Server Objects, Application Servers, and Logical Servers
About Server Objects and Server Groupings
In the SAS Metadata Repository,
each server process that executes SAS code is represented by a server
object. In the metadata, the attributes for each server object contain
information such as the following:
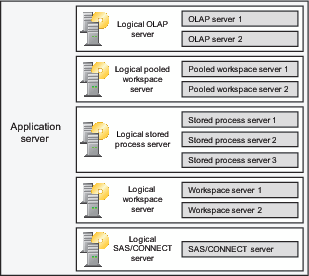
The intermediate level
of organization is called a logical server object. SAS servers of
a particular type, running either on the same machine or on different
machines, can be grouped into a logical server of the corresponding
type. For example:
Purpose of the Application Server Grouping
Application servers,
which are groupings of logical servers, provide the following functionality
in the SAS Intelligence Platform:
Purpose of the Logical Server Grouping
Logical servers, which are groupings of individual servers
of a specific type, provide the following functionality in the SAS
Intelligence Platform:
For more information about SAS Application Servers,
see the SAS Intelligence Platform: Application Server Administration Guide.
-
Load balancing can be implemented among the servers in a logical workspace server, logical stored process server, or logical OLAP server. Load balancing is configured by default for the SAS Pooled Workspace Server and SAS Stored Process Servers.
-
Workspace pooling can be implemented among the servers in a logical workspace server.