DataSelection query = buildClassroomDataSelection(); FilterItem tallPupilsFilter = buildTallPupilsFilter(query); //reset the query's filters to use the single filter we just built: query.setFilters(Collections.singletonList(tallPupilsFilter)); //execute the query
Where the actual building of the filter is done by:
/**
* Shows how to build a simple filter which says "height >= 60"
**/
private FilterItem buildTallPupilsFilter(DataSelection query) throws MetadataException {
//get all the result items
List resultItems = query.getResultItems();
//we asked for height to be the fourth result item/column, so we won't check:
DataItem height = (DataItem) resultItems.get(3);
//create a numeric constant with the value 60:
ConstantExpression sixtyConstant = new ConstantExpression();
sixtyConstant.setExpressionType(ExpressionTypes.EXP_TYPE_NUMERIC);
sixtyConstant.setValue("60");
//note that even numeric values are set as strings
//now create a >= comparison expression between height and the constant:
SimpleConditionalExpression_Comparison heightGreaterThanSixty =
new SimpleConditionalExpression_Comparison();
heightGreaterThanSixty.setLeftExpression(height);
heightGreaterThanSixty.setComparisonOperator(ComparisonOperator.COMPARE_GE);
heightGreaterThanSixty.setRightExpression(sixtyConstant);
//make a new filter which uses the expression:
FilterItem tallPupilsFilter = query.newFilterItem();
tallPupilsFilter.setExpression(heightGreaterThanSixty);
//the new filter must be added to the query as a business item:
query.addBusinessItem(tallPupilsFilter);
return tallPupilsFilter;
}
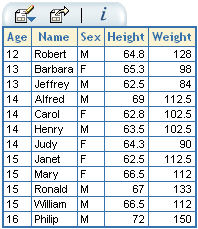
The result of this data selection query will be similar to the following:

DataSelection query = buildClassroomDataSelection(); FilterItem tallPupilsFilter = buildTallPupilsFilter(query); FilterItem bestFriendsFilter = buildBestFriendsFilter(query); List filters = new ArrayList(); filters.add(tallPupilsFilter); filters.add(bestFriendsFilter); //specifying multiple filters in the list implies an AND operation, so //that all the filters must be satisfied: query.setFilters(filters); //execute the query
The first filter is built as show in the previous example, and the second by:
/**
* Shows how to build an IN filter which includes "Alice", "Henry" and "Judy"
**/
private FilterItem buildBestFriendsFilter(DataSelection query) throws MetadataException {
//get all the result items
List resultItems = query.getResultItems();
//we asked for name to be the third result item/column, so we won't check:
DataItem name = (DataItem) resultItems.get(2);
//create character constants for "Alice", "Henry" and "Judy" and add them to a list:
ConstantExpression alice = new ConstantExpression();
alice.setExpressionType(ExpressionTypes.EXP_TYPE_CHARACTER);
alice.setValue("Alice");
ConstantExpression henry = new ConstantExpression();
henry.setExpressionType(ExpressionTypes.EXP_TYPE_CHARACTER);
henry.setValue("Henry");
ConstantExpression judy = new ConstantExpression();
judy.setExpressionType(ExpressionTypes.EXP_TYPE_CHARACTER);
judy.setValue("Judy");
List friendConstants = new ArrayList();
friendConstants.add(alice);
friendConstants.add(henry);
friendConstants.add(judy);
//now create an IN expression for the name data item and the name constants:
SimpleConditionalExpression_In bestFriendNames = new SimpleConditionalExpression_In();
bestFriendNames.setWhatToCompare(name);
bestFriendNames.setComparisonList(friendConstants);
//make a new filter which uses the expression:
FilterItem bestFriendsFilter = query.newFilterItem();
bestFriendsFilter.setExpression(bestFriendNames);
//the new filter must be added to the query as a business item:
query.addBusinessItem(bestFriendsFilter);
return bestFriendsFilter;
}The result of the combined filter should be similar to:
