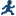Data Exploration Task
Assigning Data to Roles
To run the Data Exploration
task, you must assign either two columns to the Classification
variables role or one column to the Continuous
variables role.
|
Role
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Roles
|
|
|
Continuous
variables
|
specifies the continuous variables in the analysis.
|
|
Classification
variables
|
specifies the classification variables to use to explore the data.
|
|
Additional Roles
|
|
|
Group analysis
by
|
creates separate analyses
based on the number of BY variables.
|
Setting the Plot Options
The plot options that are available depend on the columns that you assigned on the Data tab.
|
Option Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Histogram and Box Plot
|
|
|
The combined histogram and box plot options are available when a column is assigned to the Continuous
variables role, but no column is assigned to the Classification
variables role.
|
|
|
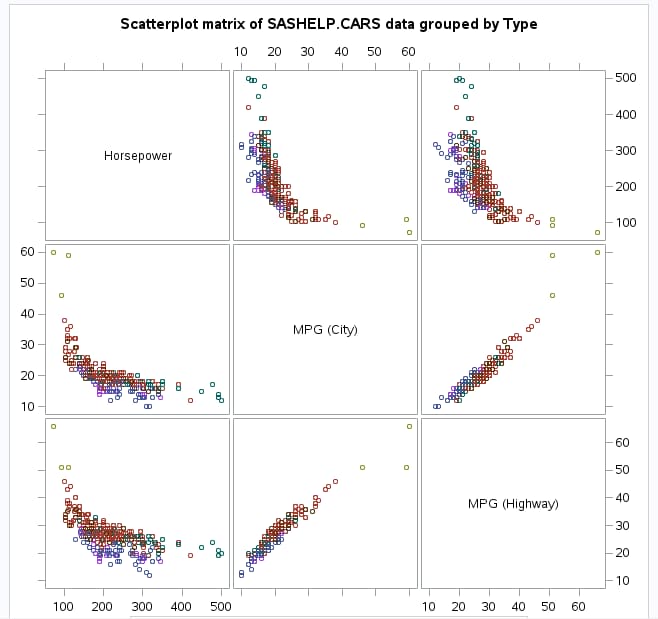
Scatter Plot Matrix
|
|
|
The scatter plot matrix options are available when at least two columns are assigned to the Continuous
variables role.
|
|
|
Add histograms
|
adds histograms to the diagonal cells of the matrix. You can add a normal density curve and the kernel density estimate to these histograms.
|
|
Add prediction
ellipses
|
adds a prediction ellipse to each cell that contains a scatter plot. You can specify the confidence level for the ellipses. Valid values are between 0 and 1.
|
|
Pairwise Scatter Plots
|
|
|
The pairwise scatter plot options are available when at least two columns are assigned to the
Continuous variables role.
|
|
|
Pairwise
scatter plots
|
plots the values of two or more variables and produces a separate cell for each combination
of Y and X variables. That is, each Y*X pair is plotted on a separate set of axes.
|
|
Add a prediction
ellipse
|
adds a prediction ellipse to each cell that contains a scatter plot. You can specify
the confidence level for the ellipses. Valid values are between 0 and 1.
|
|
Regression Scatter Plots
|
|
|
The regression scatter plot options are available when at least two columns are assigned to the
Continuous variables role.
|
|
|
Regression
scatter plots
|
adds a regression fit to the scatter plot.
|
|
Select response
variables
|
specifies the variables to use when fitting the regression line.
|
|
Add a fitted
line
|
adds a regression fit to the scatter plot.
|
|
Add a loess
fit
|
adds a loess fit to the scatter plot.
|
|
Add a fitted,
penalized B-spline curve
|
adds a fitted, penalized B-spline curve to the scatter plot.
|
|
Mosaic Plot
|
|
|
Mosaic plot
|
creates a mosaic plot, which displays tiles that correspond to the crosstabulation table cells. The areas of the tiles are proportional
to the frequencies of the table cells. The column variable is displayed on the X axis, and the tile widths are proportional to the relative frequencies of the column variable levels. The row variable is displayed on the Y axis, and the tile heights are proportional
to the relative frequencies of the row levels within column levels.
|
|
Square mosaic
plot
|
produces a square mosaic plot, where the height of the Y axis equals the width of
the X axis. In a square mosaic
plot, the scale of the relative frequencies is the same on both axes.
|
|
Specify
colors of mosaic plot tiles
|
colors the mosaic plot tiles according to the values of residuals. You can also specify
to color the tiles according
to the Pearson or standardized residuals of the corresponding table cells.
|
|
Histogram
|
|
|
Histogram
|
creates a histogram by using any numeric variables in the input data set.
|
|
Add normal
density curve
|
adds a normal density curve to the histogram.
|
|
Add kernel
density estimate
|
adds a kernel density estimate to the histogram.
|
|
Add inset
statistics
|
adds a box or table of summary statistics directly in the histogram.
|
|
Box Plot
|
|
|
The box plot options are available when at least one column is assigned to the Classification
variables role.
|
|
|
Comparative
box plot
|
creates a one-way box plot for each classification variable. This plot shows all continuous variables by the classification variable.
|
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.