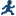One-Way ANOVA Task
About the One-Way ANOVA Task
The one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) task tests and provides graphs for differences among the means of a single
categorical variable on a single continuous dependent variable.
You might use the One-Way
ANOVA task to do the following:
-
study the effect of bacteria on the nitrogen content of red clover plants. The factor is the bacteria strain, and it has six levels.
-
compare the life spans of three different brands of batteries. The factor is the brand, and it has three levels.
Note: You must have SAS/STAT to
use this task.
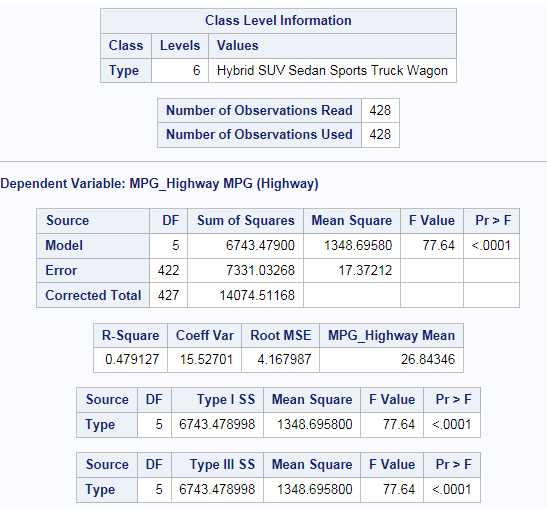
Example: Testing for Differences in the Means for MPG_Highway by Car Type
Assigning Data to Roles
To run the One-Way
ANOVA task, you must assign columns to these roles:
|
Role Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Dependent
variable
|
specifies a continuous numeric column.
|
|
Categorical
variable
|
specifies a character or numeric column with values that specify the levels of the groups. The column that
you assign to
this role must have two or more distinct values.
|
Setting Options
|
Option Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Homogeneity of Variance
|
|
|
Test
|
specifies the type of
test to perform. Here are the valid values:
None
specifies that no test
is performed.
Bartlett
computes accurate Type
I error rates when the distribution of the data is normal.
|
|
Test (continued)
|
Brown & Forsythe
is a variation of Levene's test. Equal variances are determined by using the absolute
deviations from the group medians. Although this is a good test for determining variance differences,
it can be resource intensive if your data contains several large groups.
Levene
computes the squared residuals to determine equal variance. Levene’s test is considered to be the standard homogeneity of variance test. This is the default.
O’Brien
specifies O’Brien’s test, which is a modification of Levene’s test that uses squared
residuals.
|
|
Welch’s
variance-weighted ANOVA
|
tests the group means
by using a weighted variance. You can use this test if the assumption
of equal variances is rejected.
|
|
Comparisons
|
|
|
You can select from these comparison methods:
Bonferroni
performs Bonferroni t tests
of differences between means for all means of the main effect.
Duncan multiple range
performs Duncan’s multiple range test on all means of the main effect.
Dunnett two-tail
performs Dunnett’s two-tailed t test, testing whether any treatments
are significantly different from a single control for all main-effect
means.
Dunnett lower one-tail
performs Dunnett’s one-tailed t test, testing whether any treatment
is significantly less than the control.
Dunnett upper one-tail
performs Dunnett’s one-tailed t test, testing whether any treatment
is significantly greater than the control.
Gabriel
performs Gabriel’s
multiple-comparison procedure on all means of the main effect.
Nelson
analyzes all the differences with the least squares means.
|
|
|
Ryan-Einot-Gabriel-Welsch
performs the Ryan-Einot-Gabriel-Welsch multiple range test on all means of the main
effect.
Scheffé
performs Scheffé’s
multiple-comparison procedure on all means of the main effect.
Sidak
performs pairwise t tests
on differences between means with levels adjusted according to Sidak’s
inequality for all means of the main effect.
Student-Newman-Keuls
performs the Student-Newman-Keuls multiple range test on all main effect means.
Least significant difference (LSD)
performs pairwise t tests
for all means of the main effect. In the case of equal cell sizes,
this test is equivalent to Fisher’s least significant difference
test.
Tukey
performs Tukey’s
studentized range test (HSD) on all means of the main effect. When
the group sizes are different, this is the Tukey-Kramer test.
You can also specify
the level of significance for the selected test.
|
|
|
Plots
|
|
|
By default, the results include a box plot, a means plot, and a least squares mean difference plot. You can also specify to include any diagnostic plots, which can be displayed in a panel or as individual plots.
You can also specify the maximum number of points to include in these plots.
|
|
Setting the Output Options
You can specify whether to create an output data set. You can also specify the values to include in the output data set. You can include predicted values, residuals, standard errors, and influence statistics.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.