Building a SASReferences File
Each SASReferences
file requires content that is specific to its planned use. For example,
a SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit process that creates a define.xml
file requires the specification of XML and recommends the specification
of style sheet information. A SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit process
that validates data against a standard requires the specification
of the validation checks to be run.
The SAS
Clinical Standards Toolkit offers several ways to create a SASReferences
file for use in subsequent processes.
-
Use sample SASReferences files that are provided with the SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit. These sample SASReferences files contain the required and optional contents for specific tasks. For example, the task of validating the functionality of CDISC SDTM 3.1.2 uses the SASReferences file found at the following location in SAS 9.2:
!sasroot/../../SASClinicalStandardsToolkitSDTM312/1.3/sample/cdisc-sdtm-3.1.2/sascstdemodata/controlAn excerpt of this sample SASReferences file is provided in A Sample SASReferences Data Set. -
The SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit provides SASReferences templates for use. These templates are either zero-observation data sets or data sets containing records that must be modified. A SASReferences data set template can be found in:The SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit provides default SASReferences data sets for each supported standard. These default SASReferences data sets contain records that are commonly required for certain SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit tasks (such as validation). However, all records that are required might not be included. Or, all records that are included might not be required for certain tasks. And, SAS librefs, filerefs, paths, and memname values might require modification. For example, see the StandardSASReferences data set found in:
-
The SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit provides the utility macros to build and return many SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit metadata data sets.
-
The %cst_getStandardSASReferences macro returns the StandardSASReferences data set. (See the file description in Metadata File Descriptions for the specified standard.)
-
The primary
function of the SASReferences file is to define the SAS Clinical Standards
Toolkit process inputs and outputs. What information does the process
need to reference? What does the process produce? Where does the information
come from and go? The “what” information is determined
by the use of two SASReferences fields—type and subtype. The
“where” information is determined by path and memname.
The values for all of these fields are restricted for SAS Clinical
Standards Toolkit to values itemized in the framework Standardlookup
data set found in:
Customizing
the type and subtype values in the Standardlookup data set is allowed.
Customization is a prerequisite if you want to use the field values
in any SASReferences data set that is used by the SAS Clinical Standards
Toolkit.
The following table lists and describes
the acceptable type and subtype values in the framework Standardlookup
data set.
SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit SASReferences Type and Subtype
Values
Every
instance of the SASReferences file does not require a specific path
and filename. At the beginning of this section, a call to the following
macro was described:
%cst_getStandardSASReferences(_cstStandard=CST-FRAMEWORK,_cstStandardVersion=1.2, _cstOutputDS=sasreferences);
Note the SASref and path fields. For
most rows, SASref is set to
csttmp and
path is set to &_cstGRoot/standards/cst-framework/templates. The memname field points to empty examples
of each file type. From a generic SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit framework
perspective, these are the best available file references. All SAS
Clinical Standards Toolkit processes require specification of some
of these data and metadata sources (for example, generic properties,
messages, and process results).
Here is
the information returned by the following call to %cst_getStandardSASReferences
for the CDISC SDTM standard: Standard SASReferences for CDISC SDTM.
A comparison
of Standard SASReferences File for CST-FRAMEWORK and Standard SASReferences for CDISC SDTM shows little similarity in the record types
and no overlap in references to specific files. The target inputs
and outputs for CDISC SDTM are more focused on the task (for example,
validating SDTM domains). SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit validation
processes require specification of a comparative reference standard.
Here, there are references to a standard-specific macro library (autocall),
Messages data set, and properties files. Unique SASref values by type
are provided, pointing to distinct files and folders in the global
standards library.
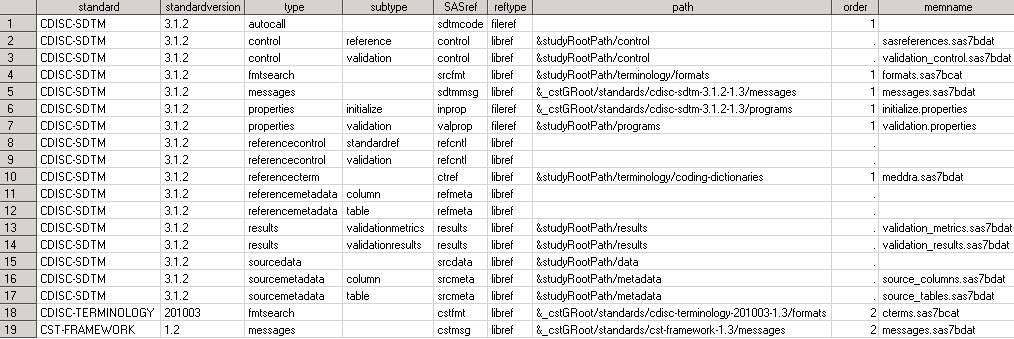
Consider
an actual SASReferences file built to support CDISC SDTM 3.1.2 validation.
The task of validating the functionality of CDISC SDTM 3.1.2 uses
the SASReferences file found at the following location in SAS 9.2:
!sasroot/../../SASClinicalStandardsToolkitSDTM312/1.3/sample/cdisc-sdtm-3.1.2/sascstdemodata/controlExplanation of Sample SASReferences File for CDISC SDTM Validation
|
Illustrates the call
to a standard-specific properties file that is used to initialize
a global macro variable that is specific to that standard. Referencing
a standard-specific properties files in the SASReferences data set
is recommended. The call to the CST-FRAMEWORK initialize.properties
file is a prerequisite setup step outside of SASReferences and performed
before processing SASReferences.
|
|
|
Points to the reference
standard for CDISC SDTM 3.1.2, but unlike the template defaults in Standard SASReferences for CDISC SDTM, path and memname are blank. Leaving them blank tells SAS
Clinical Standards Toolkit to look in the CDISC SDTM 3.1.2 StandardSASReferences
file and use the defaults for that standard and version. This convention
facilitates portability of the data set by doing a run-time lookup
for the current information. The lookup results in the inclusion of
the path and memname values as defined in Standard SASReferences for CDISC SDTM.
|
|
|
This is a new type not
in the template files (StandardSASReferences). It defines the location
of the study (source) data. The use of &studyRootPath, coupled
with the assumption of a fixed-folder hierarchy, enables portability
across studies. The memname value is not relevant for a library of
SAS data sets.
|
|
%cst_createds(_cstStandard=CST-FRAMEWORK,_cstType=control,_cstSubType=reference, _cstOutputDS=work.sasreferences); proc sql; insert into work.sasreferences values(CST-FRAMEWORK 1.2 messages messages libref 1 ); . . . quit;
This macro
copies the template. New records can be added various ways, including
the previous PROC SQL technique. There is no requirement that the
SASReferences file has to live outside the SAS Work area and be kept
beyond the SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit process. However, these
are best practices that enable future capabilities such as process
reruns and reporting.