Transform Data
Introduction
Use
the Transform Data directive to filter data, manage columns, and summarize
data in one or more Hadoop source tables.
Enable the Spark Runtime Target
Support for the Apache
Spark runtime target is enabled in the Hadoop Configuration panel
of the Configuration window. When Spark is
enabled, new instances of the following directives use Spark by default:
The default runtime target can be overridden using
the Settings menu. To learn more about runtime
targets, see Enable Support for Impala and Spark.
-
Transform Data
-
Cleanse Data
-
Cluster-Survive Data
Note: Changing the default runtime
target does not change the runtime target for saved directives. Saved
directives continue to run with their existing runtime target unless
they are opened, reconfigured, and saved.
Note: Enabling Spark changes the
truncation of character columns, as described in the Usage Notes for Spark.
Example
The following example
depicts the process of creating and running a directive that contains
several transformations. The example opens a source table of customer
information, selects columns for the target, and applies two filters.
-
On the SAS Data Loader directives page, click Transform Data. The Source Table task is displayed. For more information about data sources and tables, see Viewing Data Sources and Tables.
-
In the Source Table task, click the schema that contains the source table that you will transform. When the tables appear, select the source table and click Next.
-
In the Transformation task, click a transformation:Your job can consist of one or more transformations. Multiple transformations are executed in the order in which you define them. A logical order for all three transformations is filter data, manage columns, and summarize rows.
-
Click Filter Data to exclude unwanted rows from the target table using rules or a user-written expression.
-
Click Manage Columns to reorder, rename, or remove columns from the target table. You can also apply user-written expressions to modify column data or add new data to new columns. The Advanced Editor is provided to display available functions, provide syntax help, and load function syntax into your expression.
-
Click Summarize Rows to group rows based on the values in one or more columns. For each group, you can generate summary aggregations from selected numeric columns.
-
-
Click Filter Data.
-
In the Filter Data transformation, click Specify rules or Specify expression.
-
To specify rules, follow these steps.
-
Select the first column, operator, and value. Note that the available operators change based on the type of the column. To learn about the available operators, see About the Operators in the Filter Data Transformation.
-
Choose a logical operator (AND or OR)
-
Select the second column, logical operator, and value.
-
To add another rule, click Add Rule.
-
-
To filter rows with a user-written expression, follow these steps:
-
To paste in an existing expression, click the expression text box and press Ctrl+V or your equivalent.Your expression can use either SAS DS2 functions (with the MapReduce runtime target,) or DataFlux Expression Engine Language functions (with the Spark runtime target.) Click Settings to display the selected runtime target. To learn more about runtime targets, see Enable Support for Impala and Spark.To learn about the requirements for expressions, see Develop Expressions for Directives.
-
To write an expression, expand the Functions and categories in the Resources box.
-
Select a function for your expression and click
 . Refer to the syntax help at the bottom of the Resources box
as needed.
. Refer to the syntax help at the bottom of the Resources box
as needed.
-
In the expression text box, replace the placeholders in the default function syntax with column names and values. To insert column names, expand Columns in the Resources box.
-
-
After you define rules or an expression, click Next to end the directive, select a target table, and run the directive. To add a Manage Columns or Summarize Rows transformation, click Add Another Transformation.
-
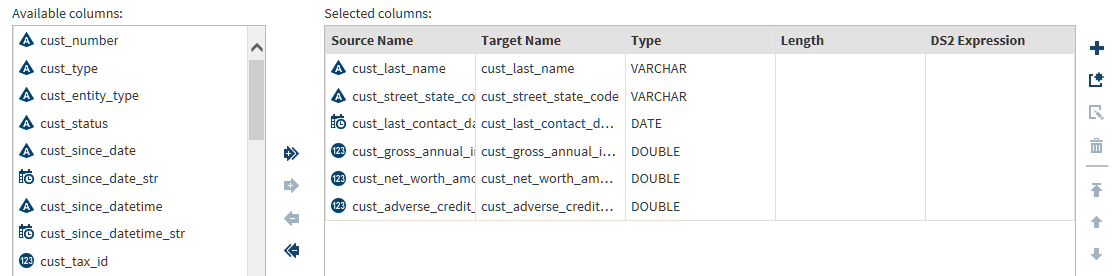
In the Transformation task, click Manage Columns.

-
In the Manage Columns transformation, you can reorder, rename, change type, change length, and remove source columns from the target. You can also apply user-written expressions to modify column data or to generate new data for new columns.
-
To reorder columns, use the vertical arrow icons. The first row in Selected columns is the target column in the first position (fully left.)
-
To change the target column name, type, or length, click Target Name, Type, or Length.
-
To remove a source column from the target, click the row in Selected columns and then click
-
To replace existing column data with data that is generated by a user-written expression, click a Selected column and click Expression. At this point, you can enter or paste an existing expression in the corresponding text field.Your expression can use either SAS DS2 functions (with the MapReduce runtime target,) or DataFlux EEL functions (with the Spark runtime target.) Click Settings to display the selected runtime target. To learn more about runtime targets, see Enable Support for Impala and Spark.To learn about the requirements for expressions, see Develop Expressions for Directives.
-
To add a new target column, and to use the Advanced Editor to write an expression for that column, click
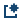 .
.
-
To use the Advanced Editor, select functions and column names from the Resources box. When your expression is complete, select Save or Save New to return to the Manage Columns transformation. The new column appears at the bottom of Selected Columns.
-
Click Add a new transformation, and then, in the Transformation task, click Summarize.
-
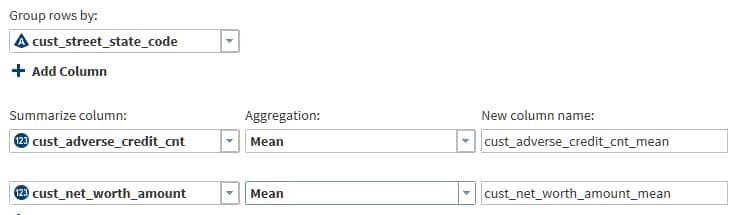
In the Summarize Rows task, click Group rows by to specify a column whose values will be used to group rows. You can specify additional columns that will form subgroups. Each group and subgroup will receive a value in each aggregation column.Note: If your source data is in Hive 13 (0.13.0 or lower), then the Summarize Rows task will not handle special characters in column names. To resolve the issue, either rename the columns or ask your Hadoop administrator to upgrade to Hive 14 (0.14.0 or higher.)
-
Click Select a column to specify a summarization, and then click and select an aggregation. To learn about the available aggregations, see About the Aggregations in the Summarize Rows Transformation.
-
Click New column name and enter or paste replacement names for the aggregation columns.
-
When your summaries are complete, click Next to conclude your job.
-
In the Target Table task, select the schema that contains or will contain your target table.
-
Click
 to create a new table, or click an existing table
that will be overwritten by your job.
TipIf you select a table and the View Profile icon is enabled, you can click that icon to display a profile report for that table.
to create a new table, or click an existing table
that will be overwritten by your job.
TipIf you select a table and the View Profile icon is enabled, you can click that icon to display a profile report for that table. -
Click Next to display the Result task. In the Result task, click Save or Save As to save your directive. If you want to run your job now, click Start transforming data. Otherwise, you can run your job later from Saved Directives.
About the Operators in the Filter Data Transformation
The following table
describes filter operators by the data type of the selected column.
|
Operator
|
Source ColumnData
Types
|
Description and Example
|
|---|---|---|
|
Equal To
|
The Equal To operator
is available for use with all source data types, which include the
following:
Character
Numeric
Datetime
|
The source value is
accepted and its row is written to the target table only when the
source value exactly matches the comparator.
Character values can
be case-sensitive. Blank spaces are included in the comparison.
Datetime values in the
comparator use the SAS format DATETIME(w.p).
Gender Equal
To MalePrefCustomer
Equal To 1SaleDate
Equal To 5/1/2014 |
|
Not Equal To
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value is anything other than the comparator.
Region Not
Equal To EuropeNumChildren
Not Equal To 0SaleDate
Not Equal To 11/25/2013 |
|
Null
|
|
When the runtime target
is MapReduce, the Null operator accepts the source row when the column
value is NULL or if no source value is present. When the runtime
target is Spark, the Null operator accepts only column values of NULL.
CreditScore
NullAnnualIncome
Null |
|
Not Null
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value is present and when the value is not NULL.
PostalCode
Not NullPhoneNumber
Not Null |
|
In
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value is included in its entirety within the comparator.
The comparator consists of a list of constant values. The list consists
of a vertical list of individual entries, without commas. Blank spaces
are interpreted literally. Case sensitivity can be enabled.
CarManuf
In BMW VWBenzWaistSize
In32343638 |
|
Not In
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value is not included anywhere within the comparator’s
list of constant values.
City Not
In New York Chicago Los
AngelesWaistSize
Not In 32 343638 |
|
Like
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value matches the result of an expression in the comparator.
The source value and the comparator are compared on a character-by-character
basis. Case-sensitivity can be enabled.
Use the pattern-matching
character
% to indicate any string of characters.
Use the underscore character _ to indicate
any single character in that position.
Note that trailing blank
characters are written to the target table when using
% at
the end of the comparator.
Use the word
escape to
include literal instances of % and _ in
the comparator.
SalesRegion
Like NorthAmer%AnnualSales
Like 199_CustSatisfaction
Like 100 escape % |
|
Not Like
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value does not match the result of an expression in
the comparator. The source value and the comparator are compared on
a character-by-character basis. Case-sensitivity can be enabled.
Pattern-matching characters
% and _ and escape are
valid as described for the Like operator.
Sports Not
Like %ballFootballFieldLength
Not Like 100% |
|
Contains
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value is found within the character string of the
comparator. Case-sensitivity can be enabled.
Address
Contains ILLicenseNumber
Contains 7227 |
|
Not Contains
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value is not found within the character string of
the comparator, or is null. Case-sensitivity can be enabled.
Month Not
Contains OctNovDecSalesMonthly
Not Contains 0 |
|
Between
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value or date is between the two values or dates in
the comparator, but is not equal to either.
GradeAverage
Between 87.5 93DailySales
Between December 20, 2014 December 27, 2014 |
|
Greater Than
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value is greater than the value of the comparator.
AnnualSales
GreaterThan 100000 |
|
Greater Than Or Equal
To
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value is equal to the comparator or greater than the
comparator.
CarsInFamily
Greater Than or Equal To 3 |
|
Less Than
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value is less than the value of the comparator.
GamerAge
Less Than 30 |
|
Less Than Or Equal To
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column value is equal to the value of the comparator, or
less than the value of the comparator.
SalesYear
Less Than Or Equal To 2010 |
|
After
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column date is later than the date in the comparator.
HomePurchaseDate
After January 1, 2013 |
|
Before
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column date is earlier than the date in the comparator.
BirthDate
Before March 17, 1980 |
|
On Or After
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column date is later than, or the same date as, the date
in the comparator.
DailySales
On Or After January 1, 2014 |
|
On Or Before
|
|
Accepts the source row
when the column date is earlier than, or the same date as, the date
in the comparator.
DailySales
On Or Before December 31, 2013 |
About the Aggregations in the Summarize Rows Transformation
The
aggregations that are available in the Summarize Rows transformation
are defined as follows:
Count
the number of rows
in the group that contain valid values.
Count Distinct
the number of unique
values in the column for each group.
Corrected Sum of Squares
measures variability
or dispersion around the mean. To learn more about this (and other)
statistical summaries, see the Introduction to Statistical
Modeling with SAS/STAT Software.
Covariance
measures the strength
of the correlation of the values in the group. A positive value indicates
that values move in the same direction within the group. A negative
value indicates that values move in opposite or random directions.
Max
the maximum value in
the column for each group.
Mean
the calculated center
value between the maximum and minimum values in the group.
Min
the minimum value in
the group.
Number of Missing Values
the number of rows
in the group that contain a blank or NULL value.
Range
the difference between
the lowest and highest values in the group.
Standard Deviation
measures the degree
of variance, or the degree in which the values in the group deviate
from the mean. A small value indicates little deviation. The standard
deviation is the square root of the Variance.
Standard Error
measures the applicability
or accuracy of the mean as it applies to the values in the group.
A small value indicates that the mean is a more accurate reflection
of the values in the group.
Sum
adds the values in
the group
Variance
the average of the
squared differences from the mean, which measure diversity in the
group
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All Rights Reserved.