

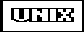
#include <sys/times.h> clock_t times(struct tms *buffer);
times stores user and system CPU time for a process and its
children. The time information is stored in a tms structure
located at the address pointed to by buffer. The tms
structure contains the following members:
clock_t tms_utime
clock_t tms_stime
clock_t tms_cutime
tms_utime and
tms_cutime values for all child processes that have
terminated.
clock_t tms_cstime
tms_stime and
tms_cstime values for all child processes that have
terminated.
clock_t type measures time in clock ticks. The amount of
time represented by
each clock tick is
determined by the CLK_TCK symbol, which is defined
in time.h.
times returns a positive value representing
elapsed time, and ((clock_t) -1) if it is
unsuccessful. The elapsed time value
is referenced from an arbitrary point; hence, it is only useful when
making more than one call to times.
Note:
OpenEdition computes elapsed time values
using fullword (long) arithmetic. If this computation overflows,
times indicates an error and sets errno to ERANGE.
times to determine
process times:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <times.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
int i, status;
pid_t pid;
time_t currentTime;
struct tms cpuTime;
if ((pid = fork()) == -1) { /* Start a child process. */
perror("fork error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else if (pid == 0) { /* This is the child. */
time(¤tTime);
printf("Child process started at %s", ctime(¤tTime));
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
printf("Counting: %dn", i); /* count for 5 seconds. */
sleep(1);
}
time(¤tTime);
printf("Child process ended at %s", ctime(¤tTime));
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else { /* This is the parent. */
time(¤tTime);
printf("Parent process started at %s", ctime(¤tTime));
if (wait(&status) == -1 ) /* Wait for child process. */
perror("wait error");
if (WIFEXITED(status))
printf("Child process ended normally.n");
else
printf("Child process did not end normally.n");
if (times(&cpuTime) < 0) /* Get process times. */
perror("times error");
else {
printf("Parent process user time = %fn",
((double) cpuTime.tms_utime)/CLK_TCK);
printf("Parent process system time = %fn",
((double) cpuTime.tms_stime)/CLK_TCK);
printf("Child process user time = %fn",
((double) cpuTime.tms_cutime)/CLK_TCK);
printf("Child process system time = %fn",
((double) cpuTime.tms_cstime)/CLK_TCK);
}
time(¤tTime);
printf("Parent process ended at %s", ctime(¤tTime));
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
}
clock
Copyright (c) 1998 SAS Institute Inc. Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.