A LineChartModel can modify plot markers by
As an alternative to using these techniques for changing plot markers, a variable role in a LineChartTableDataModel can be used to control the markers according to the values of a data column in the graph's data source.
To use the MarkerStyle class to set plot marker attributes (color, visibility, symbol, size),
For example, the following code fragment specifies a filled square as the marker shape:
LineChartModel graphModel=lineChart.getGraphModel();
MarkerStyle[] markerStyle=new MarkerStyle[] {
new MarkerStyle(MarkerStyle.SYMBOL_SQUARE_FILLED)};
graphModel.getDataElementStyles().setMarkerStyles(markerStyle);
To hide plot markers, call the LineChartModel's setMarkerEnabled() method with the argument value false.
In addition to changing the markers, the LineChartModel can be used to change other general display properties, as shown in the following example:
javax.swing.table.TableModel tableModel = <...>; // some TableModel data
LineChartTableDataModel dataModel = new LineChartTableDataModel(tableModel);
GraphStyle graphStyle = new GraphStyle(GraphStyle.STYLE_SCIENCE);
// Get a LineChart
LineChart lineChart = new LineChart(dataModel,graphStyle);
// Set a title
lineChart.getTitle1().setText("Sample LineChart");
// Get the LineChart's graphModel
LineChartModel lineChartModel = lineChart.getGraphModel();
// Change the bar outline color
lineChartModel.getDataElementStyles().getOutlineLineStyle().setColor(Color.blue);
// Define a new set of solid fills for the bar elements to be
// The colors of a rainbow: red, orange, yellow, blue, green, indigo, violet
StrokeLineStyle[] lineStyles = new StrokeLineStyle[] {
new StrokeLineStyle(Color.red)
, new StrokeLineStyle(Color.orange)
, new StrokeLineStyle(Color.yellow)
, new StrokeLineStyle(Color.blue)
, new StrokeLineStyle(Color.green)
, new StrokeLineStyle(new Color(75, 0, 130))
, new StrokeLineStyle(new Color(238, 130, 238))
};
// Set the fill styles to be used by the bar elements
lineChartModel.getDataElementStyles().setLineStyles(lineStyles);
lineChartModel.getDataElementStyles().getOutlineLineStyle().setColor(Color.darkGray);
// set some response-axis text properties
lineChartModel.getResponseAxisModel().getLabelTextStyle().setFont(new Font("TimesRoman",Font.BOLD,18));
lineChartModel.getResponseAxisModel().getValueTextStyle().setFont(new Font("TimesRoman",Font.BOLD,14));
lineChartModel.getResponseAxisModel().getValueTextStyle().setColor(Color.darkGray);
Rather than changing individual properties, it may be easier to use the LineChart to set a graph style, which makes it easier to manage multiple display properties.
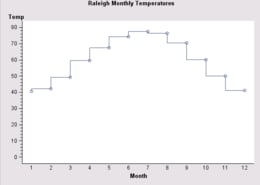
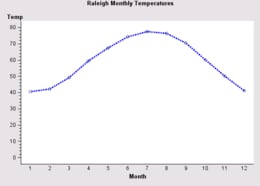
By default for a LineChartModel, plot markers are displayed and plot points are connected with an interpolated line that uses the MarkerStyle.INTERPOLATION_STRAIGHT interpolation method. You can disable the interpolation so that the plot just displays plot markers, or you can change the interpolation method.

The sort order for connecting plot points with an interpolated line is always the sort order of values along the Category axis. Thus, the interpolation line for a single plot cannot change direction and cross over itself. A LineChartTableDataModel's CategorySortVariable role can be used to base the sorting order on the values of a variable in the data.
To disable interpolation, call the setInterpolationEnabled() method with the argument value false. Because plot markers are disabled by default, you must also display plot markers by calling the setMarkerEnabled() method with the argument value true:
LineChartModel graphModel = lineChart.getGraphModel();
graphModel.setInterpolationEnabled(false);
graphModel.setMarkerEnabled(true);
To set an interpolation method when interpolation is enabled, use the plot's DataElementStyles to get the array of MarkerStyles, and then use a MarkerStyle element to set an interpolation value on the setInterpolation() method. The following code fragment sets a step-right interpolation:
LineChartModel graphModel=lineChart.getGraphModel();
DataElementStyles des=graphModel.getDataElementStyles();
MarkerStyle[] markerStyles=des.getMarkerStyles();
markerStyles[0].setInterpolation(MarkerStyle.INTERPOLATION_STEP_RIGHT);
A LineChartModel can be used to modify the line style (color, width, visibility, ...) of any of the various lines in a LineChart.
The following table shows the lines you can set and the method(s) to call to access and/or set the line attributes.
| To change ... | Call ... |
|---|---|
| marker outlines | getDataElementStyles().setOutlineLineStyle(LineStyle) |
| plot line(s) | getDataElementStyles().setLineStyles(StrokeLineStyle[] ) |
| category axis lines
(axis, grid, tick, and reference lines) |
getCategoryAxisModel() and use the returned AxisModel to set axis line style, grid line styles, major tick styles, minor tick styles, and reference line models |
| response (left) axis lines
(axis, grid, tick, and reference lines) |
getResponseAxisModel() and use the returned AxisModel to set axis line style, grid line styles, major tick styles, minor tick styles, and reference line models |
| response2 (right) axis lines
(axis, grid, tick, and reference lines) |
getResponse2AxisModel() and use the returned AxisModel to set axis line style, grid line styles, major tick styles, minor tick styles, and reference line models |
| legend frame | getLegendModel().setFrameLineStyle(LineStyle) |
| missing-values lines | getDataElementStyles().setMissingLineStyle(StrokeLineStyle) |
| column axis lines (available when ColumnVariable role is used) |
getColumnAxisModel().setFrameLineStyle(LineStyle) |
| row axis lines (available when RowVariable role is used) |
getRowAxisModel().setFrameLineStyle(LineStyle) |
| frame lines around column/row cells
(available when ColumnVariable and/or RowVariable roles are used) |
setFrameLineStyle(LineStyle) |
The following code fragment specifies a 3-point blue dashed line for a plot line:
LineChartModel graphModel=lineChart.getGraphModel();
StrokeLineStyle[] lineStyles=new StrokeLineStyle[] {
new StrokeLineStyle(StrokeLineStyle.SASGRAPH_LINE03,
java.awt.Color.blue,
new com.sas.measures.BaseLength(3, "pt"),
com.sas.components.GraphConstants.TRUE) };
graphModel.getDataElementStyles().setLineStyles(lineStyles);
When the specifications on the data model generate multiple plot lines, the areas between the lines can be filled by calling the LineChartModel's setFillAreaEnabled() method with the argument value true.
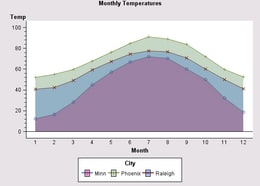
A unique FillStyle is used to fill the area under each plot. To change the fill styles, use the plot's DataElementStyles to set an alternative FillStyle array. The following code fragment creates transparent fills and then assigns them to the plot areas:
LineChartModel graphModel=lineChart.getGraphModel();
graphModel.setFillAreaEnabled(true);
// Creates new FillStyles. The fourth argument on the
// java.awt.Color constructors is the transparency level
FillStyle[] transparencies=new FillStyle[] {
new FillStyle(new Color(204,0,102,100) ), // red transparency
new FillStyle(new Color(102,153,102,100) ), // green transparency
new FillStyle(new Color(51,102,255,100) ) }; // blue transparency
// Assign the fills to the chart's areas (data elements)
graphModel.getDataElementStyles().setFillStyles(transparencies);
You can influence the order in which the filled areas are painted to the screen, depending on how the multiple plots are generated.
If changing the paint order does not provide a satisfactory display of the plot areas, try defining transparent fills for the areas, as shown by the code above.
LineChartModel properties are bound properties. Modifying a property triggers a PropertyChangeEvent. The LineChart asynchronously updates when a PropertyChangeEvent is received from the LineChartModel. Similarly, modifying a property in any of the LineChartModel's contained models triggers a PropertyChangeEvent. PropertyChangeEvent from contained models will bubble up to cause a PropertyChangeEvent to be fired from the LineChartModel.
For example, the following call
lineChartModel.getColorLegendModel().getValueTextStyle().setColor(java.awt.Color.yellow);
would cause the legend's value text style model to fire a "color" PropertyChangeEvent, causing legend model to fire a "valueTextStyle" PropertyChangeEvent, causing the LineChartModel to fire a "colorLegendModel" PropertyChangeEvent. This bubbling up of events enables the graph or any other listener to manage updates at a higher level of containment.