| What's New |
What’s New in SAS/IML 9.22
Overview
SAS/IML 9.22 includes two new features and many new functions and subroutines. The following features are new:
the ability to call SAS procedures and DATA steps from within the IML procedure.
the ability to call functions and packages in the R statistical programming language from within the IML procedure. You can use new SAS/IML subroutines to transfer data between SAS data formats and R data formats.
For more information about the new features and enhancements in SAS/IML 9.2, see What's New in SAS/IML 9.2.
New Features
SAS/IML 9.22 supports the SUBMIT and ENDSUBMIT statements. These statements delimit a block of statements that are sent to another language for processing.
The SUBMIT and ENDSUBMIT statements enable you to call SAS procedures and DATA steps without leaving the IML procedure. This feature has been very popular in SAS/IML® Studio since it was introduced in 2002, and it is now available in PROC IML.
You can use SAS data sets to transfer data between SAS/IML matrices and SAS procedures. SAS procedures require that data be in a SAS data set.
The SUBMIT and ENDSUBMIT statements also provide an interface to the R statistical programming language, so that you can to submit R statements from within your SAS/IML program. To submit statements to R, specify the R option in the SUBMIT statement.
You can transfer data from SAS/IML matrices and SAS data sets into R matrices and R data frames, and vice versa. Specifically, the subroutines shown in Table 1.1 are available to transfer data from a SAS format into an R format.
The interface to R is supported only on computers that run the Windows or Linux operating systems.
Subroutine |
SAS Source |
R Destination |
|---|---|---|
ExportDataSetToR |
SAS data set |
R data frame |
ExportMatrixToR |
SAS/IML matrix |
R matrix |
In addition, the subroutines shown in Table 1.2 are available to transfer data from an R format into a SAS format.
Subroutine |
R Source |
SAS Destination |
|---|---|---|
ImportDataSetFromR |
R expression |
SAS data set |
ImportMatrixFromR |
R expression |
SAS/IML matrix |
In Table 1.2, an "R expression" can be the name of a data frame, the name of a matrix, or an expression that results in either of these data structures.
New Functions and Subroutines
SAS/IML 9.22 provides the new functions and subroutines described in the following sections.
CORR Function
The CORR function computes a sample correlation matrix for data. The function supports Pearson product-moment correlations, Hoeffding’s 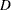 statistics, Kendall’s tau-
statistics, Kendall’s tau-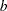 coefficients, and Spearman correlation coefficients based on the ranks of the variables. The function supports two different methods for dealing with missing values in the data.
coefficients, and Spearman correlation coefficients based on the ranks of the variables. The function supports two different methods for dealing with missing values in the data.
COV Function
The COV function computes a sample variance-covariance matrix for data. The function supports two different methods for dealing with missing values in the data.
COUNTN Function
The COUNTN function counts the number of nonmissing values in a matrix.
COUNTMISS Function
The COUNTMISS function counts the number of missing values in a matrix.
COUNTUNIQUE Function
The COUNTUNIQUE function counts the number of unique values in a matrix.
CUPROD Function
The CUPROD function computes the cumulative product of elements in a matrix.
DIF Function
The DIF function computes the differences between data values and one or more lagged (shifted) values for time series data.
FULL Function
The FULL function converts a matrix stored in a sparse format into a matrix stored in a dense format. See the SPARSE function for a description of how sparse matrices are stored.
LAG Function
The LAG function computes one or more lagged (shifted) values for time series data.
MEAN Function
The MEAN function computes a sample mean of data. The function can compute arithmetic means, trimmed means, and Winsorized means.
PROD Function
The PROD function computes the product of elements in one or more matrices.
QNTL Call
The QNTL subroutine computes sample quantiles for data.
SPARSE Function
The SPARSE function converts a matrix that contains many zeros into a matrix stored in a sparse format which suitable for use with the ITSOLVER subroutine or the SOLVELIN subroutine.
VAR Function
The VAR function computes a sample variance for each column of a data matrix.
Changes to the IMLMLIB Library
The CORR module has been removed from the IMLMLIB library. In its place is the built-in CORR function.
The MEDIAN, QUARTILE, and STANDARD modules now support missing values in the data argument.
Documentation Enhancements
The first six chapters of this documentation have been completely rewritten in order to provide new users with a gentle introduction to the SAS/IML language. Two new chapters have been written: Chapter 10, Submitting SAS Statements, describes how to call SAS procedures from within PROC IML, and Chapter 11, Calling Functions in the R Language, describes how to call R functions from within PROC IML.
Highlights of Enhancements in SAS/IML 9.2
The following are some of the major enhancements that were introduced in SAS/IML 9.2:
A new programming syntax to specify vector-matrix operations was introduced.
New modules for sampling from multivariate distributions were added to the IMLMLIB library.
The following functions and subroutines were introduced:
the ODSGRAPH subroutine, which provides an interface with ODS Statistical Graphics and the TEMPLATE procedure
the BSPLINE function, which computes a B-spline basis for a given numeric input vector, degree, and knot specification
the GEOMEAN and HARMEAN functions, which compute the geometric mean and the harmonic mean, respectively, of a matrix of positive numbers
Related Software
SAS/STAT and SAS/IML users might be interested in SAS/IML Studio, which is software for data exploration, model building, simulation, and analysis. SAS/IML Studio is distributed with the SAS/IML product.
SAS/IML Studio provides a highly flexible programming environment in which you can create and run programs and display the results with dynamically linked graphics and data tables. SAS/IML Studio is intended for data analysts who write SAS programs to solve statistical problems but need more versatility for data exploration and model building. The programming language in SAS/IML Studio, which is called IMLPlus, is an enhanced version of the SAS/IML programming language. IMLPlus extends the SAS/IML language to provide new features, including the ability to create and manipulate statistical graphics, call SAS procedures as functions, call functions in the R language, and call computational programs written in C, C++, Java, and Fortran. SAS/IML Studio runs on a PC in the Microsoft Windows operating environment.
For more information about SAS/IML Studio, see the SAS/IML Studio User's Guide and SAS/IML Studio for SAS/STAT Users.
Copyright © 2010 by SAS Institute Inc.,Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.