What’s New in SAS/QC 12.1
Overview
In previous years, SAS/QC ® software
was updated only with new releases of Base SAS® software,
but this is no longer the case. This means that SAS/QC software can
be released to customers when enhancements are ready, and the goal
is to update SAS/QC every 12 to 18 months. To mark this newfound independence,
the release numbering scheme for SAS/QC is changing with this release.
This new numbering scheme will be maintained when new versions of
Base SAS and SAS/QC ship at the same time. For example, when Base
SAS 9.4 is released, SAS/QC 13.1 will be released.
Production Status for the MVP Procedures
The MVPMODEL, MVPMONITOR,
and MVPDIAGNOSE procedures, referred to collectively as the MVP
procedures, are used together for multivariate process
monitoring. The MVPMODEL and MVPMONITOR procedures were introduced
as experimental procedures in SAS/QC 9.3 and are production for SAS/QC
12.1. The MVPDIAGNOSE procedure is new in SAS/QC 12.1.
The MVPMODEL procedure
provides computational and graphical tools for building a principal
component model from multivariate process data in which the measured
variables are continuous and correlated. It implements principal component
analysis (PCA) techniques that evolved in the field of chemometrics
for monitoring hundreds or even thousands of correlated process variables;
see Kourti and MacGregor (1995, 1996) for an introduction. A principal
component model reduces the dimensionality of the data by projecting
the process measurements to a low-dimensional subspace that is defined
by a small number of principal components. This subspace is known
as the model hyperplane.
The principal component
model and other output from PROC MVPMODEL serve as input to the MVPMONITOR
and MVPDIAGNOSE procedures.
The MVPMONITOR procedure
creates control charts for multivariate process data by using the
principal component model that is produced by the MVPMODEL procedure.
Multivariate control charts detect unusual variation that would not
be uncovered by individually monitoring the process variables with
univariate control charts, such as Shewhart charts. PROC MVPMONITOR
creates two types of multivariate control chart. 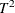 charts detect unusual variation within the model
hyperplane, whereas squared prediction error (SPE) charts detect unusual
variation from the hyperplane.
charts detect unusual variation within the model
hyperplane, whereas squared prediction error (SPE) charts detect unusual
variation from the hyperplane.
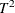 charts detect unusual variation within the model
hyperplane, whereas squared prediction error (SPE) charts detect unusual
variation from the hyperplane.
charts detect unusual variation within the model
hyperplane, whereas squared prediction error (SPE) charts detect unusual
variation from the hyperplane.
CAPABILITY Procedure Enhancements
The CAPABILITY procedure
supports several new options. The CDFPLOT, COMPHISTOGRAM, HISTOGRAM,
PPPLOT, PROBPLOT, and QQPLOT statements support the following new
options for specifying titles and footnotes in graphs that are produced
by using ODS Graphics:
You can use these options
to specify your own graph titles and footnotes without modifying ODS
graph templates or using the ODS Graphics Editor.
The CDFPLOT, COMPHISTOGRAM,
HISTOGRAM, PROBPLOT, and QQPLOT statements support the following new
options for displaying reference lines at the values of computed statistics:
For example, specifying
STATREF=MEAN in a HISTOGRAM statement produces a histogram that has
a vertical reference line at the mean of the data.
The COMPHISTOGRAM and
HISTOGRAM statements support the new CLIPCURVES option, which clips
fitted distribution curves that extend above the highest histogram
bar. This eliminates compression of the histogram bars caused by extremely
high fitted curve peaks.
In addition, the CHREF=,
CVREF=, LHREF=, and LVREF= options have been enhanced. These options
now accept lists of values so that different reference lines in a
single graph can be displayed by using different colors and line types.
They are available in the CDFPLOT, COMPHISTOGRAM, HISTOGRAM, PPPLOT,
PROBPLOT, and QQPLOT statements.
PARETO Procedure Enhancements
The HBAR and VBAR statements
now support the CHARTTYPE= option, which enables you to create variations
on the traditional Pareto chart, as described by Wilkinson (2006).
These statements also support the following new options for specifying
titles and footnotes in graphs that are produced by using ODS Graphics:
RELIABILITY Procedure Enhancements
The RELIABILITY procedure
now supports the following statements that provide further analysis
of regression models that are fit by using a MODEL statement: