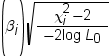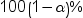Setting Options
|
Option Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Statistics
Note: In addition to the default
statistics that are included in the results, you can select the additional
statistics to include.
|
|
|
Classification
table
|
classifies the input
binary response observations according to whether the predicted event
probabilities are above or below the cut-point value z in
the range. An observation is predicted as an event if the predicted
event probability equals or exceeds z.
|
|
Partial
correlation
|
|
|
Generalized
R square
|
requests a generalized
R square measure for the fitted model.
|
|
Goodness-of-fit and
Overdispersion
|
|
|
Deviance
and Pearson goodness-of-fit
|
specifies whether to
calculate the deviance and Pearson goodness-of-fit.
|
|
Aggregate
by
|
specifies the subpopulations
on which the Pearson chi-square test statistic and the likelihood
ratio chi-square test statistic (deviance) are calculated. Observations
with common values in the given list of variables are regarded as
coming from the same subpopulation. Variables in the list can be any
variables in the input data set.
|
|
Correct
for overdispersion
|
specifies whether to
correct for overdispersion by using the Deviance or Pearson estimate.
|
|
Hosmer &
Lemeshow goodness-of-fit
|
performs the Hosmer
and Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test (Hosmer and Lemeshow 2000) for the
case of a binary response model. The subjects are divided into approximately
10 groups of approximately the same size based on the percentiles
of the estimated probabilities. The discrepancies between the observed
and expected number of observations in these groups are summarized
by the Pearson chi-square statistic. This statistic is then compared
to a chi-square distribution with t degrees
of freedom, where t is the number of groups
minus n. By default, n =
2. A small p-value suggests that the fitted
model is not an adequate model.
|
|
Multiple Comparisons
|
|
|
Perform
multiple comparisons
|
specifies whether to
compute and compare the least squares means of fixed effects.
|
|
Select the
effects to test
|
specifies the effects
that you want to compare. You specified these effects on the Model tab.
|
|
Method
|
requests a multiple
comparison adjustment for the p-values and
confidence limits for the differences of the least squares means.
Here are the valid methods: Bonferroni, Nelson, Scheffé, Sidak,
and Tukey.
|
|
Significance
level
|
requests that a t type
confidence interval be constructed for each of the least squares means
with a confidence level of 1 – number.
The value of number must be
between 0 and 1. The default value is 0.05.
|
|
Exact Tests
|
|
|
Exact test
of intercept
|
calculates the exact
test for the intercept.
|
|
Select effects
to test
|
calculates exact tests
of the parameters for the selected effects.
|
|
Significance
level
|
|
|
Parameter Estimates
|
|
|
You can calculate these
parameter estimates:
You can specify the
confidence intervals for parameters, confidence intervals for odds
ratios, and the confidence level for these estimates.
|
|
|
Diagnostics
|
|
|
Influence
diagnostics
|
displays the diagnostic
measures for identifying influential observations. For each observation,
the results include the sequence number of the observation, the values
of the explanatory variables included in the final model, and the
regression diagnostic measures developed by Pregibon (1981). You can
specify whether to include the standardized and likelihood residuals
in the results.
|
|
Plots
|
|
|
You can select whether
to include plots in the results.
Here are the additional
plots that you can include in the results:
You can specify whether
to display these plots in a panel or individually. You can also specify
whether to label the points on influence and ROC plots. You can label
these points with the observation number or the variable values. By
default, these points are not labeled.
|
|
|
Label influence
and ROC plots
|
specifies the variable
from the input data that contains the labels for the influence and
ROC plots.
|
|
Maximum
number of plot points
|
specifies the maximum
number of points to include in the plots. By default, 5,000 points
are shown.
|
|
Methods
|
|
|
Optimization
|
|
|
Method
|
specifies the optimization
technique for estimating the regression parameters. The Fisher scoring
and Newton-Raphson algorithms yield the same estimates, but the estimated
covariance matrices are slightly different except when the Logit link
function is specified for binary response data.
|
|
Maximum
number of iterations
|
specifies the maximum
number of iterations to perform. If convergence is not attained in
a specified number of iterations, the displayed output and all output
data sets created by the task contain results that are based on the
last maximum likelihood iteration.
|
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.