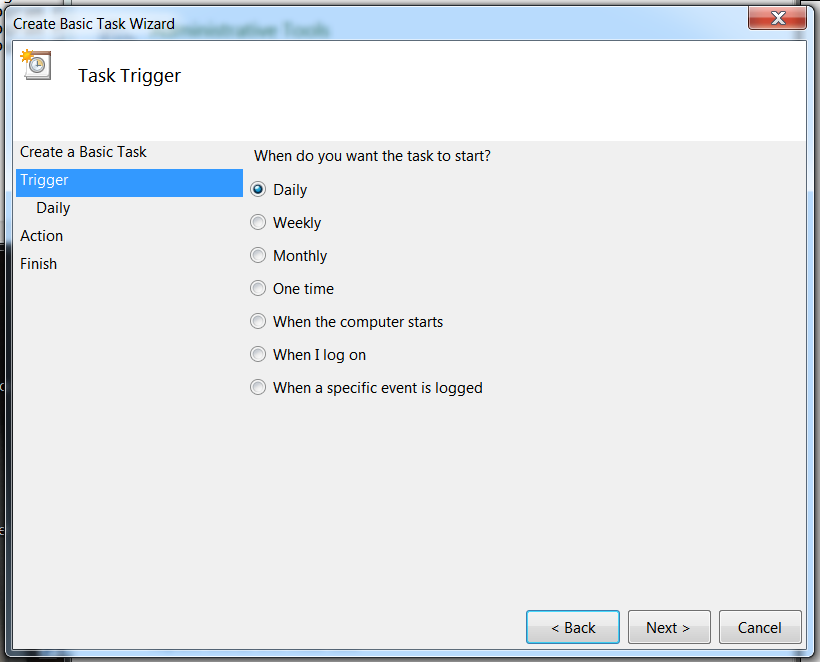
Select the time at which you want the task to start. Select Next.Task Trigger
-
Enter the user name and password that apply to this program. Select Next. A confirmation message is displayed.
-
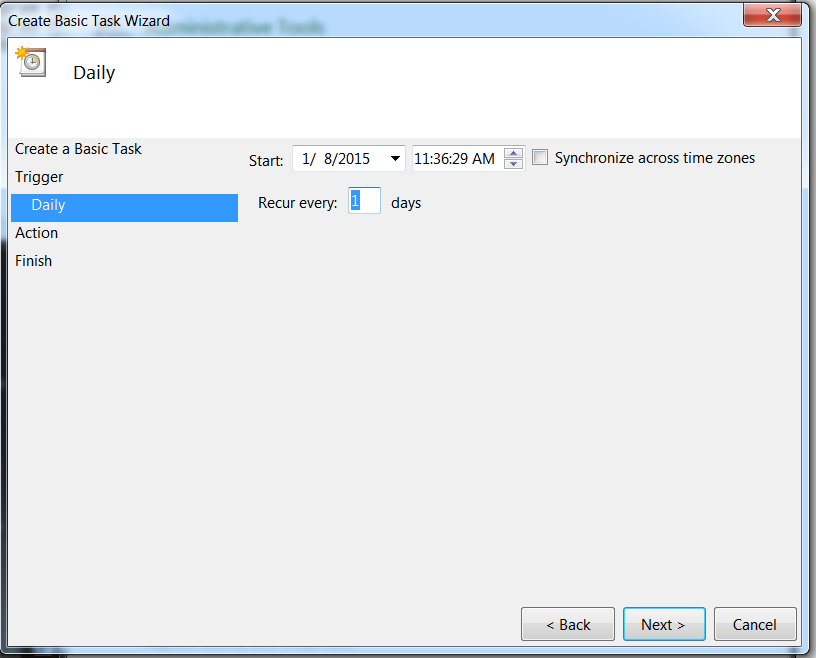
Specify the date and the time that you want the task to begin. Select Next.Processing a Daily Task
-
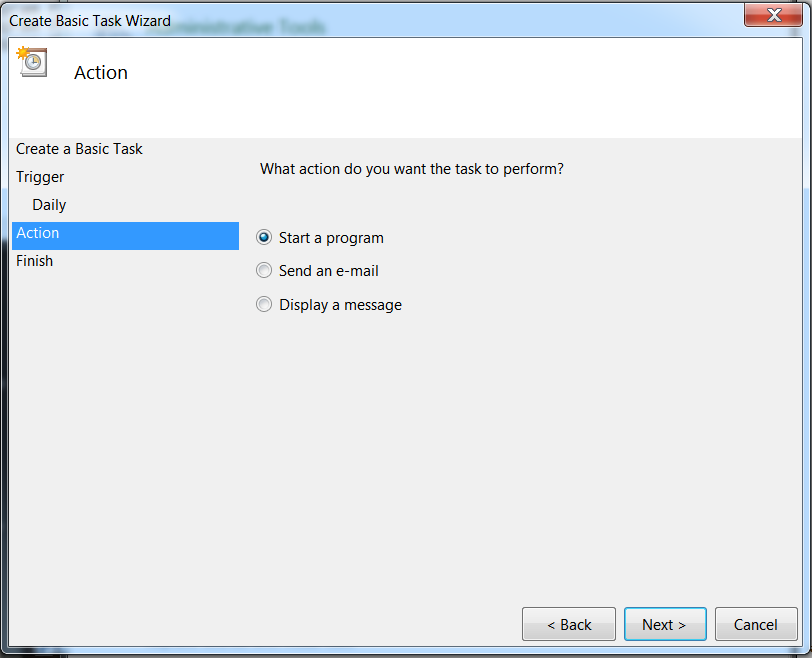
Select Start a program and select Next.Selecting Start a Program
-
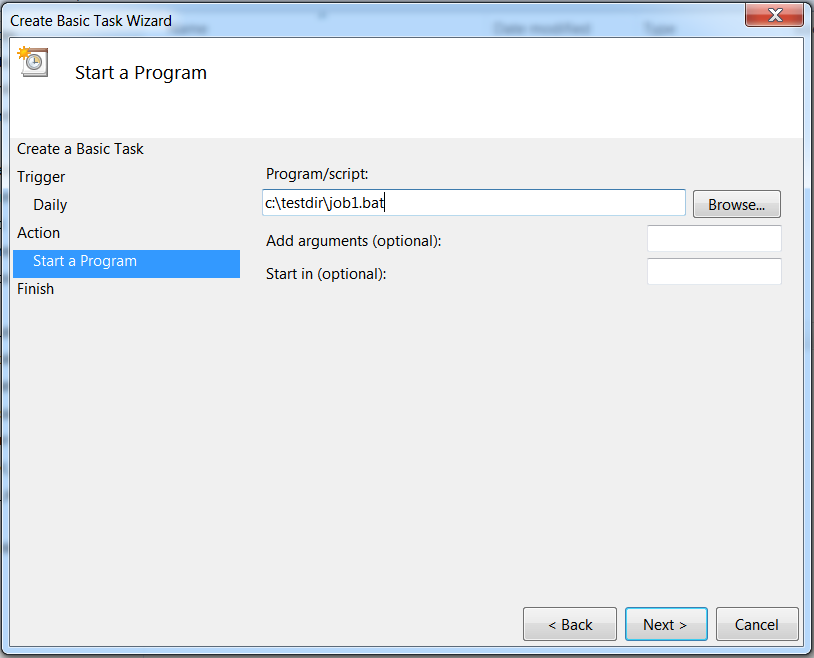
Click Browse and select the program. Select Next.Selecting Browse
-
Review your selections.Create Basic Task Summary
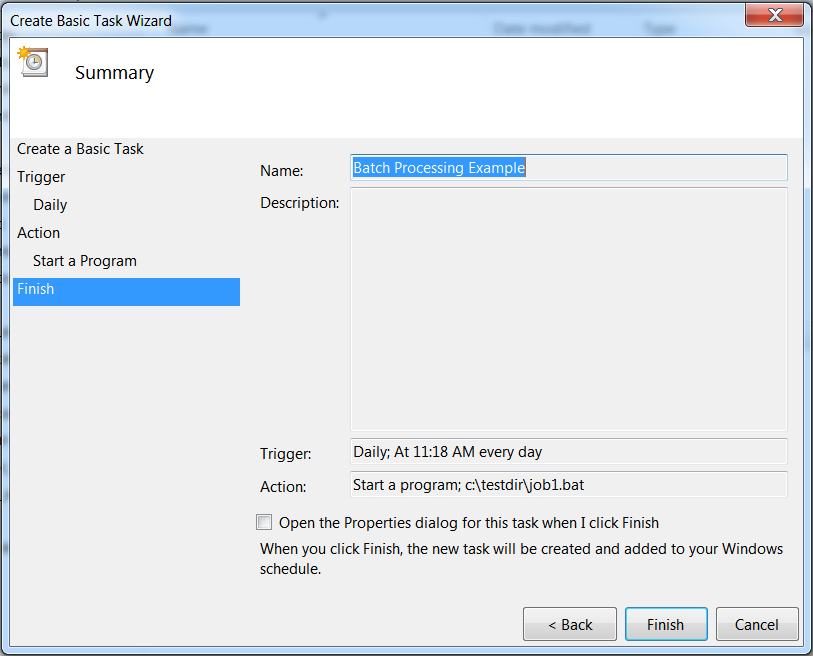
-
Select Finish.
Starting the Program Editor When SAS Starts
The Enhanced Editor is the default editor that starts when you start SAS. If you prefer to use the Program
Editor, use one of the following methods to start the Program Editor when SAS starts:
-
Start SAS with the NOENHANCEDEDITOR system option:
sas.exe -noenhancededitor
-
Disable the Enhanced Editor in the Edit tab of the Preferences dialog box.
For additional information,
see Switching from the Enhanced Editor to the Program Editor , Edit Preferences , and ENHANCEDEDITOR System Option: Windows .
Determining the Current Folder When SAS Starts
By default, SAS determines the current folder. SAS uses the current folder as the location to read and write SAS files when you
do not specify a different pathname.
SAS also searches the current folder, based on the following statements, for the
AUTOEXEC.SAS file or INITSTMT files. In this case, the path that the SASINITIALFOLDER system option
specifies is disregarded.
However, you can specify a pathname to use for the current folder by using the SASINITIALFOLDER
system option when you start SAS. Alternatively, you can use the following rules to
determine the
current folder:
-
If you use a program item or shortcut to start SAS and if a path is specified in the Windows Properties Shortcut tab (Start in field), SAS uses that path as the current folder.
-
If you use a command to start SAS by using either the Run dialog box or a command line and if the command contains a path to the SAS.EXE file, the current folder is the path that you specify as part of the SAS command, regardless of where Windows actually finds the SAS.EXE file.
-
If you use a command to start SAS and if you do not specify a path as part of the SAS command, then the current folder is specified by the path from which you issued the command.
If Windows cannot find the SAS.EXE file in the specified folder, the folder that is
specified in the SAS command still becomes the current folder and Windows searches
for the SAS.EXE file by using the Windows PATH environment variable.
For example, if you
specify the following command,
C:\MYSAS is the current folder, regardless of whether the SAS.EXE file is actually in that
folder: c:\mysas\sas.exe -config c:\mysas\sasv9.cfg
For
more information, see Changing the SAS Current Folder
and SASINITIALFOLDER System Option: Windows .
Note: Do
not confuse the current folder with the Work data library. For more
information about the Work data library, see Work Data Library .
Sample SAS Session
This section illustrates
-
invoking SAS from the Start menu
-
submitting a sample SAS program
-
examining the program output
-
ending the SAS session.
You can invoke SAS from
the Start menu by, selecting Programs SAS
SAS 9.4.
9.4.
The following display shows the Enhanced Editor and Log windows with a sample SAS
program that is ready to be submitted. This program
creates a SAS data set called Oranges, which contains the results of a taste test
on four varieties of oranges. The program sorts the data set by the total test score
and prints the data set.
Submitting the Sample SAS Program
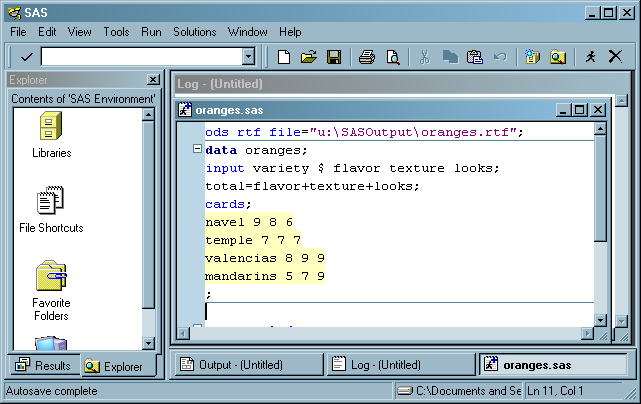
The following SAS code
appears in the Enhanced Editor window:
ods rtf file="c:\em\oranges.rtf"; data oranges; input variety $ flavor texture looks; total=flavor+texture+looks; datalines; navel 9 8 6 temple 7 7 7 valencia 8 9 9 mandarin 5 7 8 ; proc sort data=oranges; by descending total; run; proc print data=oranges; title 'Taste Test Results for Oranges'; run; ods rtf close;
After you submit the
program, the output appears in the Results Viewer window
as follows:
Looking at the Program Output
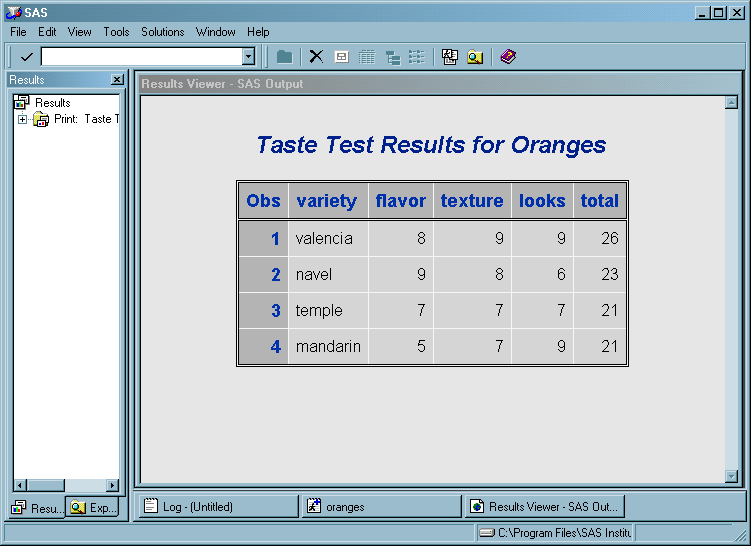
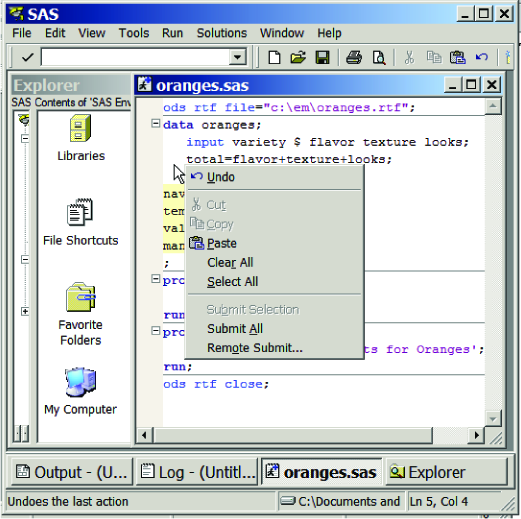
The items in the SAS
menu bar at the top of the main SAS window change, depending
on which window is active within the SAS session. In addition, you
can access window-specific pop-up menus, which offer the same menu
choices. The pop-up menu in the following display was generated by
right-clicking in an Enhanced Editor window.
Pop-up Menu in the Enhanced Editor Window
When you are ready to
end your SAS session, double-click the SAS control menu (the small
icon in the upper left corner of the main SAS window) or click the X (in
the upper right corner) and click OK when
the dialog box verifies your request.
Note: If you have disabled the Confirm
Exit of SAS option in the Preferences
dialog box, your SAS session ends without asking if you are sure you
want to end the session. For more information about how to customize
your SAS session, see Setting Session Preferences .
What If SAS Does Not Start?
If SAS does not start,
the SAS log can contain error messages that explain the error. Any
error message that SAS issues before the SAS log is initialized is
written to the MSG window, if it is available,
or to the SAS console log, which is a Windows file. Under Windows
the SAS console log is typically located in
c:\Users\user-ID\AppData. You can obtain the location and filename for the SAS console log from the application event log. To open the application event
log, submit eventvwr from
the Run dialog box and click Application.
If SAS does not start, if the screen appears and then disappears, or if SAS is very
slow to open, you might have a problem with a missing printer, a damaged printer driver,
or a failed network printer connection. Use the following steps to correct this problem:
-
Verify that the printers are linking to valid network servers. If the printers are linking to invalid servers, then delete the printers by accessing Start
 Settings
Settings Control Panel
Control Panel Printers.
Printers.
-
Download a new printer driver from the printer's website and replace the current driver with the new driver.
-
Rename profile2.SAS7bcat to profile2.old and rename profile.SAS7bcat to profile.old at
c:\Users\user-ID\Documents\My SAS Files\9.4\. -
Start SAS.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All Rights Reserved.