You must select at
least one output option.
|
Option Name
|
Description
|
|
Options
|
|
Ranking
method
|
specifies the method
to use when ranking the data. Here are the valid values:
Ranks
partitions the original
values into 100 groups, in which the smallest values receive a percentile
value of 0 and the largest values receive a percentile value of 99.
Quantiles
partitions the original
values into one of these quantiles.
-
Percentiles partitions
the data into 100 groups, in which the smallest values receive a percentage
value of 0 and the largest values receive a percentage value of 99.
-
Deciles partitions
the original values into 10 groups, in which the smallest values receive
a decile value of 0 and the largest values receive a decile value
of 9.
-
Quartiles partitions
the original values into four groups, in which the smallest values
receive a quartile value of 0 and the largest values receive a quartile
value of 3.
-
N-tile groups partitions
the original values into n groups,
in which the smallest values receive a value of 0 and the largest
values receive a value of n–1.
Specify the value of n in the Number
of groups box.
|
|
Ranking
method (continued)
|
Fractional ranks
computes the fractional
ranks by using either a denominator of N or N+1. A denominator of
N computes fractional ranks by dividing each rank by the number of
observations that have nonmissing values of the ranking variable.
A denominator of N+1 computes fractional ranks by dividing each rank
by the denominator n+1, where n is
the number of observations that have nonmissing values of the ranking
variable.
Percentages
divides each rank by
the number of observations that have nonmissing values of the variable
and multiplies the result by 100 to get a percentage.
|
|
Ranking
method (continued)
|
Normal scores of ranks
computes normal scores
from the ranks. The resulting variables appear normally distributed.
Here are the formulas:
In these formulas, 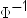 is the inverse cumulative normal (PROBIT) function, ri is
the rank of the ith observation, and n is
the number of nonmissing observations for the ranking variable.
Note: If you set the If
values are tied, use option, the Rank Data task computes
the normal score from the ranks based on non-tied values and applies
the ties specification to the resulting score.
Savage scores of ranks
computes Savage (or
exponential) scores from the ranks.
Note: If you set the If
values are tied, use option, the Rank Data task computes
the Savage score from the ranks based on non-tied values and applies
the ties specification to the resulting score.
|
|
If values
are tied, use
|
specifies how to compute
normal scores or ranks for tied data values.
Default method
assigns the default
method for your ranking method. If you select Percentages or Fractional
ranks as the ranking method, the high value is the default.
For all other ranking methods, the mean is the default.
Mean of ranks
assigns the mean of
the corresponding rank or normal scores.
High rank
assigns the largest
of the corresponding ranks or normal scores.
Low rank
assigns the smallest
of the corresponding ranks or normal scores.
Dense rank (ties are the same rank)
computes scores and
ranks by treating tied values as a single-order statistic. For the
default method, ranks are consecutive integers that begin with the
number 1 and end with the number of unique, nonmissing values of the
variable that is being ranked. Tied values are assigned the same rank.
|
|
Rank order
|
specifies whether to
list the values from smallest to largest or from largest to smallest.
|