Linear Models
Example: Linear Regression with Fixed Effects
To create this example:
-
Create the Work.Cigar data set. For more information, see CIGAR Data Set.
-
TipIf the data set is not available from the drop-down list, click
 . In the Choose a Table window,
expand the library that contains the data set that you want to use.
Select the data set for the example and click OK.
The selected data set should now appear in the drop-down list.
. In the Choose a Table window,
expand the library that contains the data set that you want to use.
Select the data set for the example and click OK.
The selected data set should now appear in the drop-down list.
Assigning Data to Roles
To perform an analysis
of a linear model, you must assign an input data set. To filter the input data source,
click  .
.
 .
.
You also must assign
a variable to the Dependent variable role.
|
Role
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Roles
|
|
|
Dependent
variable
|
specifies the numeric
variable for the analysis.
|
|
Continuous
variables
|
specifies
the independent covariates (regressors) for the regression model.
If you do not specify a continuous variable, the task fits a model
that contains only an intercept.
|
|
Categorical
variables
|
specifies
the classification variables. The task generates dummy variables for
each level of the categorical variable.
|
|
Additional Roles
|
|
|
Group analysis
by
|
enables you to obtain separate
analyses of observations for each unique group.
Note: This role is not available
if you have a categorical variable.
|
Setting the Model Options
To create a linear
model:
-
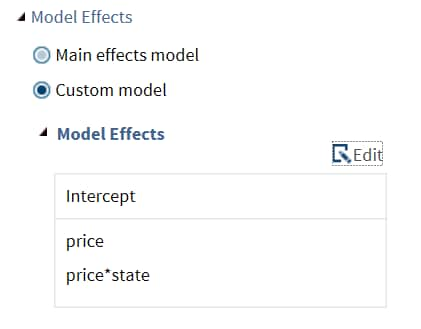
You can display the main effects model or create a custom model. To create a custom model, select the Custom Model option, and then click Edit. The Model Effects Builder opens. All continuous variables and categorical variables are listed in the Variables pane.
-
To create a main effect, select the variable in the Variables pane, and then click Add.
-
To create a crossed effect, select the variables in the Variables pane. (You can use Ctrl to select multiple variables.) Then click Cross.
When you finish, click OK. The effects that you specified now appear on the Model tab.Here is an example of model effects on the Model tab. -
Setting the Options
|
Option Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Methods
|
|
|
Covariance
matrix estimator
|
specifies the method
to calculate the covariance matrix of parameter estimates.
You can select the
default value, or you can choose from these methods:
|
|
Statistics
|
|
|
Select the statistics
to display in the results.
Here are the additional
statistics that you can include in the results:
|
|
|
Plots
|
|
|
Select the plots to
include in the results. By default, diagnostic, residual, and fit
plots are included in the results. You can include these plots:
You can choose to display
these plots as a panel of plots or as individual plots.
|
|
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.