What’s New in SAS/IML 12.1
Overview
In previous years, SAS/IML
software was updated only with new releases of Base SAS® software,
but this is no longer the case. This means that SAS/IML software can
be released to customers when enhancements are ready, and the goal
is to update SAS/IML every 12 to 18 months. To mark this newfound
independence, the release numbering scheme for SAS/IML is changing
with this release. This new numbering scheme will be maintained when
new versions of Base SAS and SAS/IML ship at the same time. For example,
when Base SAS 9.4 is released, SAS/IML 13.1 will be released.
Enhancements to the SAS/IML Syntax
-
SAS/IML supports a new syntax that defines optional arguments and default parameter values for user-defined modules. One implication of the new syntax is that you cannot omit a parameter when you call a user-defined subroutine unless the module definition explicitly specifies that the parameter is optional. This syntax change might require that you modifySAS/IML programs that parsed and ran without error in previous releases. -
There is a new syntax for reading and writing SAS data sets that enables you to read data sets whose name is given by a run-time expression rather than by a literal value. For example, the following syntax is now valid:
dsname = "Sashelp.Class"; use (dsname); read all var _NUM_ into X; close (dsname);
use Sashelp.Class; read all var _NUM_ into X; close Sashelp.Class;
-
You can now pass the same matrix into a module in several parameter locations. The first time that a variable is passed, it is passed by reference. Subsequent arguments receive a copy of the matrix. For example, the following syntax is now valid:
start DotProduct(x,y); return( x`*y ); finish; x = {1,2,3,4}; z = DotProduct(x, x); /* pass the same matrix twice */
In addition, SAS/IML
12.1 includes the following enhancements to functions, subroutines,
and modules:
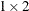 vector whose elements are the number of rows and
columns, respectively, of a matrix.
vector whose elements are the number of rows and
columns, respectively, of a matrix.
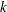 elements from a finite set of
elements from a finite set of  elements,
elements, 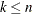 .
.