DataFlux Data Management Studio 2.6: User Guide
If you get "error loading type library/DLL" when doing any level of authentication in Data Management Studio, take the following steps. Either remove HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\TypeLib\{87AD4890-333C-451F-8986-C46885C0C8E 7}\1.0 from the registry or change the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\TypeLib\{87AD4890-333C-451F-8986-C46885C0C8E 7}\1.0\0\win32 value to reflect the value in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Classes\TypeLib\{87AD4890-333C-451F-8986-C46885C0C8E7}\1.1\0\win32.
Data Direct ODBC drivers do not update any settings for System DSNs when changes are made to the connection options in the logon dialogs. Instead, they will write any values that a user changes into the Windows registry for the current user. This prevents multiple users who are sharing a data source from changing each other's settings. However, if you need to change the settings that were written the registry, open the Registry Editor (regedit). Expand HKEY_CURRENT_USER -> Software -> ODBC -> ODBC.INI. Select the DSN with the incorrect values. Update the values as needed and click OK. Close the registry.
DataDirect provides a number of wire protocol ODBC drivers that communicate directly with a database server, without having to communicate through a client library. If these drivers are available at your site, they are available from the Drivers tab of the ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog.
If you use a wire protocol driver to create an ODBC connection, the following special considerations apply:
[00007350] ERROR DF.DAC - Operation failed: [22001]
[DataFlux][ODBC Oracle Wire Protocol driver]String data, right truncated. Error in parameter 1. (0)
Since disabling Enable N-CHAR Support is probably not an option, the recommended workaround is to add a new string, ColumnSizeAsChar, to the data source in the Windows registry, or in ODBC.INI for Unix systems.
WARNING: Using a registry editor incorrectly can cause problems with your system. If you are not sure about this procedure, contact your system administrator for assistance.
First, determine what type of DSN you are editing (system or user) because the registry path to a system DSN differs from the path for a user-defined DSN as shown below:
User DSN: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\ODBC\ODBC.INI\<DSN NAME>
System DSN: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ODBC\ODBC.INI\<DSN NAME>
To create the ColumnSizeAsChar string in the registry:
- Open the registry editor and navigate to the data source (DSN NAME) using one of the paths shown above.
- With your cursor positioned on the <DSN Name> entry, right-click and select New > String Value.
- A 'new value' object appears in the registry - key in the name ColumnSizeAsChar and enter.
- Right-click the new ColumnSizeAsChar object and select Modify.
- In the Value Data field, enter 1 and click OK. The new string now appears in the registry:
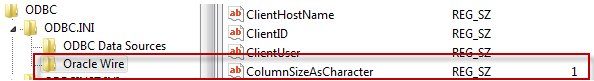
Example: New ODBC String Value
Domain-enabled connections cannot use shared logins, as defined on the Shared Login riser in the Authentication Server interface. Domain-enabled connections can use only the logins that are associated with user accounts on the Authentication Server.
Domain-enabled connections are not displayed in lineages. Instead, the regular connections that the domain-enabled connections refer to are used in lineage displays.
After saving a job with a Domain Enabled ODBC Connection, you need to change the data source from a domain enabled ODBC DSN to a regular, non-domain ODBC DSN. The change will not be saved and the domain enabled ODBC DSN will remain selected in the data source node. This behavior occurs because the application is pulling cached information from the domain enabled ODBC DSN.
Correct this behavior as follows: After saving the job, exit and restart DataFlux Data Management Studio to clear the cached information. Revisit the job and change the data source to a non-domain ODBC DSN. When the job is saved, the non-domain ODBC DSN is associated with the job.
Cloudera Impala is optimized for queries rather than inserts into the Hadoop file system (HDFS). Accordingly, avoid using an Impala table as the output of any job node.
Apache Hive has a single data type for storing text, STRING, which is a variable-length character string with a maximum size of 2Gb. As a result, this can create very large character fields when processing data. Since Hive’s string type is comparable to VARCHAR in other data sources, you can set the ODBC attribute, Max Varchar Size to specify the maximum character string size. Set the Max Varchar Size value using Advanced Options in Windows ODBC Administrator, or in Unix by editing odbc.ini in the specified path or $HOME directory.
The interfaces for profiles, some job nodes, and other components enable you to display the Query Builder dialog. This dialog provides an easy way to create complex SQL Server queries for data sources. However, the Query Builder dialog cannot generate valid queries for Apache Hive data sources or Cloudera Impala data sources.
Data can only be inserted into an Apache Hive table by reading it from another table, so you cannot use a business rule task to insert a row. Apache Hive does not support the method used by business rule tasks.
Hive indexes are not supported on Impala, so you cannot use the DSN ODBC Impala Wire Protocol driver to view Impala table fields and data.
Apache Hive does not support row-level insert, update, or delete. Accordingly, avoid using an Apache Hive table as the output of these data job nodes:
That error indicates that you used an unsupported data type . According to the ODBC User's Guide "Part 4: The Connect XE Drivers", the only data types supported by the ODBC 7.1.3 Impala Wire Protocol driver are:
Data Direct DSNs for the Oracle Wire Protocol have a Performance tab. This tab has a Wire Protocol Mode field. When the DSN is used to connect to Oracle 11 or later, the Wire Protocol Mode field should be set to a value of 2.
This error probably means that the SAP libraries (DLLs) are not installed on the computer where they are needed. See the SAP documentation for details about installing these libraries on various platforms. SAP libraries must be installed on all computers where a connection to the SAP system is attempted. This could include the computer where DataFlux Data Management Studio is installed; the DataFlux Data Management Server where jobs that use SAP connections are executed; and the Federation Server if that server is used to manage connections to an SAP system.
The custom connection that is defined for the SAP Remote Function Call node cannot reference a shared login. The SAP Remote Function Call node does not support shared logins.
A SAS Data Set Connection in DataFlux Data Management Studio 2.5 or later uses a SAS 9.4 TKTS Base driver. Accordingly, it can access any SAS version 8 or version 9 data set.
A SAS Data Set Connection in DataFlux Data Management Studio 2.4 or earlier uses a SAS 9.2 TKTS Base driver. Accordingly, it can access any SAS version 8 data set. It can also access any version 9 data set that was not created with the Extend Observation Counter turned on.
You cannot use a DSN that specifies the DataFlux SQL Server Legacy Wire Protocol driver or the DataFlux SQL Classic Wire Protocol driver. If you have an ODBC DSN that uses one of these drivers, replace that DSN with one that uses the appropriate DataFlux SQL Server Wire Protocol driver.
When using a SQL Server ODBC DSN, if you select a table using the Select Table dialog, close that dialog, and then re-open it, you will see your table name appear twice in the table list. This does not affect the functionality of the application. You can select either table listed in the tree.
If you use an SQL Server DSN connection, you can avoid locking issues by setting the DAC option Readuncommitted as described in the "Data Access Component Directives" topic in the DataFlux Data Management Studio Installation and Configuration Guide.
In the properties window for the DSN, click the Options tab and deselect the Show Selectable Tables check box.
Due to the limitations of the ODBC 32-bit XML driver, we recommend that you use the XML Input node to read an XML file in a data job.
We recommend that you extract the data from the XML file to a text file or to a database table, and then profile the text file or table. To extract the data, create a data job in which the XML Input node is used to read the XML file, and then use other nodes to output a text file or a database table.
|
Documentation Feedback: yourturn@sas.com
|
Doc ID: dfDMStd_T_DSN_Usage.html |