Model Management
About Managing Models
Using SAS Decision Manager,
you can store models, and organize them within projects or folders,
validate candidate models, assess candidate models for champion model
selection, and publish and monitor champion models in a production
environment, and retrain models. All model development and model maintenance
personnel, including data modelers, validation testers, scoring officers,
and analysts, can use SAS Decision Manager.
Here are some of the
services SAS Decision Manager provides:
-
Use a single interface to access all of your business modeling projects. All models are stored in a central, secure model repository. Models can also be accessed in one place using the model inventory list in the Inventory category.
-
Track the progress of your project’s version by creating processes, definitions, and tests. You create custom processes, definitions, and tests to meet your business requirements and to match your business processes.
-
Use data tables that are registered in the SAS Metadata Repository.
-
Import SAS Enterprise Miner models, SAS/STAT linear models, SAS/ETS COUNTREG and SEVERITY models, models that you develop using SAS code, PMML models, and R models. You can also import a generic model and the model’s files in to a folder. You can create custom model templates for SAS code models so that SAS Decision Manager knows exactly what files and metadata are associated with a model.
-
You can schedule and run scoring tests, performance monitoring, and retraining to validate models.
-
Run several reports to compare and assess candidate models. You can also write your own SAS reporting programs to run and assess candidate models. The aggregated reporting facility enables you to combine multiple reports into a single report. Dashboard reports enable you to monitor the state of projects using performance monitoring reports and can be viewed in a web browser.
-
Publish models to the SAS Metadata Repository or a SAS channel. You can also publish the champion model and challenger models to a database for scoring. The SAS Scoring Accelerator is used by SAS Decision Manager to publish models to a database or Hadoop.
Data tables are an
integral part of the modeling process. You can use project input and
output prototype tables, as well as scoring input and output prototype
tables to define variables. Data tables are used for scoring, testing,
and performance monitoring. Performance data can be created from your
operational data, provided that it has the required structure (for
example, the data contains a target variable).
You can also create
multiple projects in a portfolio. Additional versions can then be
created for all projects within the portfolio. Champion models for
all projects within the portfolio can be monitored for performance,
and published to the SAS Metadata Repository. SAS Factory Miner models
can also be registered to the SAS Decision Manager model
repository. The SAS Factory Miner projects are managed as portfolios
in SAS Model Manager. The project segments and models are available
within a portfolio and can be managed from the Portfolios category
within SAS Model Manager.
Any user who is registered
in SAS Management Console can be assigned to a SAS Decision Manager
group, and can then work in SAS Decision Manager. For more information,
see Configuring Users, Groups, and Roles in SAS Decision Manager: Administrator’s Guide.
Model Management Process
The following diagram
illustrates the model management process:
The Model Management Process
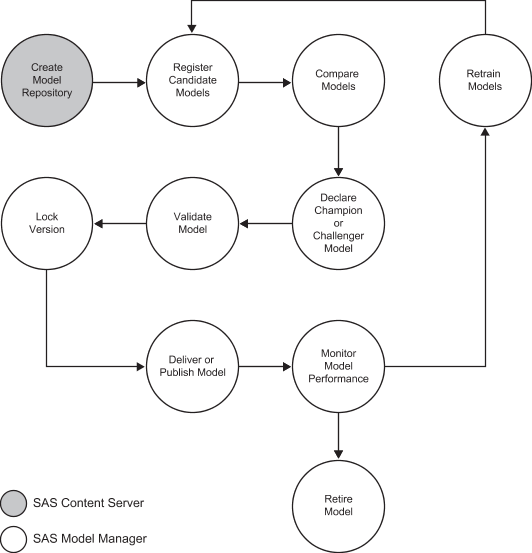
Here is a summary of
the model management process:
-
Create Model Repository: create a secure model repository on the SAS Content Server where SAS code, input and output files, and metadata that is associated with a model can be stored.
-
Register Candidate Models: register input and output files, and then import and configure a model.
-
Compare Models: perform scoring tests and create comparison reports for the models by using test data sources.
-
Declare Champion or Challenger Model: declare the model as champion or challenger to use for testing and production phases of the workflow.
-
Validate Model: perform scoring tests and create validation reports for the champion model and challenger models by using test data sources.
-
Lock Version: lock a version when the champion model is approved for production.
-
Deliver or Publish Model: publish a champion or challenger models to a SAS publish channel, to a database, or to the SAS Metadata Repository.
-
Monitor Model Performance: provide comparative model performance benchmarking.
-
Retrain Models: select models to retrain in response to data or market changes.
-
Retire Model: retire a model from production.
Here is an example of
the model management process for comparing a challenger model to the
champion model to determine the best champion model:
-
Register candidate models in the version that is under development.
-
Create a Dynamic Lift report and compare the model to the champion model. Flag the model as a challenger based on the results of the Dynamic Lift report.
-
Perform scoring tests with the champion and challenger models in real time or in batch. This step can be performed outside SAS Decision Manager.
-
Publish the challenger model to a database or to the SAS Metadata Repository.
-
Prepare performance data sources, which include both the actual outcome variable and predicted variable.
-
Create and execute the performance monitoring for the champion and challenger models to create reports to compare and validate the champion model and challenger models. One of the reports that is available for this comparison is the Champion and Challenger Performance report.
-
Set the challenger model as the project champion if the challenger is good enough to be promoted. Go to step 3, or consider building another model as a challenger with existing or a new input training data source.
-
Publish the new project champion model with or without a new challenger model.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Last updated: February 22, 2017