Example Program and Statement Details
Example Program
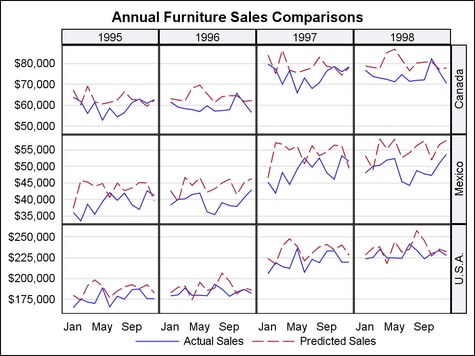
This example shows
the result of using row and column classification variables. In this
case, a four-column, three-row data lattice is created:
proc template;
define statgraph layoutdatalattice;
begingraph;
entrytitle "Annual Furniture Sales Comparisons";
layout datalattice rowvar=country columnvar=year /
rowdatarange=union
headerlabeldisplay=value
headerbackgroundcolor=GraphAltBlock:color
rowaxisopts=(display=(tickvalues) griddisplay=on
linearopts=(tickvalueformat=dollar12.))
columnaxisopts=(display=(tickvalues)
timeopts=(tickvalueformat=monname3.));
layout prototype / cycleattrs=true;
seriesplot x=month y=TotalActual / name="Actual";
seriesplot x=month y=TotalPredict / name="Predict";
endlayout;
sidebar / align=bottom;
discretelegend "Actual" "Predict" / border=false;
endsidebar;
endlayout;
endgraph;
end;
run;
proc summary data=sashelp.prdsal2 nway;
class country year month;
var actual predict;
output out=prdsal2 sum=TotalActual TotalPredict;
run;
proc sgrender data=prdsal2 template=layoutdatalattice;
run;
Statement Summary
The LAYOUT DATALATTICE
statement makes it easy to create a grid of graphs, based on the values
of one or two classifications variables. To create a grid that is
based on more than two classification variables, or to have more control
over the grid layout, use LAYOUT DATAPANEL instead.
By default, the number
of cells in the layout is determined by the number of value pairings
that are possible for the classification values plus any empty cells
needed to complete the last row or column of the grid. The contents
of each data cell are based on a graph prototype that you specify
in the graph-prototype-block.
You can enhance the display using one or more sidebar-statement-blocks.
For classification variables that have many values, you can use the COLUMNS= and or ROWS= options and the PANELNUMBER= option to generate multiple panel
displays.
Classification variables
for the layout are specified on the ROWVAR= argument (to specify a row variable), or the COLUMNVAR= argument (to specify a column variable),
or both arguments to specify both a column and a row variable. The
graph prototype for each data cell’s contents is specified
within a Prototype Block block, and
sidebars are specified within SIDEBAR blocks. The LAYOUT PROTOTYPE
and SIDEBAR blocks are nested within the LAYOUT DATALATTICE block.
By default, the first
data cell to be filled is in the layout’s top left corner.
Use the START= option to change the starting data
cell to the bottom left corner.
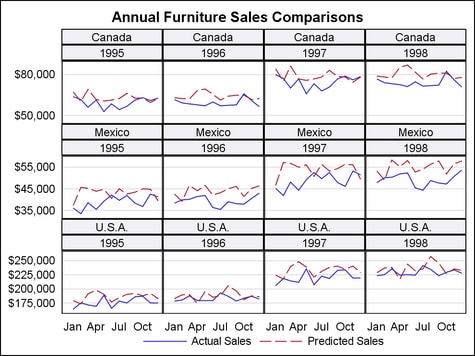
Rather than display
the header labels outside the grid, you can set HEADERLABELLOCATION= INSIDE to display them inside the
grid, as shown in the following figure:
Required Argument(s)
One of the ROWVAR= or
COLUMNVAR= arguments is required. Both can be specified. Each specifies
a single classification variable. Any one of the following uses is
valid:
LAYOUT DATALATTICE ROWVAR=class-var
LAYOUT
DATALATTICE COLUMNVAR=class-var
LAYOUT
DATALATTICE ROWVAR=class-var COLUMNVAR=class-var
If you do not explicitly
manage columns and rows using the COLUMNS= and ROWS= options, the default layout behavior
is as follows:
-
If both ROWVAR= and COLUMNVAR= are specified, a data cell is created for each of the value pairings that are possible for the classification values of the specified variables. If the ROWVAR variable has R distinct values and the COLUMNVAR variable has C distinct values, the dimension of grid produced is R x C.
If the class variable
is of type character, its values are returned in data order. To control
the ordering of the values, you can sort the input data by the classification
variables. If the class variable is of type numeric, the values are
displayed in ordinal order.
Formats can be assigned
to class variables to create classification levels (for example, an
AGEGROUPFMT. format for numeric AGE). In this case, the classification
is performed after the format is applied. For numeric data, the order
is ordinal, based on the first value in each class.
Use the INCLUDEMISSINGCLASS option to control whether cells are
displayed when any value crossing contains a missing value.
The output
size does not grow automatically as the number of cells increases.
To set a panel size for the current template, use the DESIGNHEIGHT=
and DESIGNWIDTH= options in the BEGINGRAPH statement. To set a panel
size for all templates in the current SAS session, use the HEIGHT=
and WIDTH= options in the ODS GRAPHICS statement. Size settings in
the ODS GRAPHICS statement override size settings in the BEGINGRAPH
statement. The default output width is 640px, and the default output
height is 480px.
As the number of cells
in the grid increases, the size of each cell decreases. At some point
the cells might become so small that a meaningful graph cannot be
rendered. The CELLHEIGHTMIN= and CELLWIDTHMIN= options set a threshold for the smallest
cell. If the actual cell height or width becomes smaller, no panel
is drawn. The default minimum cell size is CELLHEIGHTMIN=100px and
CELLWIDTHMIN=100px.
Using the default panel
size and cell size, the DATALATTICE layout accommodates a grid of
about 24 cells (6 columns by 4 rows). If you know that the number
of cells is larger, you should increase the overall panel size, or
decrease the minimum cell size, or both. You can also use ROWS=, COLUMNS=, and PANELNUMBER= options to partition your data so
that a number of smaller grids are produced that cumulatively show
all of the value crossings.
Prototype Block
You must specify a single graph-prototype-block within
the LAYOUT DATALATTICE block, using the following syntax:
Note: You can specify only one
LAYOUT PROTOTYPE block in the LAYOUT DATALATTICE block. If you specify
more than one, only the last prototype block specified is honored.
The remaining prototype blocks are ignored.
The graph-prototype-block determines
the graphical content of each data cell and is repeated within each
data cell based on the subsets of the classification variables.
For more information
about the LAYOUT PROTOTYPE block and the list of available options,
see LAYOUT PROTOTYPE Statement.
Sidebar Blocks
A LAYOUT DATALATTICE
enables you to display one or more sidebars outside
of the axes. A sidebar spans across columns or rows and is useful
for displaying information that applies to all of the columns or all
of the rows. For example, sidebars are useful for displaying a legend.
Options
specifies the color
of the layout background.
Interaction: OPAQUE=TRUE must be in effect in order for the color to be seen.
By default, OPAQUE=FALSE.
specifies the attributes
of the border line around the layout. See General Syntax for Attribute Options for the syntax
on using a style-element and Line Options for available line-options.
specifies the minimum
height of a cell in the grid.
Use this option in
conjunction with the CELLWIDTHMIN= option to set the minimum cell size.
The overall size of
the panel is constrained by the HEIGHT= and WIDTH= options in the
ODS GRAPHICS statement. As the number of cells in the grid increases,
the size of each cell decreases. At some point the cell becomes so
small that a meaningful graph cannot be rendered. This option sets
the minimum height threshold for all cells. If the actual cell height
becomes smaller, no panel is drawn.
specifies the minimum
width of a cell in the grid.
Use this option in
conjunction with the CELLHEIGHTMIN= option to set the minimum cell size.
The overall size of
the panel is constrained by the HEIGHT= and WIDTH= options in the
ODS GRAPHICS statement. As the number of cells in the grid increases,
the size of each cell decreases. At some point the cell becomes so
small that a meaningful graph cannot be rendered. This option sets
the minimum width threshold for all cells. If the actual cell width
becomes smaller, no panel is drawn.
specifies X-axis options
for all columns. For a list of options, see Axis Options for LAYOUT DATALATTICE/DATAPANEL.
specifies X2-axis options
for all columns. For a list of options, see Axis Options for LAYOUT DATALATTICE/DATAPANEL
Details: This option is needed only if you use a plot
statement that supports a secondary X2 axis. If you do not use that
statement’s XAXIS= option to map data to the X2 axis, this
option is ignored. For more information about how data are mapped
to the axes, see Plot Data Are Mapped to a Designated Axis
specifies how the X-axes
of instances of the graph-prototype are
scaled.
scales the X-axis data
ranges across all layout columns and panels (when PANELNUMBER= is in effect).
specifies how the X2-axes
of instances of the graph-prototype are
scaled.
scales the X2-axis
data ranges across all layout columns and panels (when PANELNUMBER= is in effect).
Details: This option is needed only if you use a plot
statement that supports a secondary X2 axis. If you do not use that
statement’s XAXIS= option to map data to the X2 axis, this
option is ignored. For more information about how data are mapped
to the axes, see Plot Data Are Mapped to a Designated Axis
specifies the number
of columns in the layout.
-
If this option is specified, that many columns are created. If the number of COLUMNVAR classifier values is greater than the specified number of columns, no graph is created for some classifier values. If the number of classifier values is smaller than the specified number of columns, extra empty columns are created.
Interaction: The
overall grid size is constrained by the HEIGHT= and WIDTH= options
in the ODS GRAPHICS statement. As the grid size grows, the cell size
shrinks. To control the minimum size of a cell use the CELLHEIGHTMIN= and CELLWIDTHMIN= options.
The START= option affects the how the columns are populated.
The PANELNUMBER= option enables you to create multiple
smaller grids that completely partition the classifier values.
specifies the color
and font attributes of the data labels. See General Syntax for Attribute Options for the syntax
on using a style-element and Text Options for available text-options.
specifies whether to
include grid cells for crossings of the ROWVAR and COLUMNVAR variables
that contain a missing value.
Default: TRUE.
Any crossing of the class variables that includes a missing value
produces a row or column of cells in the grid.
Tip: If
this option is set to FALSE, any crossing of the class variables that
contains a missing value does not produce a row or columns of cells
in the grid.
Discussion: By
default, missing class values are included in the classification levels
for the panel. When the data contains missing classification values,
cells are created in the panel for the missing classes. The classification
headers for the missing values are either blank for missing string
values or a dot for missing numeric values. You can use the INCLUDEMISSINGCLASS=FALSE
option to exclude the missing values. If you want to keep the missing
values, you can create a format that specifies more meaningful headings
for the missing classes. For example, here is a format that specifies
descriptive headers for missing product name and branch number classes.
proc format; value $prdfmt " "="Missing Product"; value branchfmt .="Missing Branch"; run;
specifies what information
is displayed in an inset. The variable-list defines
one or more variables whose names and values appear as a small table
in the data cells. The variables can be either numeric or character.
Variable names are separated by spaces.
Restriction: No
predefined information is available for the inset. You must create
the desired inset information as part of your input data. This is
most typically done as follows (see the chapter on classification
panels and the chapter on insets in SAS Graph Template Language: User's Guide for complete
examples):
-
Create a separate data set for the inset columns making sure that the column names are different from the other columns used in graph. The number observations of inset data should match the number of cells in the classification panel. The ordering of the inset observations should be the same as the population order of the classification panel’s cells, taking into account the ROWVAR= and COLUMNVAR= arguments and the START= option. Typically, the number of observations for the inset data is smaller than the other input data for the graph.
The variable values
are associated with the data cells by data order. That is, the first
observation from all the variables in variable-list are
used in the first data cell, the second observation from all variables
in variable-list are used in
the second data cell, and so on. If a value is missing for an observation,
the corresponding name-value pair
is skipped in the affected data cell.
The location and appearance
of the inset is controlled by the INSETOPTS= option.
specifies location
and appearance options for the inset information.
The appearance-options can
be any one or more of the settings that follow. The options must be
enclosed in parentheses, and each option is specified as a name
= value pair.
specifies whether the
inset is automatically aligned within the layout.
| NONE | Do not automatically align this inset. This inset’s position is set by the HALIGN= and VALIGN= appearance-options. |
| AUTO | Attempt to center this inset in the area that is farthest from any surrounding markers. Data cells might have different inset placements. |
| (location-list) | Restrict this inset’s possible locations to those locations in the specified location-list, and use the location-list position that least collides with the data cell’s other graphics features. The location-list is blank-separated and can contain any of these locations: TOPLEFT TOP TOPRIGHT LEFT CENTER RIGHT BOTTOMLEFT BOTTOM BOTTOMRIGHT. Example: AUTOALIGN = (TOPRIGHT TOPLEFT) |
specifies the text
properties of the entire inset, excluding the title. See General Syntax for Attribute Options for the syntax
on using a style-element and Text Options for available text-options.
specifies the text
properties of the inset’s title string. See General Syntax for Attribute Options for the syntax
on using a style-element and Text Options for available text-options.
specifies the amount
of extra space that is added inside the layout border.
Default: The
default padding for all sides is 0. Values without units are in pixels
(px). A unit must be provided if other than pixels.
enables separate settings
for the left, right, top, and bottom padding dimensions. Use the pad-options to
create non-uniform padding. These options must be enclosed in parentheses.
Each option is specified as a name = value pair.
Sides not assigned padding are padded with the default amount.
| LEFT=dimension | specifies the amount of extra space added to the left side. |
| RIGHT=dimension | specifies the amount of extra space added to the right side. |
| TOP=dimension | specifies the amount of extra space added to the top. |
| BOTTOM=dimension | specifies the amount of extra space added to the bottom. |
specifies the number
of the panel to produce.
This option enables
you to partition a large grid into a number of smaller grids under
these conditions:
Example: Suppose
ROWVAR=R (R has 10 unique values) and COLUMNVAR=C (C has 11 unique
values). The dynamic grid has 10 rows and 11 columns and you would
have to make the HEIGHT=and WIDTH= quite large to enable 110 plots
to be displayed. By setting some smaller grid size, say ROWS=3 and
COLUMNS=4, and by making the value of PANELNUMBER= a dynamic or macro
variable, you can create 10 panels (9 with 12 data cells and 1 with
2 data cells) that collectively display all 110 possible crossings.
You simply invoke PROC SGRENDER or a DATA step 10 times, incrementing
the dynamic value for PANELNUMBER each time.
specifies Y-axis options
for all rows. For a list of options, see Axis Options for LAYOUT DATALATTICE/DATAPANEL.
specifies Y2-axis options
for all rows. For a list of options, see Axis Options for LAYOUT DATALATTICE/DATAPANEL.
Details: This option is needed only if you use a plot
statement that supports a secondary Y2 axis. If you do not use that
statement’s YAXIS= option to map data to the Y2 axis, this
option is ignored. For more information about how data are mapped
to the axes, see Plot Data Are Mapped to a Designated Axis
specifies how the Y-axes
of instances of the graph-prototype are
scaled.
scales the Y-axis data
ranges across all layout rows and panels (when PANELNUMBER= is in effect).
specifies how the Y2-axes
of instances of the graph-prototype are
scaled.
scales the Y2-axis
data ranges across all layout rows and panels (when PANELNUMBER= is in effect).
Details: This option is needed only if you use a plot
statement that supports a secondary Y2 axis. If you do not use that
statement’s YAXIS= option to map data to the Y2 axis, this
option is ignored. For more information about how data are mapped
to the axes, see Plot Data Are Mapped to a Designated Axis
specifies where to
position the outside row header.
HEADERLABELLOCATION=OUTSIDE must be set for this option
to have any effect.
specifies the number
of rows in the layout.
-
If this option is specified, the specified number of rows is created. If the number of ROWVAR classifier values is greater than the specified number of rows, no graph is created for some classifier values. If the number of classifier values is smaller than the specified number of rows, extra empty rows are created.
Interaction: The
overall grid size is constrained by the HEIGHT= and WIDTH= options
in the ODS GRAPHICS statement. As the grid size grows, the cell size
shrinks. To control the minimum size of a cell use the CELLHEIGHTMIN= and CELLWIDTHMIN= options.
The START= option affects how the rows are populated.
The PANELNUMBER= option enables you to create multiple
smaller grids that completely partition the classifier values.
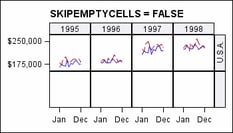
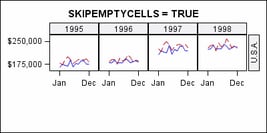
specifies whether the
external axes skip the empty cells in a partially filled grid.
Discussion: Whenever
the number of unique COLUMNVAR= classifier values (data cells) is
not evenly divisible by the COLUMNS= value, or the number of unique
ROWVAR= classifier values (data cells) is not evenly divisible by
the ROWS= value, then one or more panels is partially filled with
data cells and padded with empty cells to complete the grid.
In this example, there
are 4 column-data cells and 3 row-data cells arranged in a 4-column,
2-row grid. This is default appearance of the last panel: