Introduction to SAS Files
What Is a SAS File?
SAS creates and uses a variety of specially structured
files called SAS files. Although Windows manages the file for SAS
by storing it, the operating system cannot process it. For example,
you can list SAS files with the Windows Explorer, but SAS files must
be processed by SAS. SAS files are different from external files.
While external files can be processed by SAS statements and commands,
they are not managed by SAS.
SAS files usually reside
in SAS libraries. Under Windows, a SAS library is a named collection
of SAS files within one or more Windows folders that SAS can access.
Each SAS library has an access engine associated with it the first
time that a file in the library is accessed. The engine name specifies
the access method that SAS uses to process the files in the library.
SAS libraries are described in detail in SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
The various engines
enable SAS to access different formats or versions of SAS files and
other vendors' files. For this reason, SAS is said to have Multi Engine
Architecture. Multi Engine Architecture, combined with conversion
utilities, provides access to SAS 9.3 files and SAS files created
with previous releases of SAS (back to Version 5), whether they were
created under Windows or other operating environments. Multi Engine
Architecture also provides access to files created by other vendors'
products, including database files.
File Extensions for SAS Files
SAS files
are stored in SAS libraries and are referred to as members of a library.
Each member has a member type. SAS distinguishes between SAS files
and external Windows files in a folder by using unique file extensions.
SAS assigns certain file extensions to a general set of SAS member
types. The following table lists the Windows file extensions and their
corresponding SAS member types for the V6, V7, V8, and V9 engines.
For more information about engines, see Multi Engine Architecture. For more information about processing files from previous
releases, see Using SAS Files from Other Versions with SAS 9.3 for Windows .
CAUTION:
Do not
change the file extension of a SAS file; doing so can cause unpredictable
results.
The file extensions assigned by SAS to SAS files are
an integral part of how SAS accesses these files. Also, you should
not change the filename of a SAS file using operating system commands.
If you want to change the name of a SAS file, use the DATASETS procedure
or select the file in the SAS Explorer window or the My
Favorite Folders window and select Edit Rename.
Rename.
Note: Do not delete files from
your Work and Sasuser libraries during your SAS session. SAS creates
temporary utility files that you do not need to access directly but
that are necessary for processing SAS data. If your SAS session ends
abnormally, you might need to delete files outside SAS in order to
regain disk space. You can delete files in the Work library by using
the WORKINIT and the WORKTERM system options when you start SAS. For
more information, see WORKINIT System Option in SAS System Options: Reference and WORKTERM System Option in SAS System Options: Reference.
SAS Data Sets (Member Type: Data or View)
SAS data
set is an umbrella term for SAS data files and SAS data views, which
are both discussed here. This section provides a brief overview of
the concept of SAS data sets. For complete details, see the data sets
section in SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
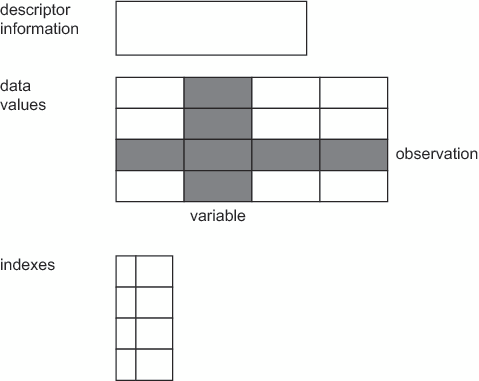
Logically, a SAS data
set consists of two types of information: descriptor information and
data values. The descriptor information includes such things as data
set name, data set type, data set label, and number of variables,
as well as the names and labels of the variables in the data set,
their types (character or numeric), their length, their position within
a record, and their formats. You can use the CONTENTS Procedure: Windows to access descriptor information.
The data values contain
values for the variables. A SAS data set can be visualized as a table
consisting of rows of observations and columns of variable values.
The following table illustrates the SAS data set model.
The SAS data file is
probably the most frequently used type of SAS file. SAS data files
have a SAS member type of Data and are created in the DATA step and
by certain SAS procedures such as the RANK procedure in Base SAS software.
SAS data files have a file extension of .sas7bdat.
SAS defines two types
of SAS data files, native and interface. Native data files store data
values and descriptor information, as described earlier, in files
formatted by SAS. These files are the SAS data sets you might be familiar
with from previous versions of SAS under other operating environments.
In SAS under Windows, native SAS data files can be indexed. The index
is an auxiliary file that you create to provide fast access to records
within a SAS data file through a variable or key. Indexes are stored
as separate files but are treated by SAS as integral parts of the
SAS data file. To learn more about indexes, see SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
The second type of
data file is the interface SAS data file. These files store data in
a file formatted by other software. Examples of interface SAS data
files are BMDP, OSIRIS and SPSS files, which SAS can access as read-only
files. For more information, see Reading BMDP, OSIRIS, and SPSS Files.
SAS data views have
a member type of View. They describe data values and tell SAS where
to find the values, but they do not contain the actual data values
themselves. SAS data views have a file extension of .sas7bvew.
Views can be native
or interface. A native SAS data view is created with the SQL procedure
or with the DATA step and describes a subset or combination of the
data in one or more SAS data files or SAS data views. For information
about SQL views, see the Base SAS Procedures Guide. For
information about DATA step views, see SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
Interface SAS data
views contain descriptor information for data formatted by other software
products, for example, a database management system. You access database
views using the SAS/ACCESS LIBNAME statement. For more information,
see SAS/ACCESS Interface to PC Files: Reference and SAS/ACCESS for Relational Databases: Reference.
SAS Catalogs (Member Type: Catalog)
A SAS catalog is a special type of SAS file that can
contain multiple entries. You can keep different types of entries
in the same SAS catalog. For example, the Sasuser.Profile catalog
contains function key definitions, fonts for graphic applications,
some of your selections from the Preferences dialog box, and other information from interactive windowing procedures.
SAS catalogs have a file extension of .sas7bcat.
SAS Stored Compiled DATA Step Programs (Member Type: Program)
A stored compiled DATA step program
is a SAS file that contains a DATA step program that has been compiled
and then stored in a SAS library. You can execute compiled DATA step
programs as needed, without having to recompile them. SAS stored compiled
DATA step programs have a file extension of .sas7bpgm.
Stored compiled programs
are available for DATA step applications only. Your stored programs
can contain all SAS language elements except global statements. If
you include global statements in your source program, SAS stores the
compiled program but not the global statements, and does not display
a warning message in the SAS log.
Access Descriptor Files (Member Type: Access)
Descriptor files created by the SAS/ACCESS LIBNAME statement
have a member type of ACCESS and are used when creating interface
SAS data views. Descriptor files describe the data formatted by other
software products supported by SAS. For more information, see SAS/ACCESS for Relational Databases: Reference , SAS/ACCESS Interface to PC Files: Reference and other available SAS/ACCESS
documentation.