The MDC Procedure
NEST Statement
-
NEST LEVEL ( level-number )= ( choices@choice, …);
The NEST statement is used when one choice variable contains all possible alternatives and the TYPE=NLOGIT option is specified. The decision tree is constructed based on the NEST statement. When the choice set is specified using multiple CHOICE= variables in the MODEL statement, the NEST statement is ignored.
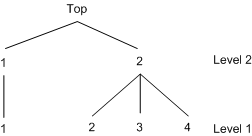
Consider the following eight choices that are nested in a three-level tree structure.
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 top
1 1 1 1
2 1 1 1
3 1 1 1
4 2 1 1
5 2 1 1
6 2 1 1
7 3 2 1
8 3 2 1
You can use the following NEST statement to specify the tree structure displayed in Figure 25.22:
nest level(1) = (1 2 3 @ 1, 4 5 6 @ 2, 7 8 @ 3),
level(2) = (1 2 @ 1, 3 @ 2),
level(3) = (1 2 @ 1);
Figure 25.22: A Three-Level Tree
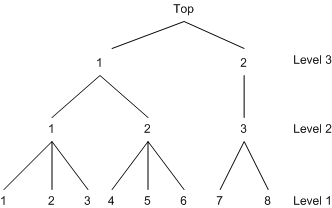
Note that the decision tree is constructed based on the sequence of first-level choice set specification. Therefore, specifying another order at Level 1 builds a different tree. The following NEST statement builds the tree displayed in Figure 25.23:
nest level(1) = (4 5 6 @ 2, 1 2 3 @ 1, 7 8 @ 3),
level(2) = (1 2 @ 1, 3 @ 2),
level(3) = (1 2 @ 1);
Figure 25.23: An Alternative Three-Level Tree
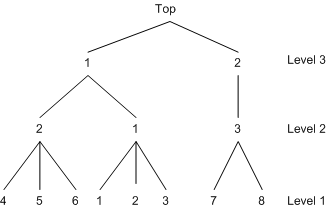
However, the NEST statement with a different sequence of choice specification at higher levels builds the same tree as displayed in Figure 25.22 if the sequence at the first level is the same:
nest level(1) = (1 2 3 @ 1, 4 5 6 @ 2, 7 8 @ 3),
level(2) = (3 @ 2, 1 2 @ 1),
level(3) = (1 2 @ 1);
The following specifications are equivalent:
nest level(2) = (3 @ 2, 1 2 @ 1) nest level(2) = (3 @ 2, 1 @ 1, 2 @ 1) nest level(2) = (1 @ 1, 2 @ 1, 3 @ 2)
Since the MDC procedure contains multiple cases for each individual, it is important to keep the data sequence in the proper
order. Consider the four-choice multinomial model with one explanatory variable cost:
pid choice y cost
1 1 1 10
1 2 0 25
1 3 0 20
1 4 0 30
2 1 0 15
2 2 0 22
2 3 1 16
2 4 0 25
The order of data needs to correspond to the value of choice. Therefore, the following data set is equivalent to the preceding data:
pid choice y cost
1 2 0 25
1 3 0 20
1 1 1 10
1 4 0 30
2 3 1 16
2 4 0 25
2 1 0 15
2 2 0 22
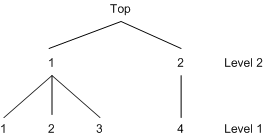
The two-level nested model is estimated with a NEST statement, as follows:
proc mdc data=one type=nlogit;
model y = cost / choice=(choice);
id pid;
utility(1,) = cost;
nest level(1) = (1 2 3 @ 1, 4 @ 2),
level(2) = (1 2 @ 1);
run;
The tree is constructed as in Figure 25.24.
Figure 25.24: A Two-Level Tree
Another model is estimated if you specify the decision tree as in Figure 25.25. The different nested tree structure is specified in the following SAS statements:
proc mdc data=one type=nlogit;
model y = cost / choice=(choice);
id pid;
utility u(1,) = cost;
nest level(1) = (1 @ 1, 2 3 4 @ 2),
level(2) = (1 2 @ 1);
run;
Figure 25.25: An Alternate Two-Level Tree