Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA)
|
|
Participating SAS servers
accept users who have successfully authenticated to their Windows
desktop.
|
|
|
For Windows desktop
clients and SAS servers on Windows and UNIX.
-
Primarily used for connections
to the metadata server and the standard workspace server.
-
Also supported for direct connections
to an OLAP server (for example, from a data provider).
|
|
|
-
Bypasses the initial logon prompt.
-
Accommodates logon mechanisms that
are not password-based (such as smart cards or biometrics).
-
No user credentials are transmitted.
-
|
|
|
-
All participating clients and servers
must authenticate against the same Windows domain (or against domains
that trust one another).
-
If you use IWA for the metadata
server, there are no cached credentials from an initial logon. For
this reason, it is a good idea to configure IWA for the standard
workspace server also, if possible (IWA is not supported on z/OS).
-
Web applications can’t participate
in this implementation of IWA. However, if you configure Web authentication,
and your Web environment offers IWA, then your Web applications can
use IWA. SAS provides instructions for configuring IWA for your Web
application server at http://support.sas.com/thirdpartysupport.
-
Desktop clients that run on UNIX
(for example, SAS Management Console on UNIX) can’t participate
in IWA.
-
Analytics platform clients (for
example, SAS Enterprise Miner) can’t participate in this implementation
of IWA. Like other clients, analytics platform clients can authenticate
to an IWA-configured server by supplying credentials, instead of using
IWA.
-
If your SAS servers use DNS aliases,
you must manually register those aliases in order to support Kerberos-based
IWA connections. See Using Custom SPNs.
-
Additional limits for servers on
Windows:
-
If you use IWA for a Windows workspace
server that accesses Windows network resources (for example, remote
data access), the Kerberos protocol must be used and the object spawner
account must have the trusted for delegation privilege. See Windows Privileges.
-
Additional limits for servers on
UNIX:
-
In order to use IWA on UNIX, you
must purchase, install, and configure an additional third-party product
(Quest Authentication Services 4.0).
-
When you use IWA on UNIX, only
Kerberos connections are supported (there is no support for NTLM on
UNIX).
-
If you use IWA for a UNIX workspace
server that makes outbound Kerberos requests, the service principal
account in Active Directory must have the trusted for
delegation privilege. See Windows Privileges.
|
|
|
|
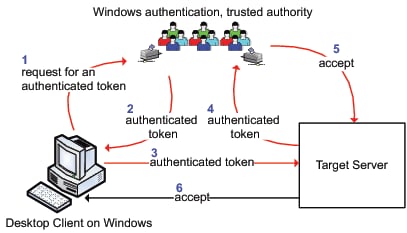
The following figure is an abstraction of how this mechanism
works.
The numbers in the figure
correspond to these actions:
-
The client asks Windows
for a token that represents the user who is currently logged on to
the client computer. This step is initiated when a user launches a
desktop client or makes a request for a workspace server.
Note: The token represents the
client who is running the SAS application. If you use the Windows
runas command
to launch a SAS application, the token represents the host account
that you chose to use.
-
Windows provides the
token to the client.
-
The client sends the
Windows token to the target server. Notice that only the token is
sent; the user's password isn't available to the target server.
-
The target server sends
the token back to Windows for verification.
-
Windows tells the target
server that the token is valid.
-
The target server accepts
the connection from the client. By default, the user's authenticated
ID is returned to the target server as follows:
-
If the target server is on Windows,
the authenticated user ID is returned in domain qualified format (for
example, WIN\joe).
-
If the target server is on UNIX,
the authentication user ID is returned in short format; the user ID
is not qualified (for example, joe).
Note: The format in which the
authenticated user ID is returned to the target server must match
the format in which that user ID is stored in the SAS metadata.
See Logins for Users Who Participate in IWA.