| Summary of Interval Types |
The interval types are summarized as follows:
- YEAR
specifies yearly intervals. Abbreviations are YEAR, YEARS, YEARLY, YR, ANNUAL, ANNUALLY, and ANNUALS. The starting subperiod s is in months (MONTH).
- YEARV
specifies ISO 8601 yearly intervals. The ISO 8601 year starts on the Monday on or immediately preceding January
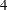 th. Note that it is possible for the ISO 8601 year to start in December of the preceding year. Also, some ISO 8601 years contain a leap week. For further discussion of ISO weeks, see Technical Committee ISO/TC 154, Documents in Commerce, and Administration (2004). The starting subperiod s is in ISO 8601 weeks (WEEKV).
th. Note that it is possible for the ISO 8601 year to start in December of the preceding year. Also, some ISO 8601 years contain a leap week. For further discussion of ISO weeks, see Technical Committee ISO/TC 154, Documents in Commerce, and Administration (2004). The starting subperiod s is in ISO 8601 weeks (WEEKV). - R445YR
is the same as YEARV except that the starting subperiod s is in retail 4-4-5 months (R445MON).
- R454YR
is the same as YEARV except that the starting subperiod s is in retail 4-5-4 months (R454MON). For a discussion of the retail 4-5-4 calendar, see National Retail Federation (2007).
- R544YR
is the same as YEARV except that the starting subperiod s is in retail 5-4-4 months (R544MON).
- SEMIYEAR
-
specifies semiannual intervals (every six months). Abbreviations are SEMIYEAR, SEMIYEARS, SEMIYEARLY, SEMIYR, SEMIANNUAL, and SEMIANN.
The starting subperiod s is in months (MONTH). For example, SEMIYEAR.3 intervals are March–August and September–February.
- QTR
specifies quarterly intervals (every three months). Abbreviations are QTR, QUARTER, QUARTERS, QUARTERLY, QTRLY, and QTRS. The starting subperiod s is in months (MONTH).
- R445QTR
specifies retail 4-4-5 quarterly intervals (every 13 ISO 8601 weeks). Some fourth quarters contain a leap week. The starting subperiod s is in retail 4-4-5 months (R445MON).
- R454QTR
specifies retail 4-5-4 quarterly intervals (every 13 ISO 8601 weeks). Some fourth quarters contain a leap week. For a discussion of the retail 4-5-4 calendar, see National Retail Federation (2007). The starting subperiod s is in retail 4-5-4 months (R454MON).
- R544QTR
specifies retail 5-4-4 quarterly intervals (every 13 ISO 8601 weeks). Some fourth quarters contain a leap week. The starting subperiod s is in retail 5-4-4 months (R544MON).
- MONTH
specifies monthly intervals. Abbreviations are MONTH, MONTHS, MONTHLY, and MON. The starting subperiod s is in months (MONTH). For example, MONTH2.2 intervals are February–March, April–May, June–July, August–September, October–November, and December–January of the following year.
- R445MON
specifies retail 4-4-5 monthly intervals. The
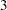 rd,
rd, 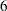 th,
th, 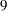 th, and
th, and 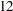 th months are five ISO 8601 weeks long with the exception that some
th months are five ISO 8601 weeks long with the exception that some 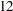 th months contain leap weeks. All other months are four ISO 8601 weeks long. R445MON intervals begin with the
th months contain leap weeks. All other months are four ISO 8601 weeks long. R445MON intervals begin with the  st,
st, 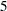 th,
th, 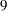 th,
th, 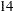 th,
th, 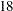 th,
th, 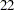 nd,
nd, 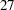 th,
th,  st,
st, 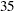 th,
th, 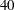 th,
th, 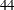 th, and
th, and 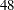 th weeks of the ISO year. The starting subperiod s is in retail 4-4-5 months (R445MON).
th weeks of the ISO year. The starting subperiod s is in retail 4-4-5 months (R445MON). - R454MON
specifies retail 4-5-4 monthly intervals. The
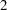 nd,
nd, 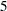 th,
th, 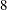 th, and
th, and 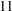 th months are five ISO 8601 weeks long. All other months are four ISO 8601 weeks long with the exception that some
th months are five ISO 8601 weeks long. All other months are four ISO 8601 weeks long with the exception that some 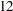 th months contain leap weeks. R454MON intervals begin with the
th months contain leap weeks. R454MON intervals begin with the  st,
st, 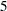 th,
th, 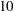 th,
th, 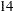 th,
th, 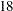 th,
th, 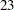 rd,
rd, 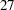 th,
th,  st,
st, 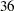 th,
th, 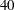 th,
th, 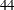 th, and
th, and 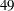 th weeks of the ISO year. For a discussion of the retail 4-5-4 calendar, see National Retail Federation (2007). The starting subperiod s is in retail 4-5-4 months (R454MON).
th weeks of the ISO year. For a discussion of the retail 4-5-4 calendar, see National Retail Federation (2007). The starting subperiod s is in retail 4-5-4 months (R454MON). - R544MON
specifies retail 5-4-4 monthly intervals. The
 st,
st, 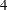 th,
th, 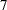 th, and
th, and 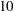 th months are five ISO 8601 weeks long. All other months are four ISO 8601 weeks long with the exception that some
th months are five ISO 8601 weeks long. All other months are four ISO 8601 weeks long with the exception that some 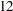 th months contain leap weeks. R544MON intervals begin with the
th months contain leap weeks. R544MON intervals begin with the  st,
st, 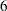 th,
th, 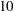 th,
th, 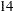 th,
th, 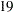 th,
th, 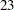 rd,
rd, 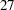 th,
th, 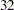 nd,
nd, 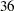 th,
th, 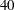 th,
th, 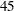 th, and
th, and 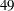 th weeks of the ISO year. The starting subperiod s is in retail 5-4-4 months (R544MON).
th weeks of the ISO year. The starting subperiod s is in retail 5-4-4 months (R544MON). - SEMIMONTH
specifies semimonthly intervals. SEMIMONTH breaks each month into two periods, starting on the
 st and
st and 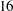 th days. Abbreviations are SEMIMONTH, SEMIMONTHS, SEMIMONTHLY, and SEMIMON. The starting subperiod s is in SEMIMONTH periods. For example, SEMIMONTH2.2 specifies intervals from the
th days. Abbreviations are SEMIMONTH, SEMIMONTHS, SEMIMONTHLY, and SEMIMON. The starting subperiod s is in SEMIMONTH periods. For example, SEMIMONTH2.2 specifies intervals from the 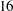 th of one month through the
th of one month through the 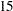 th of the next month.
th of the next month. - TENDAY
specifies 10-day intervals. TENDAY breaks the month into three periods, the
 st through the
st through the 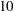 th day of the month, the
th day of the month, the 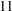 th through the
th through the 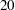 th day of the month, and the remainder of the month. (TENDAY is a special interval typically used for reporting automobile sales data.) The starting subperiod s is in TENDAY periods. For example, TENDAY4.2 defines 40-day periods that start at the second TENDAY period.
th day of the month, and the remainder of the month. (TENDAY is a special interval typically used for reporting automobile sales data.) The starting subperiod s is in TENDAY periods. For example, TENDAY4.2 defines 40-day periods that start at the second TENDAY period. - WEEK
-
specifies weekly intervals of seven days. Abbreviations are WEEK, WEEKS, and WEEKLY. The starting subperiod s is in days (DAY), with the days of the week numbered as 1=Sunday, 2=Monday, 3=Tuesday, 4=Wednesday, 5=Thursday, 6=Friday, and 7=Saturday. For example, WEEK.7 means weekly with Saturday as the first day of the week.
- WEEKV
specifies ISO 8601 weekly intervals of seven days. Each week starts on Monday. The starting subperiod s is in days (DAY). Note that WEEKV differs from WEEK in that WEEKV.1 starts on Monday, WEEKV.2 starts on Tuesday, and so forth.
- WEEKDAY
- WEEKDAYdW
- WEEKDAYddW
- WEEKDAYdddW
-
specifies daily intervals with weekend days included in the preceding weekday. Note that for a five-day work week that starts on Monday, the appropriate interval is WEEKDAY5.2. Abbreviations are WEEKDAY and WEEKDAYS. The starting subperiod s is in weekdays (WEEKDAY).
The WEEKDAY interval is the same as DAY except that weekend days are absorbed into the preceding weekday. Thus, there are five WEEKDAY intervals in a calendar week: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, and the three-day period Friday-Saturday-Sunday.
The default weekend days are Saturday and Sunday, but any one to six weekend days can be listed after the WEEKDAY string and followed by a W. Weekend days are specified as '1' for Sunday, '2' for Monday, and so forth. For example, WEEKDAY67W specifies a Friday-Saturday weekend. WEEKDAY1W specifies a six-day work week with a Sunday weekend. WEEKDAY17W is the same as WEEKDAY.
- DAY
specifies daily intervals. Abbreviations are DAY, DAYS, and DAILY. The starting subperiod s is in days (DAY).
- HOUR
specifies hourly intervals. Aliases are HOUR, DTHOUR, HOURS, DTHOURS, HOURLY, DTHOURLY, HR, and DTHR. The starting subperiod s is in hours (HOUR).
- MINUTE
specifies minute intervals. Aliases are MINUTE, DTMINUTE, MINUTES, DTMINUTES, MIN, and DTMIN. The starting subperiod s is in minutes (MINUTE).
- SECOND
specifies second intervals. Aliases are SECOND, DTSECOND, SECONDS, DTSECONDS, SEC and DTSEC. The starting subperiod s is in seconds (SECOND).