Overview of SAS BI Dashboard
About SAS BI Dashboard
A dashboard is
a container that is nested within a portlet and that contains one
or more indicators. An indicator is a composite of one or more related
objects. Each indicator has a data source, one or more gauges, hyperlinks
to additional information, and range settings for the gauges. Dashboards
display critical information in such a way that the information can
be interpreted and monitored at a glance. Dashboards can also contain
links to other pertinent information, important summary and highlights,
and personalized information such as weather, news, and stock news.
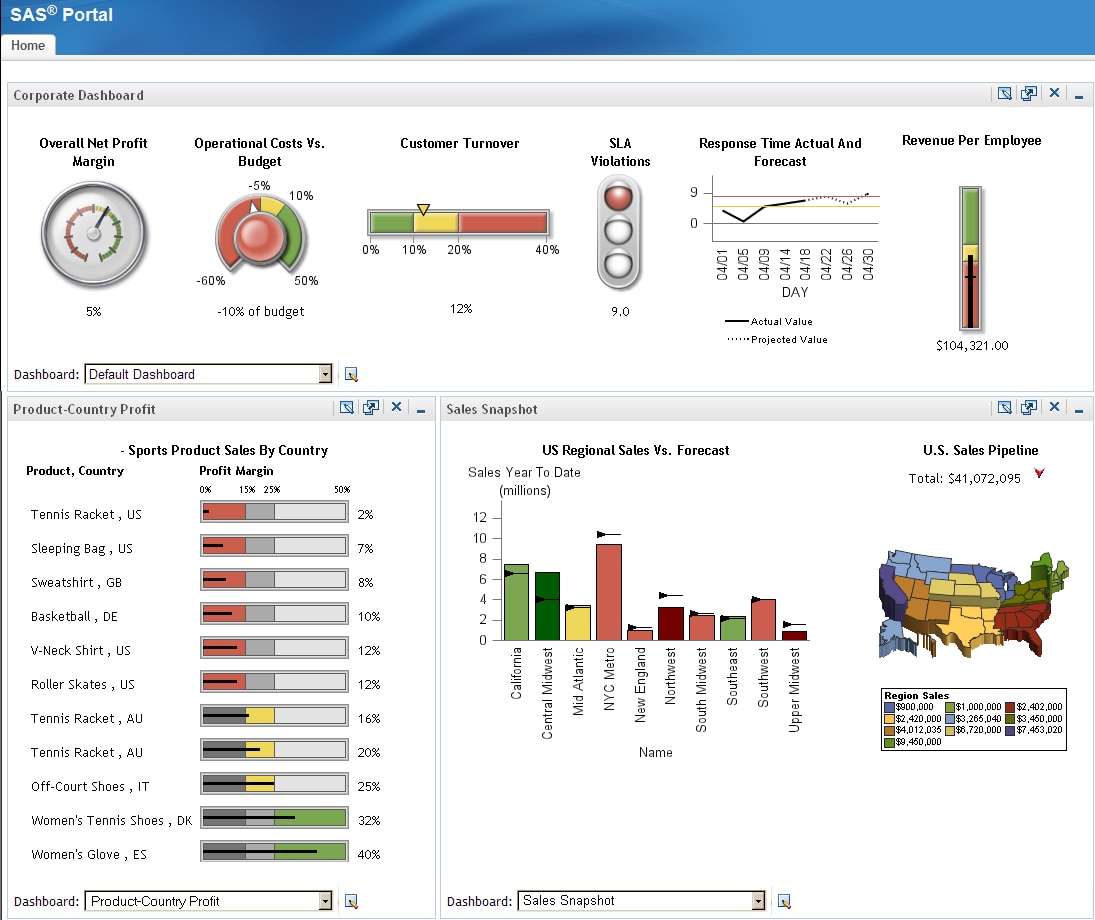
Here is an example dashboard that contains three dashboards that use
different data sources:
The SAS BI Dashboard
enables users to use dashboards to monitor key performance indicators
that convey how well an organization is performing. As shown in the
preceding display, dashboards include graphics, text, colors, and
hyperlinks. The preceding dashboard shows multiple indicators, each
with its own data model underneath. These indicators are driven by
six different SQL queries, but the data models could be all information
maps, all scorecards, or some combination of these types. This dashboard
displays gauges, graphs, bar charts, line plots, and a map.
Dashboards are created,
maintained, and viewed through an easy-to-use Web-based interface.
All content is displayed in a role-based, secure, customizable, and
extensible environment. Information consumers and performance analysts
can customize how information appears on their personal dashboards.
SAS BI Dashboard enables
users to create their own dashboards from a variety of data sources,
including information maps and SAS data sets. Users can link dashboards
to SAS business intelligence objects or to external URLs, and users
can customize the visualization of the data in a number of ways. For
more information about the SAS BI Dashboard, see the SAS
BI Dashboard: User's Guide.
Log On to SAS BI Dashboard
The SAS BI Dashboard is accessed from
within the SAS Information Delivery Portal. The current logon information
from the portal is provided to the SAS BI Dashboard. Therefore, the
SAS BI Dashboard appears immediately, without the need to log on.
For more information, see the Help for SAS Information Delivery Portal.
To access SAS BI Dashboard,
open the SAS Information Delivery Portal and log on. To do so, perform
the following steps: