CALL RANCAU Routine
Returns a random variate from a Cauchy distribution.
| Category: | Random Number |
Syntax
Required Arguments
seed
is the seed value. A new value for seed is returned each time CALL RANCAU is executed.
| Range | seed < 231 - 1 |
| Note | If seed ≤ 0, the time of day is used to initialize the seed stream. |
| See | Seed Values and Comparison of Seed Values in Random-Number Functions and CALL Routines for more information about seed values |
x
is a numeric SAS variable. A new value for the random variate x is returned each time CALL RANCAU is executed.
Details
The CALL RANCAU routine
updates seed and returns a
variate x that is generated
from a Cauchy distribution that has a location parameter of 0 and
scale parameter of 1.
By adjusting the seeds,
you can force streams of variates to agree or disagree for some or
all of the observations in the same, or in subsequent, DATA steps.
An acceptance-rejection
procedure applied to RANUNI uniform variates is used. If u and v are independent uniform (−1/2, 1/2) variables and u2+v2 ≤ 1/4, then
u/v is a Cauchy variate.
For a discussion and
example of an effective use of the random number CALL routines, see Starting,
Stopping, and Restarting a Stream.
Example
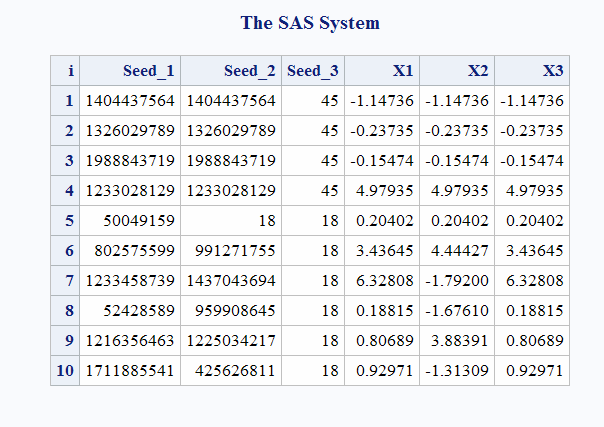
data case;
retain Seed_1 Seed_2 Seed_3 45;
do i=1 to 10;
call rancau(Seed_1,X1);
call rancau(Seed_2,X2);
X3=rancau(Seed_3);
if i=5 then
do;
Seed_2=18;
Seed_3=18;
end;
output;
end;
run;
proc print;
id i;
var Seed_1-Seed_3 X1-X3;
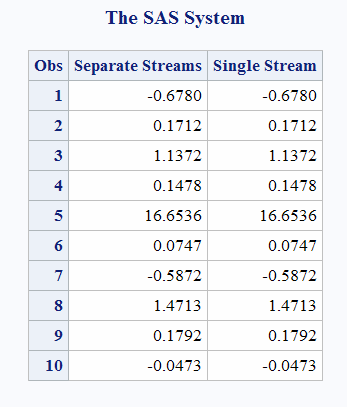
run;data u1(keep=x);
seed = 104;
do i = 1 to 5;
call rancau(seed, X);
output;
end;
call symputx('seed', seed);
run;
data u2(keep=x);
seed = &seed;
do i = 1 to 5;
call rancau(seed, X);
output;
end;
run;
data all;
set u1 u2;
z = rancau(104);
run;
proc print label;
label x = 'Separate Streams' z = 'Single Stream';
run;Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.